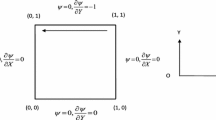
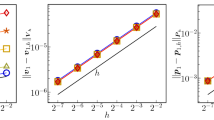
Abstract
In this paper, we study a one-continuum model approach, so-called Brinkman model, to deal with Navier–Stokes–Darcy coupling problem in which the fluid flow exist in both the open channels and porous media. A parameter re-scaling technique is used to reformulate the traditional Brinkman model to a new one in order to investigate its asymptotic accuracy to Stokes and Darcy’s equations, respectively. We attain the convergence theorem in quantitative measure with respect to the dimensionless permeability parameter. We also analyze the error estimates of mixed finite element method for Brinkman model and Forchheimer model, and obtain the optimal convergence rates for both velocity and pressure. Numerical experiments validate the convergence results with respect to the permeability parameter and mesh size for both Brinkman model and Forchheimer model.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angot, Ph, Bruneau, Ch-H, Fabrie, P.: A penalization method to take into account obstacles in an incompressible flow. Numer. Math. 81, 497–520 (1999)
Angot, Ph., Caltagirone, J.P.: New graphical and computational architecture concept for numerical simulation on supercomputers. Proceedings 2nd World Congress on Computational Mechanics, pages 973–976, Stuttgart, (1990)
Arquis, E., Caltagirone, J.P.: Sur les conditions hydrodynamiques au voisinage d’une interface milieu fluide-milieu poreux: application à la convection naturelle. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris II 299, 1–4 (1984)
Beavers, G., Joseph, D.: Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J. Fluid Mech. 30, 197–207 (1967)
Breezi, F.: On the existence, uniqueness and approximation of saddle-point problems arising from Lagrangian problems. RAIRO Anal. Numer. 2, 129–151 (1974)
Brinkman, H.C.: A calculation of the viscous force exerted by a flowing fluid on a dense swarm of particles. Appl. Sci. Res. A1, 27–34 (1949)
Bruneau, Ch-H, Mortazavi, I.: Contrôle passif d’écoulements incompressibles autour d’obstacles à l’aide de milieux poreux. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris IIb 329, 517–521 (2001)
Bruneau, Ch-H, Mortazavi, I.: Numerical modelling and passive flow control using porous media. Comput. Fluids 37, 488–498 (2008)
Cai, M., Mu, M., Xu, J.: Preconditioning techniques for a mixed Stokes/Darcy model in porous media applications. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 233, 346–355 (2009)
Carbou, G.: Brinkman model and double penalization method for the flow around a porous thin layer. J. Math. Fluid Mech. 10, 126–158 (2008)
Carman, P.C.: Fluid flow through granular beds. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 15(150), 32–48 (1937)
Chen, N., Gunzburger, M., Wang, X.: Asymptotic analysis of the differences between the Stokes–Darcy system with different interface conditions and the Stokes–Brinkman system. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 368, 658–676 (2010)
Childress, S.: Viscous flow past a random array of spheres. J. Chem. Phys. 56, 2527–2539 (1972)
Durlofsky, L., Brady, J.F.: Analysis of the brinkman equation as a model for flow in porous media. Phys. Fluids 30, 3329–3341 (1987)
Freed, K.F., Muthukumar, M.: On the Stokes problem for a suspension of spheres at finite concentrations. J. Chem. Phys. 68, 2088–2096 (1978)
He, W., Yi, J.S., Nguyen, T.: Two-phase flow model of the cathode of PEM fuel cell using interdigitated flow fields. AIChE J. 46(10), 2053–2064 (2000)
Hinch, E.J.: An averaged-equation approach to particle interactions in a fluid suspension. J. Fluid Mech. 83, 695–720 (1977)
Howells, I.D.: Drag due to the motion of a Kewtonian fluid through a sparse random array of small fixed rigid objects. J. Fluid Mech. 64, 449–475 (1974)
Jager, W., Mikelić, A.: On the interface boundary condition of Beavers, Joseph, and Saffman. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 60, 1111–1127 (2000)
