Abstract
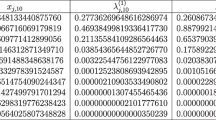
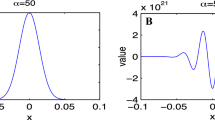
Modified Gauss–Laguerre exponentially fitted quadrature rules are introduced for the computation of integrals of oscillatory functions over the whole positive semiaxis. Their weights and nodes depend on the frequency of oscillation in the integrand, thus increasing the accuracy of classical Gauss–Laguerre formulae. The asymptotic order is discussed, and an algorithm for determining weights and nodes for a general number N of nodes is provided, resulting an improvement of the existing quadrature formulae. Numerical illustrations are also presented.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arfken, G.: Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Orlando, FL (1985)
Asheim, A., Deaño, A., Huybrechs, D., Wang, H.: A Gaussian quadrature rule for oscillatory integrals on a bounded interval. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 34(3), 883–901 (2014)
Asheim, A., Huybrechs, D.: Complex Gaussian quadrature for oscillatory integral transforms. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 33(4), 1322–1341 (2013)
Bao, G., Sun, W.: A fast algorithm for the electromagnetic scattering from a large cavity. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 27, 553–574 (2005)
Cardone, A., Ferro, M., Ixaru, L.G.R., Paternoster, B.: A family of exponential fitting direct quadrature methods for volterra integral equations. AIP Conference Proceedings. 1281, 2204–2207 (2010)
Cardone, A., Ixaru, L.G.R., Paternoster, B.: Exponential fitting direct quadrature methods for Volterra integral equations. Numer. Algorithm 55, 467–480 (2010)
Cardone, A., Ixaru, L.G.R., Paternoster, B., Santomauro, G.: Ef-Gaussian direct quadrature methods for Volterra integral equations with periodic solution. Math. Comput. Simul. 110(1), 125–143 (2015)
Cardone, A., Paternoster, B., Santomauro, G.: Exponential fitting quadrature rule for functional equations, AIP Conference Proceedings. 1479, 1169–1172 Springer (2012)
Conte, D., Esposito, E., Paternoster, B., Ixaru, L.G.R.: Some new uses of the \(\eta _m(Z)\) functions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 181, 128–137 (2010)
Conte, D., Ixaru, LGr, Paternoster, B., Santomauro, G.: Exponentially-fitted Gauss–Laguerre quadrature rule for integrals over an unbounded interval. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 255, 725–736 (2014)
Conte, D., Paternoster, B., Santomauro, G.: An Exponentially Fitted Quadrature Rule Over Unbounded Intervals, AIP Conference Proceedings 1479, 1173–1176 Springer (2012)
D’Ambrosio, R., Esposito, E., Paternoster, B.: Exponentially fitted two-step hybrid for \(y^{\prime \prime }=f(x, y)\). J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235, 4888–4897 (2011)
D’Ambrosio, R., Esposito, E., Paternoster, B.: Parameter estimation in exponentially fitted hybrid methods for second order differential problems. J. Math. Chem. 50(1), 155–168 (2012)
D’Ambrosio, R., Esposito, E., Paternoster, B.: Exponentially fitted two-step Runge–Kutta methods: construction and parameter selection. Appl. Math. Comput. 218, 7468–7480 (2012)
D’Ambrosio, R., Ferro, M., Paternoster, B.: Two-step hybrid collocation methods for \(y^{\prime \prime }= f(x, y)\). Appl. Math. Lett. 22, 1076–1080 (2009)
D’Ambrosio, R., Ferro, M., Paternoster, B.: Trigonometrically fitted two-step hybrid methods for special second order ordinary differential equations. Math. Comput. Simul. 81, 1068–1084 (2011)
D’Ambrosio, R., Ixaru, L.G.R., Paternoster, B.: Construction of the ef-based Runge–Kutta methods revisited. Comput. Phys. Commun. 182, 322–329 (2011)
D’Ambrosio, R., Paternoster, B.: numerical solution of a diffusion problem by exponentially fitted finite difference methods. SpringerPlus 3(425), 1–7 (2014)
D’Ambrosio, R., Paternoster, B.: Exponentially fitted singly diagonally implicit Runge–Kutta methods. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 263, 277–287 (2014)
D’Ambrosio, R., Paternoster, B., Santomauro, G.: Revised exponentially fitted Runge–Kutta–Nystrom methods. Appl. Math. Lett. 30, 56–60 (2014)
