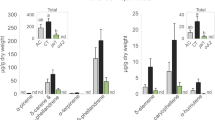
Abstract
Plant defenses to insect herbivores have been studied in response to several insect behaviors on plants such as feeding, crawling, and oviposition. However, we have only scratched the surface about how insect feces induce plant defenses. In this study, we measured frass-induced plant defenses in maize, rice, cabbage, and tomato by chewing herbivores such as European corn borer (ECB), fall armyworm (FAW), cabbage looper (CL), and tomato fruit worm (TFW). We observed that caterpillar frass induced plant defenses are specific to each host-herbivore system, and they may induce herbivore or pathogen defense responses in the host plant depending on the composition of the frass deposited on the plant, the plant organ where it is deposited, and the species of insect. This study adds another layer of complexity in plant-insect interactions where analysis of frass-induced defenses has been neglected even in host-herbivore systems where naturally frass accumulates in enclosed feeding sites over extended periods of time.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo FE, Rivera-Vega LJ, Chung SH, Ray S, Felton GW (2015) Cues from chewing insects - the intersection of DAMPs, HAMPs, MAMPs and effectors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 26:80–86
Alborn HT, Turlings TC, Jones TH, Stenhagen G, Loughrin JH, Tumlinson JH (1997) An elicitor of plant volatiles from beet armyworm oral secretion. Science 276:945–949
Alborn HT, Hansen TV, Jones TH, Bennett DC, Tumlinson JH, Schmelz EA, Teal PE (2007) Disulfooxy fatty acids from the American bird grasshopper Schistocerca americana, elicitors of plant volatiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:12976–12981
Ali JG, Agrawal A (2012) Specialist versus generalist insect herbivores and plant defense. Trends Plant Sci 17:293–302
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Broadway RM, Colvin AA (1992) Influence of cabbage proteinase inhibitors in situ on the growth of larval Trichoplusia ni and Pieris rapae. J Chem Ecol 18:1009–1024
Chen MS (2008) Inducible direct plant defense against insect herbivores: a review. Instr Sci 15:101–114
Chen H, Wilkerson CG, Kuchar JA, Phinney BS, Howe GA (2005) Jasmonate-inducible plant enzymes degrade essential amino acids in the herbivore midgut. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:19237–19242
Chen H, Gonzales-Vigil E, Wilkerson CG, Howe GA (2007) Stability of plant defense proteins in the gut of insect herbivores. Plant Physiol 143:1954–1967
Chern M, Fitzgerald HA, Canlas PE, Navarre DA, Ronald PC (2005) Overexpression of a rice NPR1 homolog leads to constitutive activation of defense response and hypersensitivity to light. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 18:511–520
Chuang WP, Ray S, Acevedo FE, Peiffer M, Felton GW, Luthe DS (2014) Herbivore cues from the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) larvae trigger direct defenses in maize. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 27:461–470
Chung SH, Felton GW (2011) Specificity of induced resistance in tomato against specialist lepidopteran and coleopteran species. J Chem Ecol 37:378–386
Chung SH, Rosa C, Scully ED, Peiffer M, Tooker JF, Hoover K, Luthe DS, Felton GW (2013) Herbivore exploits orally secreted bacteria to suppress plant defenses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:15728–15733
Erb M, Flors V, Karlen D, de Lange E, Planchamp C, D’Alessandro M, Turlings TCJ, Ton J (2009) Signal signature of aboveground-induced resistance upon belowground herbivory in maize. Plant J 59:292–302
Erb M, Meldau S, Howe GA (2012) Role of phytohormones in insect-specific plant reactions. Trends Plant Sci 17:250–259
Felton GW (2005) Indigestion is a plant’s best defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:18771–18772
Felton GW, Tumlinson JH (2008) Plant-insect dialogs: complex interactions at the plant-insect interface. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:457–463
Hilfiker O, Groux R, Bruessow F, Kiefer K, Zeier J, Reymond P (2014) Insect eggs induce a systemic acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 80:1085–1094
Houseman JG, Campos F, Thie NMR, Philogene BJ, Atkinson J, Morand P, Arnason JT (1992) Effect of the maize-derived compounds dimboa and mboa on growth and digestive processes of european corn-borer (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae. J Econ Entomol 85:669–674
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329
Karban R, Baldwin IT (1997) Induced responses to herbivory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Kim J, Tooker JF, Luthe DS, De Moraes CM, Felton GW (2012) Insect eggs can enhance wound response in plants: a study system of tomato Solanum lycopersicum L. And Helicoverpa zea Boddie. PLoS One 7:e37420
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Louis J, Luthe DS, Felton GW (2013a) Salivary signals of European corn borer induce indirect defenses in tomato. Plant Signal Behav 8:e27318
Louis J, Peiffer M, Ray S, Luthe DS, Felton GW (2013b) Host-specific salivary elicitor(s) of European corn borer induce defenses in tomato and maize. New Phytol 199:66–73
