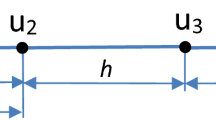
We present finite difference schemes for solving the variable coefficient Poisson and heat equations on irregular domains with Dirichlet boundary conditions. The computational domain is discretized with non-graded Cartesian grids, i.e., grids for which the difference in size between two adjacent cells is not constrained. Refinement criteria is based on proximity to the irregular interface such that cells with the finest resolution is placed on the interface. We sample the solution at the cell vertices (nodes) and use quadtree (in 2D) or octree (in 3D) data structures as efficient means to represent the grids. The boundary of the irregular domain is represented by the zero level set of a signed distance function. For cells cut by the interface, the location of the intersection point is found by a quadratic fitting of the signed distance function, and the Dirichlet boundary value is obtained by quadratic interpolation. Instead of using ghost nodes outside the interface, we use directly this intersection point in the discretization of the variable coefficient Laplacian. These methods can be applied in a dimension-by-dimension fashion, producing schemes that are straightforward to implement. Our method combines the ability of adaptivity on quadtrees/octrees with a quadratic treatment of the Dirichlet boundary condition on the interface. Numerical results in two and three spatial dimensions demonstrate second-order accuracy for both the solution and its gradients in the L 1 and L ∞ norms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aftosmis, M. J., Berger, M. J., and Melton, J. E. (1998). Adaptive Cartesian mesh generation. In CRC Handbook of Mesh Generation (Contributed Chapter).
Almgren, A. (1991). A Fast Adaptive Vortex Method Using Local Corrections. PhD thesis, University of California, Berkeley.
Almgren A., Bell J., Colella P., Howell L., Welcome M. (1998) A conservative adaptive projection method for the variable density incompressible navier-stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys 142: 1–46
Almgren A., Buttke R., Colella P. (1994) A fast adaptive vortex method in three dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 113: 177–200
Berger M., Olige J. (1984) Adaptive mesh refinement for hyperbolic partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 53: 484–512
Chen S., Merriman B., Osher S., Smereka P. (1997) A simple level set method for solving Stefan problems. J. Comput. Phys. 135: 8–29
Babuska I., Flaherty J.E., Henshaw W.D., Hopcroft J.E., Oliger J.E., Tezduyar T. (eds) (1995) Modeling, Mesh Generation, and Adaptive Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations. Springer Verlag, Berlin, 450 pp
Fedkiw R., Aslam T., Merriman B., Osher S. (1999) A non-oscillatory Eulerian approach to interfaces in multimaterial flows (the ghost fluid method). J. Comput. Phys. 152: 457–492
Gibou F., Fedkiw R. (2005) A fourth order accurate discretization for the laplace and heat equations on arbitrary domains, with applications to the stefan problem. J, Comput. Phys. 202: 577–601
Gibou F., Fedkiw R., Caflisch R., Osher S. (2003) A level set approach for the numerical simulation of dendritic growth. J. Sci. Comput. 19: 183–199
Gibou F., Fedkiw R., Cheng L.-T., Kang M. (2002) A second–order–accurate symmetric discretization of the poisson equation on irregular domains. J. Comput. Phys. 176: 205–227
Johansen H., Colella P. (1998) A cartesian grid embedded boundary method for poisson’s equation on irregular domains. J. Comput. Phys. 147: 60–85
Johnson C. (1987) Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations by the Finite Element Method. Cambridge University Press, New York, NY
Jomaa Z., Macaskill C. (2005) The embedded finite difference method for the poisson equation in a domain with an irregular boundary and dirichlet boundary conditions. J. Comput. Phys. 202: 488–506
Kreiss H.O., Manteuffel H.-O., Schwartz T.A., Wendroff B., White A.B. Jr. (1986) Supra-convergent schemes on irregular grids. Math. Comp. 47: 537–554
LeVeque R., Li Z. (1994) The immersed interface method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31: 1019–1044
Lipnikov K., Morel J., Shashkov M. (2004) Mimetic finite difference methods for diffusion equations on non-orthogonal non-conformal meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 199: 589–597
Liu X., Fedkiw R., Kang M. (2000) A boundary condition capturing method for Poisson’s equation on irregular domains. J. Comput. Phys. 154: 151
Losasso F., Fedkiw R., Osher S. (2006) Spatially adaptive techniques for level set methods and incompressible flow. Comput. Fluids 35: 995–1010
Losasso F., Gibou F., Fedkiw R. (2004) Simulating water and smoke with an octree data structure. SIGGRAPH 2004, ACM TOG 23: 457–462
Manteuffel T., White A. (1986) The numerical solution of second-order boundary value problems on nonuniform meshes. Math. Comput. 47(176): 511–535
Mayo A. (1984) The fast solution of poisson’s and the biharmonic equations on irregular regions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 21: 285–299
McCorquodale P., Colella P., Grote D., Vay J.-L. (2004) A node-centered local refinement algorithm for poisson’s equation in complex geometries. J. Comput. Phys. 201: 34–60
McKenney A., Greengard L. (1995) A fast poisson solver for complex geometries. J. Comput. Phys. 118: 348–355
Min C., Gibou F., Ceniceros H.D. (2006) A supra-convergent finite difference scheme for the variable coefficient poisson equation on non-graded grids. J. Comput. Phys. 218(1): 123–140
Peskin C. (1977) Numerical analysis of blood flow in the heart. J. Comput. Phys. 25: 220–252
Popinet S. (2003) Gerris: a tree-based adaptive solver for the incompressible euler equations in complex geometries. J. Comput. Phys. 190: 572–600
Saad Y. (1996) Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems. PWS Publishing, New York, NY
Samet H. (1989) The Design and Analysis of Spatial Data Structures. Addison-Wesley, New York
Samet H. (1990) Applications of Spatial Data Structures: Computer Graphics, Image Processing and GIS. Addison-Wesley, New York
Schmidt A. (1996) Computation of three dimensional dendrites with finite elements. J. Comput. Phys. 125: 293–312
Shortley G.H., Weller R. (1938) The numerical solution of laplace’s equation. J. Appl. Phys. 9: 334–348
Strain J. (1999) Tree methods for moving interfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 151: 616–648
Verfurth R. (1996) A Review of a Posteriori Error Estimation and Adaptive Mesh-Refinement Techniques. Wiley-Teubner, Berlin
Young D., Melvin R., Bieterman M., Johnson F., Samant S., Bussoletti J. (1991) A locally refined rectangular grid finite element method: application to computational fluid dynamics and computational physics. J. Comput. Phys. 92: 1–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Min, C. & Gibou, F. A Supra-Convergent Finite Difference Scheme for the Poisson and Heat Equations on Irregular Domains and Non-Graded Adaptive Cartesian Grids. J Sci Comput 31, 19–60 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-006-9122-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-006-9122-8