Davies, P.J., Duncan, D.B.: Stability and convergence of collocation schemes for retarded potential integral equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42, 1167–1188 (2004)
Davis, P. J., Rabinowitz, P.: Methods of numerical integration, Computer Science and Applied Mathematics. Academic Press [A subsidiary of Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers] New York (1975)
Frontczak, R., Schoebel, R.: On modified Mellin transforms, Gauss–Laguerre quadrature, and the valuation of American call options. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 234, 1559–1571 (2010)
Hasheminejad, S.M., Aghabeigi, M.: Liquid sloshing in half-full horizontal elliptical tanks. J. Sound Vib. 324, 332–349 (2009)
Huybrechs, D., Vandewalle, S.: A sparse discretization for integral equation formulations of high frequency scattering problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 29, 2305–2328 (2007)
Ixaru, L.G.R.: Numerical Methods for Differential Equations and Applications. Reidel, Dordrecht (1984)
Ixaru, L.G.R.: Operations on oscillatory functions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 105, 1–19 (1997)
Ixaru, L.G.R.: Runge–Kutta method with equation dependent coefficients. Comput. Phys. Commun. 183, 63–69 (2012)
Ixaru, L.G.R., Paternoster, B.: A Gauss quadrature rule for oscillatory integrands. Comput. Phys. Commun. 133, 177–188 (2001)
Ixaru, L.G.R., Vanden Berghe, G.: Exponential Fitting. Kluwer, Boston (2004)
Kim, K.J.: Quadrature rules for the integration of the product of two oscillatory functions with different frequencies. Comput. Phys. Commun. 153, 135–144 (2003)
Kim, K.J.: Two-frequency-dependent Gauss quadrature rules. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 174, 43–55 (2005)
Kim, K.J., Cools, R., Ixaru, L.G.R.: Quadrature rules using first derivatives for oscillatory integrands. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 140, 479–497 (2002)
Kim, K.J., Cools, R., Ixaru, L.G.R.: Extended quadrature rules for oscillatory integrands. Appl. Numer. Math. 46, 59–73 (2003)
Ledoux, V., Van Daele, M.: Interpolatory quadrature rules for oscillatory integrals. J. Sci. Comput. 53, 586–607 (2012)
Majidian, H.: Numerical approximation of highly oscillatory integrals on semi-finite intervals by steepest descent method. Numer. Algorithm 63(3), 537–548 (2013)
Milovanovic, G.V., Cvetkovic, A.S., Stanic, M.P.: Gaussian quadratures for oscillatory integrands. Appl. Math. Lett. 20, 853–860 (2007)
Paternoster, B.: Present state-of-the-art in exponential fitting. A contribution dedicated to Liviu Ixaru on his 70-th anniversary. Comput. Phys. Commun. 183, 2499–2512 (2012)
Simos, T.E.: An exponentially-fitted Runge–Kutta method for the numerical integration of initial-value problems with periodic or oscillating solutions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 115, 1–8 (1998)
Sun, W., Zamani, N.G.: Adaptive mesh redistribution for the boundary element method in elastostatics. Comput. Struct. 36, 1081–1088 (1990)
Van Daele, M., Vanden Berghe, G., Vande Vyver, H.: Exponentially fitted quadrature rules of Gauss type for oscillatory integrands. Appl. Numer. Math. 53, 509–526 (2005)
Van Daele, M., Van Hecke, T., Vanden Berghe, G., De Meyer, H.: Deferred correction with mono-implicit Runge–Kutta methods for first-order IVPs. Numerical methods for differential equations (Coimbra, 1998). J. Comput. Appl. Math. 111(1–2), 37–47 (1999)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by GNCS-INdAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
The set of functions \(\eta _m(Z),\,m=-1,0,1,2,\ldots \), has been originally introduced in [26] in the context of CP methods for the Schrödinger equation. The functions \(\eta _{m}(Z)\) with \(m=-1,0\) are first defined by some formulae, namely:
and those with \(m>0\) are further generated by recurrence
if \(\ Z\ne 0,\) and by following values at \(Z=0\):
The differentiation of these functions is of direct concern for this paper. The rule is
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conte, D., Paternoster, B. Modified Gauss–Laguerre Exponential Fitting Based Formulae. J Sci Comput 69, 227–243 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0190-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0190-0