Abstract
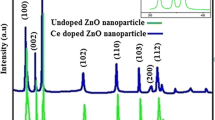
We report synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles and thin films of undoped and cerium doped zinc oxide (Ce:ZnO).Samples were prepared by sol–gel and spin coating method. The effect of cerium concentrations, as a rare- earth impurity, on structural and optical properties of ZnO is examined. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements have proven that the films are polycrystalline with the (101) as preferential crystallographic orientation. Grain size of the prepared ZnO NPs is approximately 20 nm and for the doped samples is ~43 nm. From the differential thermal analysis crystallization thermal threshold was detected to be 400 °C. As observed by field emission scanning electron microscopy, XRD and optical transmission, the film microstructure is strongly dependent on the dopant concentration. Data obtained from the UV–Visible spectroscopy shows a blue shift in the absorption edge of cerium doped ZnO which is confirmed by optical band gap calculation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Goldberger, D. Sirbuly, M. Law, P. Yang, ZnO nanowire transistors. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 9–14 (2005)
P. Morvillo, R. Diana, A. Mucci, E. Bobeico, R. Ricciardi, C. Minarini, Influence of annealing treatments on solution-processed ZnO film deposited on ITO substrate as electron transport layer for inverted polymer solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 141, 210–217 (2015)
P. Pauzauskie, P. Yang, Nanowire photonics. Mater. Today 9, 36–45 (2006)
Q. Wan, C.L. Lin, X.B. Yu, T. Wang, Room temperature hydrogen storage characteristics of ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 124 (2004)
A. Sanchez-Juarez, A. Tiburcio-Silver, A. Ortiz, Properties of fluorine-doped ZnO deposited onto glass by spray pyrolysis. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 52, 301 (1998)
D. Fangli, W. Dongmei, S. Yingzhong, Preparation, characterization and infrared emissivity study of Ce-doped ZnO films. J. Rare Earths 28, 391 (2010)
M. Khanlary, S. Isazadeh, Structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. Micro Nano Lett. 6, 767–769 (2011)
M. Tokumoto, V. Briois, Preparation of ZnO nanoparticles: structural study of the molecular precursor. J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 26, 547 (2003)
M. Lim, S. Seok, S. Hong, Near infrared luminescence of Er ions in sol–gel ZnO/zirconium-oxo-alkylsiloxane nanocomposite films. Thin Solid Films 515, 2423–2427 (2006)
D. Raoufi, T. Raoufi, The effect of heat treatment on the physical properties of sol–gel derived ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 5812–5817 (2009)
G. Neri, A. Bonavita, G. Rizzo, S. Galvagno, S. Capone, P. Siciliano, A study of the catalytic activity and sensitivity to different alcohols of CeO2–Fe2O3 thin films. Sens. Actuators B 112, 78–83 (2005)
V. Gupta, A. Mansingh, Influence of postdeposition annealing on the structural and optical properties of sputtered zinc oxide film. J. Appl. Phys. 80(2), 1063 (1996)
G.R. Li, X.H. Lu, W.X. Zhao, C.Y. Su, Y.X. Tong, Controllable electrochemical synthesis of Ce4+-doped ZnO nanostructures from nanotubes to nanorods and nanocages. Cryst. Growth Des. 8(4), 1276–1281 (2008)
M. Ferhat, A. Zaoui, R. Ahuja, Agnetism and band gap narrowing in Cu-doped Zn. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 142–502 (2009)
K. Vanheusden, W. Warren, C. Seager, D. Tallant, J. Voigt, Fabrication of three-dimensional ZnO with hierarchical structure via an electro deposition process. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 79–83 (1996)
R. Cebulla, R. Wendt, K. Ellmer, Al-doped zinc oxide films deposited by simultaneous rf and dc excitation of a magnetron plasma: relationships between plasma parameters and structural and electrical film properties. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 1087 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanlary, M.R., Hajinorozi, A. & Baghshahi, S. Influence of Ce Doping Concentration on the Structural and Optical Properties of Sol–Gel Derived ZnO:Ce Nanostructures. J Inorg Organomet Polym 25, 1521–1528 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-015-0271-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-015-0271-9