Mithöfer A, Wanner G, Boland W (2005) Effects of feeding Spodoptera Littoralis on lima bean leaves. II. Continuous mechanical wounding resembling insect feeding is sufficient to elicit herbivory-related volatile emission. Plant Physiol 137:1160–1168
Mohan S, Ma PWK, Williams WP, Luthe DS (2008) A naturally occurring plant cysteine protease possesses remarkable toxicity against insect pests and synergizes bacillus thuringiensis toxin. PLoS One 3:e1786
Musser RO, Hum-Musser SM, Eichenseer H, Peiffer M, Ervin G, Murphy JB, Felton GW (2002) Herbivory: Caterpillar saliva beats plant defences. Nature 416:599–600
Park Y-S, Jeon MH, Lee S-H, Moon JS, Cha J-S, Kim HY, Cho T-J (2005) Activation of defense responses in Chinese cabbage by a nonhost pathogen, Pseudomonas syringae pv. Tomato. J Biochem Mol Biol 38:748–754
Pashley DP (1986) Host-associated genetic differentiation in fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): a sibling species complex? Ann Entomol Soc Am 79:898–904
Peiffer M, Tooker JF, Luthe DS, Felton GW (2009) Plants on early alert: glandular trichomes as sensors for insect herbivores. New Phytol 184:644–656
Ray S, Gaffor I, Acevedo FE, Helms A, Chuang WP, Tooker J, Felton GW, Luthe DS (2015) Maize plants recognize herbivore-associated cues from caterpillar frass. J Chem Ecol 41:781–792
Ritchie JT, Singh U, Godwin DC, Bowen WT (1998) Cereal growth, development and yield. In: Tsuji G, Hoogenboom G, Thornton P (eds) Understanding options for agricultural production SE - 5. Springer, Netherlands, pp. 79–98
Schäfer M, Fischer C, Meldau S, Seebald E, Oelmüller R, Baldwin IT (2011) Lipase activity in insect oral secretions mediates defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156:1520–1534
Schaffrath U, Zabbai F, Dudler R (2000) Characterization of RCI-1, a chloroplastic rice lipoxygenase whose synthesis is induced by chemical plant resistance activators. Eur J Biochem 267:5935–5942
Schmelz EA, Carroll MJ, LeClere S, Phipps SM, Meredith J, Chourey PS, Alborn HT, Teal PE (2006) Fragments of ATP synthase mediate plant perception of insect attack. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:8894–8899
Schwartzberg EG, Tumlinson JH (2014) Aphid honeydew alters plant defence responses. Funct Ecol 28:386–394
Thaler JS, Humphrey PT, Whiteman NK (2012) Evolution of jasmonate and salicylate signal crosstalk. Trends Plant Sci 17:260–270
Tian D, Peiffer M, Shoemaker E, Tooker J, Haubruge E, Francis F, Luthe DS, Felton GW (2012) Salivary glucose oxidase from caterpillars mediates the induction of rapid and delayed-induced defenses in the tomato plant. PLoS One 7:e36168
van der Linde K, Hemetsberger C, Kastner C, Kaschani F, van der Hoorn RA, Kumlehn J, Doehlemann G (2012) A maize cystatin suppresses host immunity by inhibiting apoplastic cysteine proteases. Plant Cell 24:1285–1300
van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CMJ (2006) Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:135–162
Venu RC, Sheshu Madhav M, Sreerekha MV, Nobuta K, Zhang Y, Carswell P, Boehm MJ, Meyers BC, Korth KL, Wang GL (2010) Deep and comparative transcriptome analysis of rice plants infested by the beet armyworm (Spodoptera exigua) and water weevil (Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus. Rice 3:22–35
Voelckel C, Baldwin IT (2004) Generalist and specialist lepidopteran larvae elicit different transcriptional responses in Nicotiana attenuata, which correlate with larval FAC profiles. Ecol Lett 7:770–775
Wu S, Peiffer M, Luthe DS, Felton GW (2012) ATP hydrolyzing salivary enzymes of caterpillars suppress plant defenses. PLoS One 7:e41947
Xu T, Zhou Q, Chen W, Zhang G, He G, Gu D, Zhang W (2003) Involvement of jasmonate-signaling pathway in the herbivore-induced rice plant defense. Chin Sci Bull 48:1982–1987
Yuan Y, Zhong S, Li Q, Zhu Z, Lou Y, Wang L, Wang J, Wang M, Li Q, Yang D, He Z (2007) Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility. Plant Biotechnol J 5:313–324
Zheng S-J, van Dijk JP, Bruinsma M, Dicke M (2007) Sensitivity and speed of induced defense of cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.): dynamics of BoLOX expression patterns during insect and pathogen attack. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 20:1332–1345
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges Dr. Kelli Hoover’s lab for their help in quantifying RNA samples with Nanodrop (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The author thanks Michelle Peiffer for the tomato seeds, primers for tomato and Ching-Wen Tan for providing the eggs of tomato fruitworm larva.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by grants from USDA NIFA (2010–65,105-20,639 and 2011–67,013-30,352) awarded to D.S. L and G.W. F; NSF (IOS-1,256,326) awarded to G.W.F. and start-up funds of J.L. at University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ray, S., Basu, S., Rivera-Vega, L.J. et al. Lessons from the Far End: Caterpillar FRASS-Induced Defenses in Maize, Rice, Cabbage, and Tomato. J Chem Ecol 42, 1130–1141 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-016-0776-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-016-0776-x