Abstract
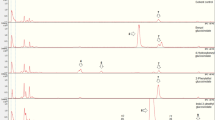
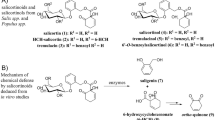
As a specialist on the reproductive structures of Pastinaca sativa and species in the related genus Heracleum, the parsnip webworm (Depressaria pastinacella) routinely encounters a distinctive suite of phytochemicals in hostplant tissues. Little is known, however, about the detoxification mechanisms upon which this species relies to metabolize these compounds. In this study, larval guts containing hostplant tissues were homogenized, and metabolism was determined by incubating reactions with and without NADPH and analyzing for substrate disappearance and product appearance by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Using this approach, we found indications of carboxylesterase activity, in the form of appropriate alcohol metabolites for three aliphatic esters in hostplant tissues—octyl acetate, octyl butyrate, and hexyl butyrate. Involvement of webworm esterases in hostplant detoxification subsequently was confirmed with metabolism assays with pure compounds. This study is the first to implicate esterases in lepidopteran larval midgut metabolism of aliphatic esters, ubiquitous constituents of flowers and fruits. In addition, this method confirmed that webworms detoxify furanocoumarins and myristicin in their hostplants via cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism, and demonstrated that these enzymes also metabolize the coumarin osthol and the fatty acid derivative palmitolactone.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Latif, A. O. and Subrahmanyam, B. 2010. Pyrethroid resistance and esterase activity in three strains of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Pesticide Biochem. Physiol. 96:155–159.
Carroll, M. J. and Berenbaum, M. R. 2001. Behavioral responses of the parsnip webworm to hostplant volatiles. J. Chem. Ecol. 28: 1365–1375.
Carroll, M. J., Zangerl, A. R., and Berenbaum, M. R. 2000. Heritability estimates for octyl acetate and octyl butyrate in the mature fruits of the wild parsnip, Pastinaca sativa (Apiaceae). J. Heredity 91:68–71.
Claudianos, C., Ranson, H., Johnson, R. M., Biswas, S., Schuler, M. A., Berenbaum, M. R., Feyereisen, R., and Oakeshott, J. G. 2006. A deficit of detoxification enzymes: Pesticide sensitivity and environmental response in the honeybee. Insect Mol. Biol. 15:615–636.
Cohen, M. B., Schuler, M. A., and Berenbaum, M. R. 1992. A host-inducible cytochrome P450 from a host-specific caterpillar: molecular cloning and evolution. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10920–10924.
Crankshaw, D. L., Hetnarski, H. K. and Wilkinson, C. F. 1979. Microsomal NADPH-cytochrome c reductase from the midgut of the Southern armyworm (Spodoptera eridania). Insect Biochem. 9: 43–48.
Durand, N., Carot-Sans, G., Chertemps, T., Montagne, N., Jacquin-Joly, E., Debernard, S., and Maibeche-Coisne, M. 2010. A diversity of putative carboxylesterases are expressed in the antennae of the noctuid moth Spodoptera littoralis. Insect Mol. Biol. 19:87–97.
Farnsworth, C. A., Teese, M. G., Yan, G., Li, Y., Scott, C., Zhang, X., Wu, Y., Russell, R. J. and Oakeshott, J. G. 2010. Esterase-based metabolic resistance to insecticides in heliothine and spodopteran pests. J. Pesticide Sci. 35:275–289.
Feng, Y.-N., Yan, J., Sun, W., Zhao, S., Lu, W.-C., Li, M., and He, L. 2011. Transcription and induction profiles of two esterase genes in susceptible and acaricide-resistance Tetranychus cinnabarinus. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 100:70–73.
Ferreres, F., Fernandes, F., Pereira, D. M., Pereira, J. A., Valentão, P., and Andrade, P. B. 2009a. Phenolics metabolism in insects: Pieris brassicae-Brassica oleracea var. costata ecological duo. J. Ag. Food Chem. 57:9035–9043.
Ferreres, F., Fernandes, F., Sousa, C., Valentão, P., Pereira, J. A., and Andrade, P. B. 2009b. Metabolic and bioactivity insights into Brassica oleracea var. acephala. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57:8884–8892.
Glauser, G., Marti, G., Villard, N., Doyen, G. A., Wolfender, J.-L., Turlings, T. C. J., and Erb, M. 2011. Induction and detoxification of maize 1,4-benzoxozan-3-ones by insect herbivores. The Plant Journal 68:901–911.
Gui, Z. Z., Kim, B. Y., Lee, K. S., Wei, Y. D., Guo, X., Sohn, H. D., and Jin, B. R. 2008. Glutathione S-transferases from the larval gut of the silkworm Bombyx mori: cDNA cloning, gene structure, expression and distribution. Eur. J. Entomol. 105:567–574.
Jansen, J. J., Allwood, J. W., Marsden-Edwards, E., Van Der Putten, W. H., Goodacre, R., and Van Dam, N. M. 2009. Metabolomic analysis of the interaction between plants and herbivores. Metabolomics 5:150–161.
