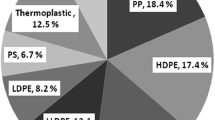
Abstract
Promiscuous and frequently deliberate release of plastics is responsible for growing environmental pollution. Low cost, efficient technology, eco-friendly treatments capable of reducing and even eliminating plastics, are developed by the researchers. Among biological agents, microbial enzymes are one of the most powerful tools for the biodegradation of plastics. Activity of biodegradation of most enzymes is higher in fungi than in bacteria. This review focuses on induced biodegradation rate of plastics by fungal and bacterial enzymes and the mode of action of biodegradation. Following a brief discussion of the enzymes and the factors affecting the production of enzymes, a descriptive survey is presented on various individual group of enzymes such as laccase, cutinase, hydrolase, esterase, protease and urease etc. and the microbial species that were predominant are Streptococcus, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus comprise the bacterial species and the fungal species include Aspergillus, Penicillium, Phaenarochete, Pestalotiopsis etc. In plastics surface aspects, significant changes indicate its biodegradation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen AB, Hilliard NP, Howard GT (1999) Purification and characterization of a soluble polyurethane degrading enzyme from Comamonas acidovorans. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 43:37–41
Arkatkar A, Arutchelvi J (2009) Approaches to enhance the biodegradation of polyolefin. Open Environ Eng J 2:68–80
Artham T, Doble M (2008) Biodegradation of aliphatic and aromatic polycarbonates. Macromol Biosci 8(1):14–24
Arutchelvi J, Sudhakar M (2008) Biodegradation of polyethylene and polypropylene. Indian J Biotechnol 7(1):9–22
Barnes D, Galgani F, Thompson R, Barlaz M (2009) Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 364:1985–1998
Barratt SR (2003) Fungi are the predominant micro-organisms responsible for degradation of soil-buried polyester polyurethane over a range of soil water holding capacities. J Appl Microbiol 95:78–85
Bentham RH, Morton LHG, Allen NG (1987) Rapid assessment of the microbial deterioration of polyurethanes. Int Biodeterior 23:377–386
Bikiaris D, Aburto J, Alric I, Borredon E, Botev M, Betchev C (1999) Mechanical properties and biodegradability of LDPE blends with fatty-acid esters of amylase and starch. J Appl Polym Sci 71:1089–1100
Dashtban M, Schraft H, Syed TA (2010) Fungal biodegradation and enzymatic modification of lignin. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 1(1):36–50
Doi Y (1990) Microbial polyesters. VCH, New York
Frazer AC (1994) O-methylation and other transformations of aromatic compounds by acetogenic bacteria. In: Drake HL (ed) Acetogenesis. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 445–483
Glass JE, Swift G (1989) Agricultural and synthetic polymers, biodegradation and utilization, ACS symposium series, 433. American Chemical Society, Washington, pp 9–64
Gu JD, Ford TE, Mitton DB, Mitchell R (2000a) Microbial corrosion of metals. In: Revie W (ed) The Uhlig corrosion handbook, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 915–927
Gu JD, Ford TE, Mitton DB, Mitchell R (2000b) Microbial degradation and deterioration of polymeric materials. In: Revie W (ed) The Uhlig Corrosion Handbook, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 439–460
Gu JD (2003) Microbiological deterioration and degradation of synthetic polymeric materials: recent research advances. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 52:69–91
Hadad D, Geresh S, Sivan A (2005) Biodegradation of polyethylene by the thermophilic bacterium Brevibacillus borstelensis. J Appl Microbiol 98:1093–1100
Hofrichter M, Lundell T, Hatakka A (2001) Conversion of milled pine wood by manganese peroxidase from Phlebia radiata. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4588–4593
Howard GT, Blake RC (1998) Growth of Pseudomonas fluorescens on a polyester-based polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-protease enzyme. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 42:7–12
Howard GT (2002) Biodegradation of polyurethane: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 49:245–252
Imam SH, Gould JM, Gordon SH, Kinney MP, Ramsey AM, Tosteson TR (1992) Fate of starch-containing plastic 61 ms exposed in aquatic habitats. Curr Microbiol 25:1–8
Kwpp LR, Jewell WJ (1992) Biodegradability of modified plastic films in controlled biological environments. Environ Technol 26:193–198
Lee B, Pometto AL, Fratzke A, Bailey TB (1991) Biodegradation of degradable plastic polyethylene by Phanerochaete and Streptomyces species. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:678–685
Maeda H, Yamagata Y (2005) Purification and characterization of a biodegradable plastic-degrading enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:778–788
Masaki K, Kamini NR, Ikeda H (2005) Cutinase-like enzyme from the yeast Cryptococcus sp. strain S-2 hydrolyzes polylactic acid and other biodegradable plastics. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7548–7550
Mayer AM, Staples RC (2002) Laccase new functions for an old enzyme. Phytochemistry 60:561–565
Nakajima K, Onuma T, Kimpara N, Nakahara T (1995) Isolation and characterization of a bacterium which utilizes polyester polyurethane as a sole carbon and nitrogen source. FEMS Microbiol Lett 129:39–42
Pathirana RA, Seal KJ (1983) Gliocladium roseum (Bainer), a potential biodeteriogen of polyester polyurethane elastomers. In: Oxley TA, Barry S (eds) Biodeterioration, 5th edn. Wiley, Chichester, pp 679–689
Phua SK, Castillo E, Anderson JM, Hiltner A (1987) Biodegradation of a polyurethane in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res 21:231–246
Pospisil J, Nespurek S (1997) Highlights in chemistry and physics of polymer stabilization. Macromol Symp 115:143–163
Rivard C, Moens L, Roberts K, Brigham J, Kelley S (1995) Starch esters as biodegradable plastics: effects of ester group chain length and degree of substitution on anaerobic biodegradation. Enzym Microb Technol 17:848–852
Rowe L, Howard GT (2002) Growth of Bacillus subtilis on polyurethane and the purification and characterization of a polyurethanase-lipase enzyme. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 50:33–40
Ruiz C, Main T, Hilliard N, Howard GT (1999) Purification and characterization of two polyurethanase enzymes from Pseudomonas chlororaphis. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 43:43–47
Russell JR (2011) Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by endophytic fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6076–6084
Scott G (1999) Polymers in modern life. Polymers and the Environment. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Seymour RB (1989) Polymer science before & after 1899: notable developments during the lifetime of Maurtis Dekker. J Macromol Sci, Pure Appl Chem 26:1023–1032
Shah AA, Fariha H (2008) Biological degradation of plastics: a comprehensive review. Biotechnol Adv 26:246–265
Shimao M (2001) Biodegradation of plastics. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12:242–247
Sivan A (2011) New perspectives in plastic biodegradation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:422–426
Tokiwa Y, Calabia BP (2004) Review degradation of microbial polyesters. Biotechnol Lett 26:1181–1189
Tokiwa Y, Calabia BP (2009) Biodegradability of plastics. Int J Mol Sci 10:3722–3742
Treviño AL, Garcia G (2011) Polyurethane foam as substrate for fungal strains. Adv Biosci Biotechnol 2:52–58
Underkofler LA (1958) Production of microbial enzymes and their applications. Appl Microbiol 6:212–221
Yang HS, Yoon JS, Kim MN (2004) Effects of storage of a mature compost on its potential for biodegradation of plastics. Polym Degrad Stab 84:411–417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhardwaj, H., Gupta, R. & Tiwari, A. Communities of Microbial Enzymes Associated with Biodegradation of Plastics. J Polym Environ 21, 575–579 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0456-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0456-z