Abstract
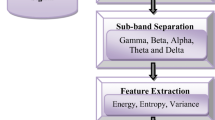
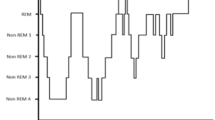
A novel multimodal and bio–inspired approach to biomedical signal processing and classification is presented in the paper. This approach allows for an automatic semantic labeling (interpretation) of sleep apnea events based the proposed data–driven biomedical signal processing and classification. The presented signal processing and classification methods have been already successfully applied to real–time unimodal brainwaves (EEG only) decoding in brain–computer interfaces developed by the author. In the current project the very encouraging results are obtained using multimodal biomedical (brainwaves and peripheral physiological) signals in a unified processing approach allowing for the automatic semantic data description. The results thus support a hypothesis of the data–driven and bio–inspired signal processing approach validity for medical data semantic interpretation based on the sleep apnea events machine–learning–related classification.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
St. Vincent’s University Hospital / University College Dublin sleep apnea database (2011). doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.13026/C26C7D. http://physionet.org/physiobank/database/ucddb/
Ahrabian, A., Looney, D., Stanković, L., and Mandic, D. P., Synchrosqueezing-based time-frequency analysis of multivariate data. Signal Process. 106:331–341, 2015.
Ahrabian, A., and Mandic, D. P., A class of multivariate denoising algorithms based on synchrosqueezing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(9):2196–2208, 2015.
Ahrabian, A., and Mandic, D.P., Selective time-frequency reassignment based on synchrosqueezing. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(11):2039–2043, 2015.
Amari, S., and Wu, S.: An information-geometrical method for improving the performance of support vector machine classifiers. In: Ninth International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, ICANN 99. (Conf. Publ. No. 470), Vol. 1, pp. 85–90. IET (1999)
Barachant, A., Bonnet, S., Congedo, M., and Jutten, C., Multiclass brain–computer interface classification by riemannian geometry. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(4):920–928, 2012.
Barachant, A., and Congedo, M.: A plug&play P300 BCI using information geometry. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0107 (2014)
Congedo, M., Barachant, A., and Andreev, A.: A new generation of brain-computer interface based on Riemannian geometry. arXiv preprint arXiv:1310.8115 (2013)
Daubechies, I., Lu, J., and Wu, H. T., Synchrosqueezed wavelet transforms: An empirical mode decomposition-like tool. Appl. Comput. Harmonic Anal. 30(2):243–261, 2011. doi:10.1016/j.acha.2010.08.002. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1063520310001016.
Hachaj, T., and Ogiela, M. R., Cad system for automatic analysis of ct perfusion maps. Opto-Electron. Rev. 19(1):95–103 , 2011.
Huang, N., Shen, Z., Long, S., Wu, M., Shih, H., Zheng, Q., Yen, N. C., Tung, C., and Liu, H., The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454(1971):903–995, 1998.
Mandic, D., Rehman, N., Wu, Z., and Huang, N., Empirical mode decomposition-based time-frequency analysis of multivariate signals: The power of adaptive data analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 30(6):74–86, 2013. doi:10.1109/MSP.2013.2267931.
Molla, M., Tanaka, T., Rutkowski, T., and Tanaka, K.: Phase synchronization analysis of eeg channels using bivariate empirical mode decomposition. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1182–1186. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6637837 (2013)
Molla, M. K. I., Tanaka, T., and Rutkowski, T.: Multivariate emd based approach to eog artifacts separation from eeg. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 653–656. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2012.6287968 (2012)
Ogiela, L., and Ogiela, M. R.: Semantic analysis processes in advanced pattern understanding systems. In: Advanced Computer Science and Information Technology, pp. 26–30. Springer (2011)
Rehman, N., and Mandic, D. P., Multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Proc. R. Soc. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 466(2117):1291–1302, 2010. doi:10.1098/rspa.2009.0502. http://rspa.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/466/2117/1291.abstract.
Rutkowski, T., Cichocki, A., Tanaka, T., Mandic, D., Cao, J., and Ralescu, A.: Multichannel spectral pattern separation - an eeg processing application. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2009. ICASSP 2009. pp. 373–376. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2009.4959598 (2009)
Rutkowski, T. M., Cichocki, A., Tanaka, T., Ralescu, A.L., and Mandic, D. P.: Clustering of spectral patterns based on emd components of eeg channels with applications to neurophysiological signals separation. In: Advances in Neuro-Information Processing, pp. 453–460. Springer (2008)
Rutkowski, T. M., and Mori, H., Tactile and bone-conduction auditory brain computer interface for vision and hearing impaired users. J. Neurosci. Methods 244:45–51, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.04.010. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165027014001265.
Rutkowski, T. M., Struzik, Z. R., Mandic, D. P.: EEG epileptic seizures separation with multivariate empirical mode decomposition for diagnostic purposes. In: 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 7128–7131. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE Press, Osaka. Japan. doi:10.1109/EMBC.2013.6611201 (2013)
Rutkowski, T. M., Vialatte, F., Cichocki, A., Mandic, D., Barros, A. K., Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems, Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, vol. 4253, chap. Auditory Feedback for Brain Computer Interface Management - An EEG Data Sonification Approach, pp. 1232–1239. Berlin & Heidelberg: Springer, 2006.
Theodoridis, S., and Koutroumbas, K.: Pattern Recognition, 4th edn. Acedemic Press (2009)
Vapnik, V.: The Nature of Statistical Learnig Theory. Springer Verlag (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Transactional Processing Systems
The author is currently with The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rutkowski, T.M. Data–Driven Multimodal Sleep Apnea Events Detection. J Med Syst 40, 162 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0520-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0520-7