Abstract
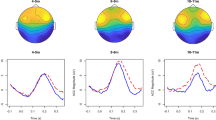
This combined ERP and behavioral experiment explores the dynamics of processing during the discrimination of vowels in a non-native regional variety. Southern listeners were presented with three word forms, two of which are encountered in both Standard and Southern French ([kot] and [kut]), whereas the third one exists in Standard but not Southern French ([kot]). EEG recordings suggest that all of the word pairs were discriminated by the listeners, although discrimination arose about 100ms later for the pairs which included the non-native word form than for those which contained word forms common to both French varieties. Behavioral data provide evidence that vowel discrimination is sensitive to the influence of the listeners’ native phonemic inventory at a late decisional stage of processing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Best C. T. (1994) The emergence of language-specific phonemic influences in infant speech perception. In: Goodman J., Nusbaum H. C. (Eds.) The development of speech perception: The transition from speech sounds to spoken words. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 167–224
Best C. T., McRoberts G. W., Sithole N. M. (1988) Examination of perceptual reorganization for nonnative speech contrasts: Zulu click discrimination by English-speaking adults and infants. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 14: 345–360
Brunellière A., Dufour S., Nguyen N., Frauenfelder U. (2009) Behavioral and electrophysiological evidence for the impact of regional variation on phoneme perception. Cognition 111: 390–396
Conrey B., Potts G., Niedzielski N. (2005) Effects of dialect on merger perception: ERP and behavioral correlates. Brain and Language 95: 435–449
Cutler A., Weber A., Otake T. (2006) Asymmetric mapping from phonetic to lexical representations in second-language listening. Journal of Phonetics 34: 269–284
Dehaene-Lambertz G. (1997) Electrophysiological correlates of categorical phoneme perception in adults. Neuroreport 8: 919–924
Dehaene-Lambertz G., Dupoux E., Gout A. (2000) Electrophysiological correlates of phonological processing: A cross-linguistic study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 12: 635–647
Diesch E., Luce T. (2000) Topographic and temporal indices of vowel spectral envelope extraction in the human auditory cortex. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 12: 878–893
Dufour S., Nguyen N., Frauenfelder U. H. (2007) The perception of phonemic contrasts in a non-native dialect. Journal of Acoustical Society of America 121: EL131–EL136
Dupoux E., Peperkamp S., Sebastián-Gallés N. (2001) A robust method to study stress ‘deafness’. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 110: 1606–1618
Ettlinger M., Johnson K. (2009) Vowel discrimination by English, French and Turkish Speakers: An exemplar-based approach to speech perception. Phonetica 66: 222–242
Eulitz C., Lahiri A. (2004) Neurobiological evidence for abstract phonological representations in the mental lexicon during speech recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 16: 577–583
Flege J., Yeni-Komshian G., Liu S. (1999) Age constraints on second language learning. Journal of Memory and Language 41: 78–104
Ingram J. C. L., Park S. -G. (1997) Cross-language vowel perception and production by Japanese and Korean learners of English. Journal of Phonetics 25: 437–470
Janson T., Schulman R. (1983) Non-distinctive features and their use. Journal of Linguistics 19: 321–336
Labov W., Karan M., Miller C. (1991) Near-mergers and the suspension of phonemic contrast. Language Variation and Change 3: 33–74
Logan J. S., Lively S. E., Pisoni D. B. (1991) Training Japanese listeners to identify English /r/ and /l/: A first report. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 89: 874–886
Näätänen R., Winkler I. (1999) The concept of auditory stimulus representation in neuroscience. Psychological Bulletin 125: 826–859
Näätänen R., Lehtokoski A., Lennes M., Cheour M., Huotilainen M., Iivonen A., Vainio M., Alku P., Ilmoniemi R. J., Luuk A., Allik J., Sinkkonen J., Alho K. (1997) Language-specific phoneme representations revealed by electric and magnetic brain responses. Nature 358: 432–434
Näätänen R., Paavilainen P., Rinne T., Ahlo K. (2007) The mismatch negativity (MMN) in basic research of central auditory processing: A review. Clinical Neurophysiology 11: 2544–2590
Obleser J., Elbert T., Lahiri A., Eulitz C. (2003) Cortical representation of vowels reflects acoustic dissimilarity determined by formant frequencies. Cognitive Brain Research 15: 207–213
Oldfield R. C. (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9: 97–113
Pallier C., Bosch L., Sebastian-Galles N. (1997a) A limit on behavioural plasticity in speech perception. Cognition 64: B9–B17
Pallier C., Christophe A., Mehler J. (1997b) Language-specific listening. Trends in Cognitive Science 1: 129–132
Pallier C., Colomé A., Sebastián-Gallés N. (2001) The influence of native-language phonology on lexical access: Exemplar-based versus abstract lexical entries. Psychological Science 12: 445–449
Phillips C. (2001) Levels of representation in the electrophysiology of speech perception. Cognitive Science 25: 711–731
Polka L., Bohn O. -S. (2003) Asymmetries in vowel perception. Speech Communication 41: 221–231
Strange W., Dittmann S. (1984) Effects of discrimination training on the perception of /r-l/ by Japanese adults learning English. Perception Psychophysics 36: 131–145
Trehub S. (1976) The discrimination of foreign speech contrasts by infants and adults. Child Development 47: 466–472
Werker J. F. (1994) Cross-language speech perception: Developmental change does not involve loss. In: Goodman J., Nusbaum H. C. (Eds.) The development of speech perception: The transition from speech sounds to spoken words. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 93–120
Werker J. F., Tees R. C. (1984) Phonemic and phonetic factors in adult cross-language speech perception. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 75: 1866–1878
Werker J. F., Gilbert J. H. V., Humphrey G. K., Tees R. C. (1981) Developmental aspects of cross-language speech perception. Child Development 52: 349–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dufour, S., Brunellière, A. & Nguyen, N. To What Extent do we Hear Phonemic Contrasts in a Non-native Regional Variety? Tracking the Dynamics of Perceptual Processing with EEG. J Psycholinguist Res 42, 161–173 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-012-9212-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-012-9212-8