Abstract
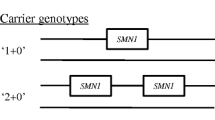
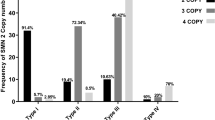
Spinal muscular atrophy is an autosomal recessive neuromuscular disease mainly caused by homozygous deletion of SMN1. The 2-copy SMN1 allele may present in the families of SMA patients with homozygous deletion of SMN1, one of whose parents has two SMN1 copies. In such families, individuals having two SMN1 copies still have a chance to be “2 + 0” carriers. In this study, the risks for the parents, fetuses and other siblings having two SMN1 copies to be “2 + 0” carriers were estimated based on Chinese meta-analysis data and turned out to be rather striking. Our findings would help to optimize genetic counseling regarding spinal muscular atrophy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
References marked with an asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analysis
Alías, L., Barcelo, M. J., Bernal, S., Martínez-Hernández, R., Also-Rallo, E., Vázquez, C., et al. (2014). Improving detection and genetic counseling in carriers of spinal muscular atrophy with two copies of the SMN1 gene. Clinical Genetics, 85, 470–475.
Burghes, A. H. M. (1997). When is a deletion not a deletion: when it is converted. American Journal of Human Genetics, 61, 9–15.
Burglen, L., Lefebvre, S., Clermont, O., Burlet, P., Viollet, L., Cruaud, C., et al. (1996). Structure and organization of the human survival motor neurone (SMN) gene. Genomics, 32, 479–482.
*Cao, D., Ren, M., Lin, C., Cui, W., Ma, H., Wu, Y., et al. (2009). Gene diagnosis for spinal muscular atrophy and its application study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 26, 306–309.
*Cao, Y., Qu, Y., Song, F., Bai, J., Jin, Y., Wang, H., et al. (2013). ection of homozygous deletions in spinal muscular atrophy with genomic DNA sequencing. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 30, 410–414.
*Chan, V., Yip, B., Yam, I., Au, P., Lin, C., Wong, V., et al. (2004). Carrier incidence for spinal muscular atrophy in southern Chinese. Journal of Neurology, 251, 1089–1093.
*Chen, W. (2004). Study on the gene diagnosis and the genotype-phenotype correlation of spinal muscular atrophy. (Master’s thesis). Retrieved from CNKI database.
*Chen, K., Wang, Y., Rennert, H., Joshi, I., Mills, J. K., Leonard, D. G., et al. (1999). Duplications and de novo deletions of the SMNt gene demonstrated by fluorescence-based carrier testing for spinal muscular atrophy. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 85, 463–469.
*Chen, W., Wu, Z., Wang, N., Lin, M., & Mu-rong, S. (2005). Quantitative studies on SMN1 gene and carrier testing of spinal muscular atrophy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 22, 599–602.
*Chen, T., Tzeng, C., Wang, C., Wu, S., Chang, J., Yang, S., et al. (2011). Identification of bidirectional gene conversion between SMN1 and SMN2 by simultaneous analysis of SMN dosage and hybrid genes in a Chinese population. Journal of Neurological Sciences, 308, 83–87.
*Chen, H., Meng, Y., Shu, J., & Song, L. (2012a). Genetic diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy using MLPA. Tian Jin Yi Yao, 40, 1095–1098.
*Chen, Y., He, J., Zhang, Q., Lin, X., Wang, N., & Chen, W. (2012b). Studies on the prenatal diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Zhongguo Xian Dai Shen Jing Ji Bing Za Zhi, 12, 294–299.
*Ding, Y., Yu, Y., Ye, X., & Wang, Y. (2012). Application of multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification in molecular diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy. Lin Chuang Er Ke Za Zhi, 30, 1001–1005.
*Fang, P., Li, L., Zeng, J., Zhou, W., Wu, W., Zhong, Y., et al. (2015). Molecular characterization and copy number of SMN1, SMN2 and NAIP in Chinese patients with spinal muscular atrophy and unrelated healthy controls. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 16, 11.