Jones, I.: Reynolds number flow past a porous spherical shell. Soc. Proc. Camb. Philos. 73, 231–238 (1973)
Kim, S., Russel, W.B.: Modelling of porous media by renormalization of the Stokes equations. J. Fliud Mech. 154, 269–286 (1985)
Layton, W., Schieweck, F., Yotov, I.: Coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40, 2195–2218 (2003)
Liu, F.Q., Wang, C.-Y.: Mixed potential in a direct methanol fuel cell modeling and experiments. J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, B514–B522 (2007)
Liu, W., Wang, C.-Y.: Three-dimensional simulations of liquid feed direct methanol fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, B352–B361 (2007)
Mehdaoui, R., Elmir, M., Draoui, B., Imine, O., Mojtabi, A.: Comparative study between the Darcy–Brinkman model and the modified Navier–Stokes equations in the case of natural convection in a porous cavity. Leonardo J. Sci. 12, 121–134 (2008)
Mu, M., Xu, J.: A two-grid method of a mixed Stokes–Darcy model for coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45, 1801–1813 (2007)
Mu, M., Zhu, X.: Decoupled schemes for a non-stationary mixed Stokes–Darcy model. Math. Comp. 79, 707–731 (2010)
Muthukumar, M., Freed, K.F.: On the Stokes problem for a suspension of spheres at nonzero concentration. II. Calculations for effective medium theory. J. Chem. Phys. 70, 5875 (1979)
Nield, D.A.: The boundary correction for the Rayleigh–Darcy problem: limitations of the Brinkman equation. J. Fluid Mech. 128, 37–46 (1983)
Pasaogullari, U., Mukherjee, P., Wang, C.-Y., Chen, K.: Anisotropic heat and water transport in a pefc cathode gas diffusion layer. J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, B823–B834 (2007)
Pasaogullari, U., Wang, C.-Y.: Liquid water transport in gas diffusion layer of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 151, A399–A406 (2004)
Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Numerical Approximation of Partial Differential Equations. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Rubinstein, J.: Effective equations for flow in random porous media with a large number of scales. J. Fluid Mech. 170, 379–383 (1986)
Saffman, P.: On the boundary condition at the interface of a porous medium. Stud. Appl. Math. 1, 77–84 (1971)
Shi, Z., Wang, X.: Comparison of Darcy’s law, the Brinkman equation, the modified N–S equation and the pure diffusion equation in PEM fuel cell modeling. In: COMSOL Conference (2007)
Sun, P.: Modeling studies and efficient numerical methods for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200, 3324–3340 (2011)
Tam, C.K.W.: The drag on a cloud of spherical particles in low Reynolds number flow. J. Fluid Mech. 38, 537 (1969)
Wang, C.-Y.: Fundamental models for fuel cell engineering. Chem. Rev. 104, 4727–4766 (2004)
Wang, C.-Y., Cheng, P.: A multiphase mixture model for multiphase, multicomponent transport in capillary porous media I. Model development. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 39, 3607–3618 (1996)
Wang, C.-Y., Cheng, P.: Multiphase flow and heat transfer in porous media. Adv. Heat Transf. 30, 93–196 (1997)
Wang, C.-Y., Wang, Z.H., Pan, Y.: Two-phase transport in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. In: International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exhibits, Nashville, TN (1999)
Wang, Z.H., Wang, C.-Y., Chen, K.S.: Two-phase flow and transport in the air cathode of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 94, 40–50 (2001)
Acknowledgments
P. Sun is supported by NSF Grant DMS-1418806.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, P., Sun, Y. Asymptotic Analysis and Error Estimates of Mixed Finite Element Method for Brinkman Model. J Sci Comput 68, 116–142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-015-0131-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-015-0131-3