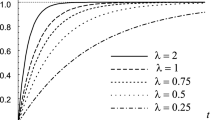
Abstract
In this paper, we present a quasi-analytical method to calculate the optimal enzyme concentrations in a chemical process, considering the minimization of the operation time. The resulting constrained optimal control problem is solved using Pontryagin’s Minimum Principle. First, our method allows us to obtain the generalized solution of an \(n\)-step system with an unbranched scheme and bilinear kinetic models and non-equal catalytic efficiencies of the enzymes. Second, we discuss the sensitivity analysis of these catalytic parameters in detail.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Klipp, R. Heinrich, H.G. Holzhutter, Prediction of temporal gene expression. Metabolic optimization by re-distribution of enzyme activities. Eur. J. Biochem. 269(22), 5406–5413 (2002)
M. Bartl, P. Li, S. Schuster, Modelling the optimal timing in metabolic pathway activation-use of pontryagin’s maximum principle and role of the golden section. BioSystems 101, 67–77 (2010)
D. Oyarzun, B. Ingalls, R. Middleton, D. Kalamatianos, Sequential activation of metabolic pathways: a dynamic optimization approach. Bull. Math. Biol. 71(8), 1851–1872 (2009)
L. Bayón, J.M. Grau, M.M. Ruiz, P.M. Suárez, Optimal control of a linear unbranched chemical process with steps: the quasi-analytical solution. J. Math. Chem. 52(4), 1036–1049 (2014)
T. Turanyi, Sensitivity analysis of complex kinetic systems. Tools and applications. J. Math. Chem. 5(3), 203–248 (1990)
D.M. Hamby, A review of techniques for parameter sensitivity analysis of environmental models. Environ. Monit. Assess. 32(2), 135–154 (1994)
M. Llorens, J.C. Nuno, Y. Rodriguez, E. Melendez-Hevia, F. Montero, Generalization of the theory of transition times in metabolic pathways: a geometrical approach. Biophys. J. 77(1), 23–36 (1999)
N. Torres, Application of the transition time of metabolic systems as a criterion for optimization of metabolic processes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 44, 291–296 (1994)
R. Vinter, Optimal Control, Systems and Control: Foundations and Applications (Birkhäuser Boston Inc, Boston, 2000)
H. Maurer, C. Buskens, J.H.R. Kim, C.Y. Kaya, Optimization methods for the verification of second order sufficient conditions for bang-bang controls. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 26, 129–156 (2005)
A. Saltelli, M. Ratto, S. Tarantola, F. Campolongo, Sensitivity analysis for chemical models. Chem. Rev. 105(7), 2811–2828 (2005)
M. Komorowski, M. Costa, D. Rand, M. Stumpf, Sensitivity, robustness, and identifiability in stochastic chemical kinetics models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108(21), 8645–8650 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayón, L., Otero, J.A., Ruiz, M.M. et al. Sensitivity analysis of a linear and unbranched chemical process with \(n\) steps. J Math Chem 53, 925–940 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10910-014-0458-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10910-014-0458-2