*Gong, B., Zhang, L., Hou, Y., Hu, H., Li, H., Tan, M., et al. (2013). Carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy in 4719 pregnant women in Shanghai region. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 30, 670–672.
*Gu, Y. (2010). Combined application of MLPA and DNA/cDNA sequencing for the genetic diagnosis of DMD/SMA patients and high-risk fetuses. (Master’s thesis). Retrieved from CNKI database.
*He, J. (2013). Molecular analysis of genes in 5q13 region in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. (Master’s thesis). Retrieved from CNKI database.
Hendrickson, B. C., Donohoe, C., Akmaev, V. R., Sugarman, E. A., Labrousse, P., Boguslavskiy, L., et al. (2009). Differences in SMN1 allele frequencies among ethnic groups within North America. Journal of Medical Genetics, 46, 641–644.
*Hu, X. (2010). The application of MLPA in gene diagnosis of single gene disorders DMD/BMD and SMA. (Master’s thesis). Retrieved from CNKI database.
*Jiang, Y., Peng, G., Wu, Q., & Zhou, Y. (2014). Clinical application of real-time PCR for the detection of genetic mutations underlying spinal muscular atrophy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 31, 180–184.
Lefebvre, S., Bürglen, L., Reboullet, S., Clermont, O., Burlet, P., Viollet, L., et al. (1995). Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell, 80, 155–165.
*Li, X. (2011). Quantitative analysis of SMN1 gene and carrier testing of spinal muscular atrophy. (Master’s thesis). Retrieved from CNKI database.
*Long, M., Song, F., Qu, Y., Meng, Y., Wang, H., Jin, Y., et al. (2008). Quantitative analysis of SMN1 and SMN2 genes based on DHPLC: a reliable method for detection of non-homozygous patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 88, 1259–1263.
*Lu, L. (2005). The studies on the detection and expression of SMN gene of spinal muscular atrophy. (Master’s thesis). Retrieved from CNKI database.
*Lu, L., Ma, H., Jiang, J., Wang, T., & Hu, B. (2007). Application of real-time PCR analysis of the SMN1 gene in the carrier testing of spinal muscular atrophy. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi, 9, 458–460.
*Luo, F., Wu, W., Wang, H., Geng, Q., Deng, X., & Xie, J. (2013). Genetic diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification technology. Zhongguo You Sheng Yu Yi Chuan Za Zhi, 21, 14–16.
McAndrew, P. E., Parsons, D. W., Simard, L. R., Rochette, C., Ray, P., Mendell, J. R., et al. (1997). Identification of proximal spinal muscular atrophy carriers and patients by analysis of SMNt and SMNc gene copy number. American Journal of Human Genetics, 60, 1411–1422.
Ogino, S., Wilson, R. B., & Gold, B. (2004). New insights on the evolution of the SMN1 and SMN2 region: simulation and meta-analysis for allele and haplotype frequency calculations. European Journal of Human Genetics, 12, 1015–1023.
Pearn, J. (1980). Classification of spinal muscular atrophies. Lancet, 1, 919–922.
Prior, T. W., Nagan, N., Sugarman, E. A., Batish, S. D., & Braastad, C. (2011). Technical standards and guidelines for spinal muscular atrophy testing. Genetics in Medicine, 13, 686–694.
*Qu, X., Xiao, B., Ji, X., Jiang, W., Yang, Z., & Tao, J. (2013). A pilot study on spinal muscular atrophy carrier screening in Shanghai region using real-time PCR. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 30, 1–4.
*Song, F., Qu, Y., Zou, L., Wang, L., Long, M., Wang, X., et al. (2008). Molecular analysis of survival motor neuron gene in 338 suspicious children patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi, 46, 919–923.
*Su, Y. N., Hung, C. C., Lin, S. Y., Chen, F. Y., Chern, J. P. S., Tsai, C., et al. (2011). Carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) in 107,611 pregnant women during the period 2005–2009: a prospective population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE, 6, e17067.
*Tsai, C. H., Jong, Y. J., Hu, C. J., Chen, C. M., Shih, M. C., Chang, C. P., et al. (2001). Molecular analysis of SMN, NAIP and P44 genes of SMA patients and their families. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 190, 35–40.
