Abstract
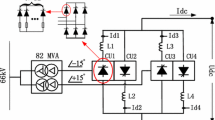
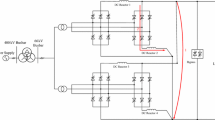
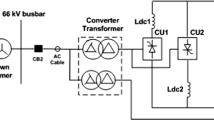
This paper introduces a high power dc testing platform for components test of ITER poloidal field converter prototype. The platform is composed of four phase-controlled rectifiers in parallel with the same direction and output up to rated 120 kA long pulse and 400 kA maximum impulse dc current. In this paper, the circuit model is built and circuit analysis is performed to observe the dynamic behaviors. Due to the feature of strong coupling among paralleled branches, two different control strategies are compared, which respectively are decoupling control and dual closed-loop control. Two operation modes, long pulse model and impulse model adopt their own strategy. Experiments results are performed and the operation modes make an agreement with the theoretical analysis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Shimada, D.J. Campbell, V. Mukhovatov et al., Progress in the ITER physics basis-chapter 1: overview and summary. Nucl. Fusion 47, 1–17 (2007)
J. Tao, I. Benfatto, J. Goff et al., ITER coil power supply and distribution system. in 24th Symposium on Fusion Engineering, Chicago, IL, 2011
J. Goff, J. Gascon, A. Mankani et al., The ITER magnet power supplies and control system. in 2010 International conference on electrical machines and systems (ICEMS), Incheon, Korea, 2010
H. Yuan, P. Fu, G. Gao et al., On the circulating current control of ITER poloidal field converter. J. Fusion Eng. 33, 269–274 (2014)
H. Yuan, P. Fu, G. Gao et al., On the current sharing control of ITER poloidal field converter. J. Fusion Eng. 33, 294–298 (2014)
S.G. Bosga, J.L. Duarte, L.J. Offringa, A.J. Vandenput, Natural circulating current control of a Cycloconverter. Ind. Appl. Soci. Annu. Meet. 2, 1160–1165 (1993)
J. Rajagopalan. Modeling and dynamic analysis of paralleled dc/dc converters with master-slave current sharing control. in Proceedings of the 11th IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC ‘96), vol. 2, pp. 678–684 (1996)
Tian-You Chai, Heng Yue, Multivariable intelligent decoupling control system and its application. Acta Autom. Sin. 31(1), 123–131 (2005)
Peng Li, Brad Lehman, A design method for paralleling current mode controlled dc–dc converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electr. 19(3), 748–756 (2004)
S. Luo, Z. Ye, R.-L. Lin et al., Classification and evaluation of paralleling methods for power supply modules. in Proceedings of the 30th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference (PESC’99), vol. 2, pp. 901–908 (1999)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to show their gratitude to Ministry of Science and Technology of China for the foundation and thank their colleagues in the ASIPP for their contributions to our works.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Disclaimer: The view and opinion expressed herein does not necessarily reflect those of the ITER organization.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Y., Yuan, H., Xu, L. et al. Control and Operation Mode of ITER High-Power DC Testing Platform. J Fusion Energ 34, 1483–1488 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-015-9953-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-015-9953-0