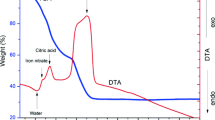
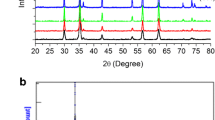
Abstract
Single-phase nanoparticles of Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2 O 4 (MZF) with improved magnetic properties were prepared from the precursor (formed by chemical route) by microwave processing technique at 500 ∘C in only 3 min. Crystallographically, these were found to be of spinel phase. Using Debye-Scherrer formula, the particle size of conventionally sintered powder is estimated to be about 20 nm, whereas that of microwave processed is nearly 50 nm with improved grain size. The field emission scanning electron (FESEM) and transmission electron (TEM) micrographs revealed the particles in microwave-processed samples to be spherical in shape and confirmed the sample size (to be nearly 50 nm). Room temperature magnetization measurement of conventionally sintered samples (by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM)) showed their superparamagnetic nature with saturation magnetization of nearly 19 emu/g. The microwave-processed samples showed improved saturation magnetization of nearly 36 emu/g, which is even better than the reported value.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibrahim, E.M.M.: The effect of sintering time and temperature on the electrical properties of MnZn ferrites. Appl. Phys. A 89, 203 (2007)
Fukuda, Y., Nagata, S., Echizenya, K.: Electrical conductivity of MnZn ferrite single crystals with a small number of Fe 2+ions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 279, 325 (2004)
Pankhurst, Q.A., Connolly, J., Jones, S.K., Dobson, J.: Application of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 36, R167 (2003)
Son, S., Swaminathan, R., Mchenry, M.E.: Structure and magnetic properties of rf thermally plasma synthesized Mn and Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 7495 (2003)
Sugimoto, M.: The past, present, and future of ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 269 (1999)
Ghazanfar, U., Siddiqi, S.A., Abbas, G.: Structural analysis of the Mn–Zn ferrites using XRD technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 118, 84 (2005)
Ott, G., Wrba, J., Lucke, R.: Recent developments of Mn–Zn ferrites for high permeability applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 254, 535 (2003)
Yan, Q., Gambino, R.J., Sampath, S., Lewis, L.H., Li, L., Baumberger, E., Vaidya, A., Xiong, H.: Effects of zinc loss on the magnetic properties of plasma-sprayed MnZn ferrites. Acta Mater. 52, 3347 (2004)
Hirota, K., Aoyama, T., Enomoto, S., Yoshinaka, M., Yamaguchi, O.: Microstructures and magnetic and electric properties of low-temperature sintering Mn-Zn ferrites without and with addition of lithium borosilicate glass. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 205, 283 (1999)
Xi, G., Yang, Li., Maixi, Lu.: Study on preparation of nanocrystalline ferrites using spent alkaline Zn–Mn batteries. Mater. Lett. 60, 3582 (2006)
Kanemaru, T., Iwasaki, T., Suda, S., Kitagawa, T.: Preparation of ferrite from used dry cells . United States Patent 5,707,541 (1998)
Kashyap, S.C.: Applied electromagnetic conference (AEMC) 2009, 14-16 Dec. Kolkata IEEExplore doi:10.1109/AEMC.2009.5430602
Geetanjali, C.L., Dube, S.C., Kashyap, R.K. Kotnala: Effect of microwave processing on polycrystalline hard barium hexaferrite. J. Supercond. Novel Mag. 24, 567 (2011)
Dube, C.L., Kashyap, S.C., Dube, D.C., Agarwal, D.K.: Growth of Si0.75Ge0.25 alloy nanowires in a separated H-field by microwave processing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 213107 (2009)
Xiao, L., Zhou, T., Meng, J.: Hydrothermal synthesis of Mn–Zn ferrites from spent alkaline Zn–Mn batteries. Particuology 491, 7 (2009)
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-ray diffraction. Addisson Wesely, Calfornia (1978)
Tsakaloudi, V., PapaZoglou, E., Zaspalis, V.T.: Microwave firing of MnZn-ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 106, 289 (2004)
Xuan, Y., Li, Q., Yang, G.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 312, 464 (2007)
Goya, G.F., Berquo, T.S., Fonseca, F.C., Morales, M.P.: Static and dynamic magnetic properties of spherical magnetite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 94(5), 3520 (2003)
Giri, J., Pradhan, P., Somani, V., Chelawat, H., Chhatre, S., Banerjee, R., Bahadur, D.: Synthesis and characterizations of water-based ferrofluids of substituted ferrites [Fe1-x B x Fe2 O 4, B = Mn, Co (x = 0 – 1)] for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 724 (2008)
Jeppson, P., Sailer, R., Jarabek, E., Sandstrom, J., Anderson, B., Bremer, M., Grier, D.G., Schulz, D.L., Caruso, A.N., Payne, S.A., Eames, P., Tondara, M., He, H., Chrisey, D.B.: Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: achieving the superparamagnetic limit by chemical reduction. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 114324 (2006)
Vejpravova, J., Sechovsky, V., Plocek, J., Niznansky, D., Hutlova, A.: Magnetism of sol-gel fabricated CoFe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 124304 (2005)
Hessien, M.M., Rashad, M.M., El-Barawy, K., Ibrahim, I.A.: Influence of manganese substitution and annealing temperature on the formation, microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 1615 (2008)
Wang, J., Zhang, K., Peng, Z., Chen, Q.: Magnetic properties improvement in Fe3O4 nanoparticles grown under magnetic fields. J. Cryst. Growth 266, 500 (2004)
Teja, A.S., Koh, P.-Y.: Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 55, 22 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thota, S., Kashyap, S.C., Gupta, H.C. et al. Improved Magnetic Properties of Microwave-Processed Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 28, 131–136 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2820-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2820-9