*Wang, J., An, Y., Zhou, S., Wang, Y., & Liu, R. (2013). Copy number variation of SMN1 and SMN2 genes in spinal muscular atrophy and analysis of its clinical significance. Zhongguo Xun Zheng Er Ke Za Zhi, 8, 216–219.
Wirth, B., Schmidt, T., Hahnen, E., Rudnik-Schöneborn, S., Krawczak, M., Müller-Myhsok, B., et al. (1997). De novo rearrangements found in 2% of index patients with spinal muscular atrophy: mutational mechanisms, parental origin, mutation rate, and implications for genetic counseling. American Journal of Human Genetics, 61, 1102–1111.
Wirth, B., Herz, M., Wetter, A., Moskau, S., Hahnen, E., Rudnik-Schoneborn, S., et al. (1999). Quantitative analysis of survival motor neuron copies: identification of subtle SMN1 mutations in patients with spinal muscular atrophy, genotype–phenotype correlation, and implications for genetic counseling. American Journal of Human Genetics, 64, 1340–1356.
*Wu, Y., Wu, D., Yin, G., Zhai, Y., Du, H., Zhai, Q., et al. (2008). Gene diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy using MLPA and PCR-RFLP. Zhongguo Ji Hua Sheng Yu Xue Za Zhi, 155, 535–539.
*Xiao, X., Cai, L., Wang, R., Zhou, H., Li, J., & Xie, J. (2009). The application of DHPLC in the gene diagnosis of the childhood type spinal muscular atrophy and in the gene screening of SMA carriers. Jiang Xi Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao, 49, 99–102.
*Yao, R., Yu, Y., Geng, J., Zheng, Z., Wang, J., Shen, Y., et al. (2013). Application of MLPA technology in molecular diagnosis of three inherited diseases. Zhonghua Jian Yan Yi Xue Za Zhi, 36, 136–141.
*Zeng, J., Ke, L., Zeng, X., Cai, M., Tu, X., & Lan, F. (2008). Molecular diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 88, 3262–3264.
*Zeng, J., Lin, Y., Yan, A., Ke, L., Zhu, Z., & Lan, F. H. (2011). Establishment of a molecular diagnostic system for spinal muscular atrophy. Journal of Molecular Diagnosis, 13, 41–47.
*Zeng, G., Zheng, H., Cheng, J., Chen, R., Lin, H., Yang, J., et al. (2014). Analysis and carrier screening for copy numbers of SMN and NAIP in children with spinal muscular atrophy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 31, 152–155.
*Zhang, S., Wu, S., & Li, H. (2013). Clinical features of spinal muscular atrophy type II: 53 cases report. Zhongguo Kang Fu Li Lun Yu Shi Jian, 19, 586–588.
*Zhang, X., Wang, L., Yu, Y., & Fu, Q. (2015). Comparison of three methods for the genetic diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy. Zhonghua Jian Yan Yi Xue Za Zhi, 38, 16–20.
*Zhu, H., Hu, Y., Li, J., Yang, Y., & Wu, X. (2010a). Studies on the molecular diagnosis and prenatal diagnosis of the spinal muscular atrophy carriers by multiplex ligation-dependent probe. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 27, 38–41.
*Zhu, S., Xiong, F., Chen, Y., Yan, T., Zeng, J., Li, L., et al. (2010b). Molecular characterization of SMN copy number derived from carrier screening and from core families with SMA in a Chinese population. European Journal of Human Genetics, 18, 978–984.
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Xiangmin Xu and Jianjiu Chen for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (Grant No. 2014FY110700).
Conflict of Interest
The authors of the article declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
This article is a meta-analysis and does not contain any studies with human participants. Therefore, an informed consent was not necessary.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, X., Tan, H., Yang, P. et al. Notable Carrier Risks for Individuals Having Two Copies of SMN1 in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Families with 2-copy Alleles: Estimation Based on Chinese Meta-analysis Data. J Genet Counsel 26, 72–78 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10897-016-9980-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10897-016-9980-7