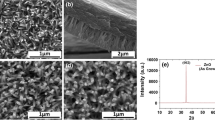
Abstract
A piezoelectric nanogenerator based on Al-doped ZnO (AZO) nanorods with a V-zigzag layer is investigated at a low temperature. The growth temperature, growth time, growth concentration, photoluminescence (PL) spectrum, and AZO epitaxial growth on the ITO glass substrate using aqueous solution are reported and the associated electromechanical and PL properties are discussed. In general, the properties of piezoelectric nanogenerators and their functionality at ultralow temperatures (near liquid helium temperature) are important for applications in extreme environments. A V-zigzag layer is used to enhance the bending and compression deformation of the piezoelectric nanogenerator. The electromechanical properties of AZO nanorods are tested using an ultrasonic wave generator. Results show that the percent transmittance decreases with increasing growth time and growth temperature. The intensities of the PL spectrum and the (002) peak orientation increases with increasing growth temperature. AZO at a low growth temperature of 90 \(^{\circ }\)C has good piezoelectric harvesting efficiency when the piezoelectric nanogenerator has a zigzag structure. The average current, voltage, and power density of the piezoelectric harvesting are 0.76 \(\upmu \)A, 1.35 mV, and 1.026 nW/mm\(^{2}\), respectively. These results confirm the feasibility of growing AZO at low temperature. AZO nanorods have potential for energy harvester applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.Y. Yeon, J.H. Yoon, S.Y. Jin, J.C. Won, High-power properties of piezoelectric hard materials sintered at low temperature for multilayer ceramic actuators. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33(1), 1769–1778 (2013)
V.P. Mineev, Half-quantum vortices in polar phase of superfluid He-3. J. Low Temp. Phys. 177(1–2), 48–58 (2014)
J.B. Ketterson, Probing the frequency and wavevector dependent response of 3He using patterned piezoelectric transducers. J. Low Temp. Phys. 159(5–6), 606–613 (2010)
Q. Chen, T. Wang, J. Wu, X. Cheng, X. Wang, B. Zhang, D. Xiao, J. Zhu, Low temperature sintering of Ba\(_0.91\)Ca\(_0.09\)Ti\(_0.916\)Sn\(_0.084\)O\(_3\) lead-free piezoelectric ceramics with the additives of ZnO and MnO\(_2\). J. Electroceram. 32(2–3), 175–179 (2014)
G. Wei, J. Dafei, W. Wanchun, J.M. Humphrey, Low temperature piezoelectric and dielectric properties of lead magnesium niobate titanate single crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 084104 (2007)
T.A. El-Brolossy, O. Saber, S.S. Ibrahim, Determining the thermophysical properties of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles by the photoacoustic technique. Chin. Phys. B 22(1), 074401 (2013)
A.E. Jimenez-Gonzalez, Modification of ZnO thin films by Ni, Cu, and Cd doping. J. Solid State Chem. 28(2), 176–180 (1997)
O. Bamiduro, H. Mustafa, R. Mundle, R.B. Konda, A.K. Pradhan, Metal-like conductivity in transparent Al:ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(25), 252108–252110 (2007)
P. Kadam, C. Agashe, S.J. Mahamuni, Al-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 104(10), 103501–103501-4 (2008)
K.Y. Wu, C.C. Wang, D.H. Chen, Preparation and conductivity enhancement of Al-doped zinc oxide thin films containing trace Ag nanoparticles by the sol-gel process. Nanotechnology 18(30), 305604 (2007)
X.Y. Xue, L.M. Li, H.C. Yu, Y.J. Chen, Y.G. Yang, Extremely stable field emission from AlZnO nanowire arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89(4), 043118 (2006)
B.H. Kong, M.K. Choi, H.K. Cho, J.H. Kim, S. Baek, J.H. Lee, Conformal coating of conductive ZnO:Al films as transparent electrodes on high aspect ratio Si microrods. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 13(2), K12–K14 (2010)
S. Mondal, K.P. Kanta, P. Mitra, Preparation of Al-doped ZnO AZO thin film by SILAR. J. Phys. Sci. 12(1), 221–229 (2008)
W.Y. Chang, T.H. Fang, C.I. Weng, S.S. Yang, Flexible piezoelectric harvesting based on epitaxial growth of ZnO. Appl. Phys. A 102(3), 705–711 (2010)
