Abstract
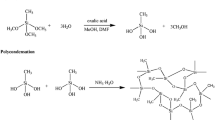
We developed an eco-friendly method to facilely prepare the good-formability methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS)-based silica aerogels via water solvent system and ambient pressure drying in one-step. In the whole procedure, water was used not only as a reaction agent but also as a solvent, avoiding the expensive cost and environmental pollution caused by solvent exchange. The structural properties of MTMS-based silica aerogels were characterized by the scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller methods. The results indicated that compared with other silica aerogels prepared by traditional water solvent methods, this MTMS-based silica aerogels had the classic nanostructure with the high specific surface area of 450 m2/g as well as hydrophobic property.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Zhao, Y.Y. Duan, X.D. Wang et al., Radiative properties and heat transfer characteristics of fiber-loaded silica aerogel composites for thermal insulation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55(19), 5196–5204 (2012)
S.S. Kistler, Coherent expanded aerogels and jellies. Nature 127(3211), 741 (1931)
J. Fricke, Aerogels—highly tenuous solids with fascinating properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 100(1–3), 169–173 (1988)
R. Ciriminna, A. Fidalgo, V. Pandarus et al., The sol–gel route to advanced silica-based materials and recent applications. Chem. Rev. 113(8), 6592–6620 (2013)
H. Yang, F. Ye, Q. Liu et al., A novel silica aerogel/porous Si3N4, composite prepared by freeze casting and sol–gel impregnation with high-performance thermal insulation and wave-transparent. Mater. Lett. 138, 135–138 (2015)
C.H. Lee, D.H. Jo, S.H. Kim, Effect of surfactant on CO2 adsorption of APS-grafted silica gel by one-pot process. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 89(7), 823–832 (2016)
H. Ren, J. Zhu, Y. Bi et al., One-step fabrication of transparent hydrophobic silica aerogels via in situ surface modification in drying process. J. Sol–Gel. Sci. Technol. 80(3), 635–641 (2016)
G.M. Pajonk, Transparent silica aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 225(1), 307–314 (1998)
X. Du, F. Kleitz, X. Li et al., Disulfide-bridged organosilica frameworks: designed, synthesis, redox-triggered biodegradation, and nanobiomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201707325
P.C. Thapliyal, K. Singh, Aerogels as promising thermal insulating materials: an overview. J. Mater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/127049
Y. Pan, S. He, L. Gong et al., Low thermal-conductivity and high thermal stable silica aerogel based on MTMS/water-glass co-precursor prepared by freeze drying. Mater. Des. 113, 246–253 (2017)
A.P. Rao, A.V. Rao, U.K.H. Bangi, Low thermalconductive, transparent and hydrophobic ambient pressure dried silica aerogels with various preparation conditions using sodium silicate solutions. J. Sol–Gel. Sci. Technol. 47(1), 85–94 (2008)
X. Du, X. Li, L. Xiong et al., Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with organo-bridged silsesquioxane framework as innovative platforms for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery. Biomaterials 91(June), 90–127 (2016)
W. Rupp, N. Hüsing, U. Schubert, Preparation of silica–titania xerogels and aerogels by sol–gel processing of new single-source precursors. J. Mater. Chem. 12(9), 2594–2596 (2002)
P.H. Tewari, A.J. Hunt, K.D. Lofftus, Ambient-temperature supercritical drying of transparent silica aerogels. Mater. Lett. 3(9–10), 363–367 (1985)
X. Du, S.Z. Qiao, Dendritic silica particles with center-radial pore channels: promising platforms for catalysis and biomedical applications. Small 11(4), 392–413 (2015)
M. Shi, C. Tang, X. Yang et al., Superhydrophobic silica aerogels reinforced with polyacrylonitrile fibers for adsorbing oil from water and oil mixtures. RSC Adv. 7(7), 4039–4045 (2017)
D.M. Smith, R. Deshpande, C.J. Brinke. Preparation of low-density aerogels at ambient pressure. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. (1992). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-271-567
A.P. Rao, A.V. Rao, G.M. Pajonk, Hydrophobic and physical properties of the ambient pressure dried silica aerogels with sodium silicate precursor using various surface modification agents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(14), 6032–6040 (2007)
A.P. Rao, G.M. Pajonk, A.V. Rao, Effect of preparation conditions on the physical and hydrophobic properties of two step processed ambient pressure dried silica aerogels. J. Mater. Sci. 40(13), 3481–3489 (2005)
S. Yun, H. Luo, Y. Gao, Superhydrophobic silica aerogel microspheres from methyltrimethoxysilane: rapid synthesis via ambient pressure drying and excellent absorption properties. RSC Adv. 4(9), 4535–4542 (2013)
K. Kanamori, M. Aizawa, K. Nakanishi et al., New transparent methylsilsesquioxane aerogels and xerogels with improved mechanical properties. Adv. Mater. 19(12), 1589–1593 (2007)
X. Cheng, C. Li, X. Shi et al., Rapid synthesis of ambient pressure dried monolithic silica aerogels using water as the only solvent. Mater. Lett. 204, 157–160 (2017)
S. Yun, T. Guo, J. Zhang et al., Facile synthesis of large-sized monolithic methyltrimethoxysilane-based silica aerogel via ambient pressure drying. J. Sol–Gel. Sci. Technol. 83(1), 53–63 (2017)
Q. Xu, H. Ren, J. Zhu et al., Facile fabrication of graphite-doped silica aerogels with ultralow thermal conductivity by precise control. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 469, 14–18 (2017)
S. Li, H. Ren, J. Zhu et al., Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic, mechanically strong multifunctional silica-based aerogels at benign temperature. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 473, 59–63 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 2018RZ0127), the Project of State Key Laboratory of Environment-friendly Energy Materials, Southwest University of Science and Technology (No. 18zxhk16) and the Doctoral Research Fund of Southwest University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 16zx7142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, L., Ren, H., Zhu, J. et al. One-step eco-friendly fabrication of classically monolithic silica aerogels via water solvent system and ambient pressure drying. J Porous Mater 26, 785–791 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-018-0674-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-018-0674-4