Abstract
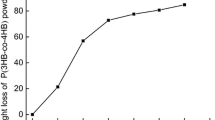
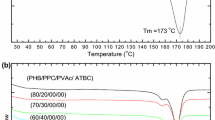
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) is a biodegradable polymer synthesized in microorganisms. The application of PHBV is limited by certain material disadvantages. Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) possesses excellent thermodynamic and mechanical properties and was used to modify PHBV in the presence of triethyl citrate (TEC) and dicumyl peroxide (DCP), which was used as plasticizer and grafting agent, respectively. The effects of PCL and additive agents on the mechanical, thermal, amphipathic and degradability behaviors of the blends were investigated. The results showed that the mechanical properties of the PHBV blends improved by PCL incorporation and improved even further after TEC and DCP addition. The addition of DCP could not induce an increase in crystallization temperature but improved the crystallization degree of the blends. The presence of hydrophilic groups in TEC leads to an apparent increases in the hydrophilicity of the PHBV blends. A PHBV/PCL blend (40/60) with TEC (20 wt.%) and DCP (0.5 wt.%) was chosen for its good mechanical properties and hydrophilicity. The chosen ratio of the blends was also shown a preferable degradation activity by biodegradation assay using Pseudomonas mendocina. The addition of TEC and DCP has no conspicuous negative effect on the biodegradation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carolina L, Betina MPF, Eliana ARD, Arnaldo RSJ, Paulo PJ (2008) J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:635–643
Meng W, Xing ZC, Jung KH, Kim SY, Yuan J, Kang IK, Sung CY, Hong ISJ (2008) J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:2799–2807
Avella M, Martuscelli E, Raimo M (2000) J Mater Sci 35:523–545
Zhang KY, Amar KM, Misra M (2012) ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:3091–3101
Wang BJ, Zhang YJ, Zhang JQ, Gou QT, Wang ZB, Chen P, Gu Q (2013) Chin J Polym Sci 3:670–678
Yottha S, Thomas E, Jun P, Ronald S, Craig C, Turng LS, Srikanth P (2013) Polym Degrad Stab 98:1439–1449
Jost V, Langowski HC (2015) Eur Polym J 68:302–312
Li X, Loh XJ, Wang K, He CB, Li J (2015) Biomacromolecules 6:2740–2747
Ma PM, Denka GHB, Lemstra PJ, Zhang Y, Wang SF (2012) Macromol Mater Eng 297:402–410
Wang S, Ma PM, Wang RY, Wang SF, Zhang Y, Zhang YX (2008) Polym Degrad Stab 93:1364–1369
Pierre L, Estelle R, Jean G, Christelle SC, Valerie L (2012) React Funct Polym 72:487–494
Hala FN, Mohamed SAA, Sherif MS, Gamal RS (2011) J Polym Res 18:1217–1227
Khodaverdi E, Heidari Z, Tabassi SAS, Tafaghodi M, Alibolandi M, Tekie FSM, Khameneh B, Hadizadeh F (2015) AAPS Pharm Sci Tech 16:140–149
Li Y, Xin S, Bian Y, Xu K, Han C, Dong L (2016) Int J Biol Macromol 85:63–73
Liu QS, Zhu MF, Chen YM (2010) Polym Int 59:842–550
Li X, Loh XJ, Wang K, He CB, Li J (2005) Biomacromolecules 6:2740–2747
Jia L, Yin LZ, Li Y, Li QB, Yang J, Yu JY, Shi Z, Fang Q, Cao AM (2005) Macromol Biosci 5:526–538
Dekoning GJM, Scheeren AHC, Lemstra PJ, Peeters M, Reynaers H (1994) Polymer 35:4598–4605
Francisco REC, Suzan AC, Jose AMA (2013) J Polym Environ 21:789–794
Liu QS, Shyr TW, Tung CH, Zhu MF, Deng BY (2011) Macromol Res 19:1220–1223
Xiang HX, Wang SC, Wang RL, Zhou Z, Peng C, Zhu MF (2013) Sci China Chem 56:716–723
Zhao HB, Cui ZX, Wang XF, Turng LS, Peng XF (2013) Compos B 51:79–91
Nagarajan V, Misra M, Mohanty AK (2013) Ind Crop Prod 42:461–468
Guan Q, Naguib HE (2014) J Polym Environ 22:119–130
Badia JD, Kittikorn T, Strömberg E, Santonja-Blasco L, Martínez-Felipe A, Ribes-Greus A, Ek M, Karlsson S (2014) Polym Degrad Stab 108:166–174
Mao HL, Jiang HS, Su TT, Wang ZY (2013) Biotechnol Lett 35:1919–1924
Wang ZY, Lin XD, An J, Ren C, Yan X (2013) Polym Plast Technol Eng 52:195–199
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31100099 and 31570097) and Program for Liaoning Excellent Talents in University (Grant No. LJQ2014040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Gao, Z., Hu, X. et al. Blending Modification of PHBV/PCL and its Biodegradation by Pseudomonas mendocina . J Polym Environ 25, 156–164 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0795-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0795-2