Y. Zhou, W. Wu, G. Hu, H. Wu, S. Cui, Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanorod arrays with the addition of polyethyleneimine. Mater. Res. Bull. 43(8–9), 2113–2118 (2008)
K. Elen, H.V. den Rul, A. Hardy, M.K.V. Bael, J. DHaen, R. Peeters, D. Franco, J. Mullens, Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanorods: a statistical determination of the significant parameters in view of reducing the diameter’. Nanotechnology 20(5), 055608 (2009)
S.K. Park, J.H. Park, K.Y. Ko, S. Yoon, K.S. Chu, W. Kim, Y.R. Do, Hydrothermal-electrochemical synthesis of ZnO nanorods. Cryst. Growth Des. 9(8), 3615–3620 (2009)
J. Kim, J.H. Yun, S.W. Jee, Y.C. Park, M. Ju, S. Han, Y. Kim, J.H. Kim, W.A. Anderson, J.H. Lee, J. Yi, Rapid thermal annealed Al-doped ZnO film for a UV detector. Mater. Lett. 65(4), 786–789 (2011)
Z. Zhan, J. Zhang, Q. Zheng, D. Pan, J. Huang, F. Huang, Z. Lin’, Strategy for preparing Al-doped ZnO thin film with high mobility and high stability. Cryst. Growth Des. 11(1), 21–25 (2011)
S. Cho, S.H. Jung, J.W. Jang, E. Oh, K.H. Lee, Simultaneous synthesis of Al-doped ZnO nanoneedles and zinc aluminum hydroxides through use of a seed layer. Cryst. Growth Des. 8(12), 4553–4558 (2008)
W.Y. Chang, T.H. Fang, C.-H. Syu, Material characteristics of zinc oxide doped aluminum for microharvesting. Appl. Mech. Mater. 80–81(1), 245–249 (2011)
J. Ma, F. Ji, D.H. Zhang, H.L. Ma, S.Y. Li, Optical and electronic properties of transparent conducting ZnO and ZnO:Al films prepared by evaporating method. Thin Solid Films 357(1), 98–101 (1999)
Y. Liu, J. Lian, Optical and electrical properties of aluminum-doped ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(7), 3727–3730 (2007)
X.J. Wang, Q.S. Lei, W. Xu, W.L. Zhou, J. Yu, Preparation of ZnO:Al thin film on transparent TPT substrate at room temperature by RF magnetron sputtering technique. Mater. Lett. 63(16), 1371–1373 (2009)
K.H. Kim, R. Wibowo, A.B. Munir, Properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films sputtered from powder compacted target. Mater. Lett. 60(15), 1931–1935 (2006)
A.F. Aktaruzzaman, G.L. Sharma, L.K. Malthotra, Electrical, optical and annealing characteristics of ZnO:Al films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 198(1–2), 67–74 (1991)
Y.T. Yin, W.X. Que, C.H. Kam, ZnO nanorods on ZnO seed layer derived by sol–gel process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 53(3), 605–612 (2010)
T.H. Fang, S.H. Kang, Physical properties of ZnO:Al nanorods for piezoelectric nanogenerator application. Curr. Nanosci. 7(1), 505–511 (2010)
W.Y. Chang, C.H. Yang, Energy harvesting simulation of piezoelectric ZnO for electromechanical nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Eng. 1(1), 102–107 (2013)
W.L. Wu, G.G. Siu, C.L. Fu, H.C. Ong, Photoluminescence and cathodoluminescence studies of stoichiometric and oxygen-deficient ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(1), 2285–2287 (2001)
Water W., Fang T. H., Ji L. W., Lee C. C., Effect of growth temperature on photoluminescence and piezoelectric characteristics of ZnO nanowires. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 158(1–3), 75–78 (2009)
H.M. Kim, S.K. Jung, J.S. Ahn, Y.J. Kang, K.C. Je, Electrical and optical properties of in2o3-ZnO films deposited on polyethylene terephthalate substrates by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42(1), 223–227 (2003)
X. Wang, J. Song, J. Liu, Z.L. Wang, Drect-current nanogenerator driven by ultrasonic waves. Science 316(1), 102–105 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grants NSC 100-2628-E-151-003-MY3, NSC 100-2221-E-151-018-MY3, and MOST 103-2221-E-150-017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, WY., Fang, TH. & Tsai, JH. Electromechanical and Photoluminescence Properties of Al-doped ZnO Nanorods Applied in Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. J Low Temp Phys 178, 174–187 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-014-1249-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-014-1249-7