Li, W., Schuler, M. A. and Berenbaum, M. R. 2003. Diversification of furanocoumarin-metabolizing cytochrome P450 monooxygenases in two papilionids: Specificity and substrate encounter rate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 25:14593–14598.
Li, W., Schuler, M. A. and Berenbaum, M. R. 2007. Molecular mechanisms of metabolic resistance to synthetic and natural xenobiotics. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 52:231–253.
Li, X., Budry, J., Berenbaum, M. R., and Schuler, M. A. 2004. Structural and functional divergence of insect CYP6B proteins: From specialist to generalist cytochrome P450. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:2939–2944.
Lindroth, R. L. 1989a. Biochemical detoxication: Mechanism of differential tiger swallowtail tolerance to phenolic glycosides. Oecologica 81:219–224.
Lindroth, R. L. 1989b. Differential esterase activity in Papilio glaucus subspecies: Absence of cross-resistance between allelochemicals and insecticides. Pesticide Biochem. Physiol. 35:185–191.
Mao, W., Berhow, M. A., Zangerl, A. R., Mcgovern, J., and Berenbaum, M. R. 2006. Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of xanthotoxin by Papilio multicaudatus. J. Chem. Ecol. 32:523–536.
Mao, W., Zangerl, A. R., Berenbaum, M. R., and Schuler, M. A. 2008. Metabolism of myristicin by Depressaria pastincella CYP6AB3v2 and inhibition by its metabolite. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 38:645–651.
Nitao J. K. 1989. Enzymatic adaptations in a specialist herbivore for feeding on furanocoumarin-containing plants. Ecology 70:629–635
Nitao, J. and Berenbaum, M. R. 1988. Laboratory rearing of the parsnip webworm, Depressaria pastinacella (Lepidoptera: Oecophoridae). Ann. Ent. Soc. Amer. 81:485–487.
Nitao, J. K., Berhow, M., Duval, S. M. Weisler, D. Vaughn, S. F. Zangerl, A. R., and Berenbaum, M. R. 2003. Characterization of furanocoumarin metabolites in parsnip webworm, Depressaria pastinacella. J. Chem. Ecol. 29:671–682.
Niu, G., Rupasinghe, S., Zangerl, A. R., Siegel, J. P., Schuler, M. A., and Berenbaum, M. R. 2011. A substrate-specific cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, CYP6AB11, from the polyphagous navel orangeworm (Amyelois transitella). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41:244–253.
Ranson, H. and Hemingway, J. 2005. Mosquito glutathione transferases. Meth. Enzymol. 401:226–241.
Rose, C. J., Chapman, J. R., Marshall, S. D. G., Lee, S. F., Batterham, P., Ross, H. A., and R. D. Newcomb, 2011. Selective sweeps at the organophosphorus insecticide resistance locus, Rop-1, have affected variation across and beyond the α-esterase gene cluster in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28:1835–1846.
Salminen, J.-P., Lahtinen, Lempa, K., Kapari, L., Haukioja, E., and Pihlaja, K. 2004. Metabolic modifications of birch leaf phenolics by an herbivorous insect: detoxification of flavonoid aglycones via glycosylation. Z. Naturforsch. 59c:437–444.
Srigiriraju, L., Semtner, P. J., Anderson, T. D., and Bloomquist, J. R. 2009. Esterase-based resistance in the tobacco-adapted form of the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in the eastern United States. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 72:105–123.
Tu, C.-P. D. and Akgul, B. 2005. Drosophila glutathione S-transferases. Meth. Enzymol. 401:204–226.
Yu, Q., Lu, C., Li, B., Fang, S., Zuo, W., Dai, F., Zhang, Z., and Xiang, Z. 2008. Identification, genomic organization and expression pattern of glutathione S transferase in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Bioch. Mol. Biol. 12:1158–1164.
Yu, Q-Y., Lu, C., Li, W-L., Xiang, Z.-H., and Zhang, Z. 2009. Annotation and expression of carboxylesterases in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genomics 10:553–567.
Zangerl, A. R. and Berenbaum, M. R. 2009. Effects of florivory on floral volatile emissions and pollination success in the wild parsnip. Arthropod-Plant Interactions 3:181–191.
Zangerl, A. R., Green, E. S., Lampman, R. L., and Berenbaum, M. R. 1997. Phenological changes in primary and secondary chemistry of reproductive parts in wild parsnip. Phytochemistry 44:825–831.
Zangerl, A. R., Stanley, M. C., and Berenbaum, M. R. 2008. Selection for chemical trait remixing in an invasive weed after reassociation with a coevolved specialist Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105:4547–4552
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation (DEB 0816616).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Although this project was the brainchild of Arthur Zangerl, his untimely death prevented him from seeing this work in print. His quarter-century-long dedication to studying the interaction between parsnip webworms and wild parsnips was essential to making this system a model for chemical ecology studies.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zangerl, A.R., Liao, LH., Jogesh, T. et al. Aliphatic Esters as Targets of Esterase Activity in the Parsnip Webworm (Depressaria pastinacella). J Chem Ecol 38, 188–194 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-012-0073-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-012-0073-2