Abstract
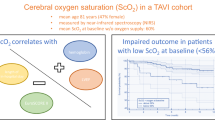
This study assessed the influence of the evolution in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation technology on cerebral oxygenation. Cerebral oxygenation was measured continuously with Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and compared retrospectively between balloon-expandable, self-expandable and differential deployment valves which were implanted in 12 (34%), 17 (49%) and 6 patients (17%), respectively. Left and right SctO2 values were averaged at four time points and used for analysis (i.e. at baseline, balloon-aortic valvuloplasty, valve deployment, and at the end of the procedure). During balloon-aortic valvuloplasty and valve deployment, cerebral oxygenation decreased in patients treated with balloon or self-expandable valves (balloon-expandable: p = 0.003 and p = 0.002; self-expandable: p < 0.001 and p = 0.003, respectively). The incidence of cerebral desaturations below 80% of baseline was significantly larger in patients treated with balloon-expandable valves (p = 0.001). In contrast, patients who received differential deployment valves never experienced a cerebral desaturation below 80% of baseline. Furthermore, both the incidence and duration below a cerebral oxygenation of 55% was significantly different between balloon and self-expandable valves (p = 0.038 and p = 0.018, respectively). This study demonstrated that Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation procedures are associated with significant cerebral desaturations, especially during balloon-aortic valvuloplasty and valve deployment. Moreover, our results showed that latest innovations in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation technology beneficially influenced the adequacy of cerebral perfusion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M, Miller DC, Moses JW, Svensson LG, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(17):1597–607.
Smith CR, Leon MB, Mack MJ, Miller DC, Moses JW, Svensson LG, et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic-valve replacement in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(23):2187–98.
Adams DH, Popma JJ, Reardon MJ, Yakubov SJ, Coselli JS, Deeb GM, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a self-expanding prosthesis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(19):1790–8.
Cribier A, Eltchaninoff H, Bash A, Borenstein N, Tron C, Bauer F, et al. Percutaneous transcatheter implantation of an aortic valve prosthesis for calcific aortic stenosis: first human case description. Circulation. 2002;106(24):3006–8.
Rodes-Cabau J. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation: current and future approaches. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012;9(1):15–29.
Fanning JP, Platts DG, Walters DL, Fraser JF. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI): valve design and evolution. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(3):1822–31.
Nuis RJ, Van Mieghem NM, Schultz CJ, Moelker A, van der Boon RM, van Geuns RJ, et al. Frequency and causes of stroke during or after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am J Cardiol. 2012;109(11):1637–43.
Rodes-Cabau J, Dumont E, Boone RH, Larose E, Bagur R, Gurvitch R, et al. Cerebral embolism following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: comparison of transfemoral and transapical approaches. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(1):18–28.
Sack S, Kahlert P, Khandanpour S, Naber C, Philipp S, Mohlenkamp S, et al. Revival of an old method with new techniques: balloon aortic valvuloplasty of the calcified aortic stenosis in the elderly. Clin Res cardiol. 2008;97(5):288–97.
Selle A, Figulla HR, Ferrari M, Rademacher W, Goebel B, Hamadanchi A, et al. Impact of rapid ventricular pacing during TAVI on microvascular tissue perfusion. Clin Res cardiol. 2014;103(11):902–11.
Ikeda K, MacLeod DB, Grocott HP, Moretti EW, Ames W, Vacchiano C. The accuracy of a near-infrared spectroscopy cerebral oximetry device and its potential value for estimating jugular venous oxygen saturation. Anesth Analg. 2014;119(6):1381–92.
Slater JP, Guarino T, Stack J, Vinod K, Bustami RT, Brown JM 3rd, et al. Cerebral oxygen desaturation predicts cognitive decline and longer hospital stay after cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;87(1):36–44.
Yao FS, Tseng CC, Ho CY, Levin SK, Illner P. Cerebral oxygen desaturation is associated with early postoperative neuropsychological dysfunction in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2004;18(5):552–8.
De Deyne C, Meex I, Jans F, Engelen K, Gutermann H, Dens J. Non-invasive monitoring of cerebral perfusion during transcatheter aortic valve implantation procedure. Am J Cardiol. 2013;111(2):302.
Argiriadou H, Anastasiadis K, Karapanagiotidis G, Papakonstantinou C. Subclinical decline in cerebral oxymetry saturation during rapid pacing in transfemoral aortic valve replacement. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90(3):1023.
Brodt J, Vladinov G, Castillo-Pedraza C, Cooper L, Maratea E. Changes in cerebral oxygen saturation during transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J Clin Monit Comput. 2016. Doi: 10.1007/s10877-015-9758-8.
Meredith IT, Hood KL, Haratani N, Allocco DJ, Dawkins KD. Boston scientific lotus valve. EuroIntervention. 2012;8(Suppl Q):Q70–4.
Grube E, Naber C, Abizaid A, Sousa E, Mendiz O, Lemos P, et al. Feasibility of transcatheter aortic valve implantation without balloon pre-dilation: a pilot study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4(7):751–7.
Ameloot K, Meex I, Genbrugge C, Jans F, Boer W, Verhaert D, et al. Hemodynamic targets during therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest: a prospective observational study. Resuscitation. 2015;91:56–62.
Paarmann H, Heringlake M, Heinze H, Hanke T, Sier H, Karsten J, et al. Non-invasive cerebral oxygenation reflects mixed venous oxygen saturation during the varying haemodynamic conditions in patients undergoing transapical transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2012;14(3):268–72.
Tang L, Kazan R, Taddei R, Zaouter C, Cyr S, Hemmerling TM. Reduced cerebral oxygen saturation during thoracic surgery predicts early postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108(4):623–9.
Murkin JM, Adams SJ, Novick RJ, Quantz M, Bainbridge D, Iglesias I, et al. Monitoring brain oxygen saturation during coronary bypass surgery: a randomized, prospective study. Anesth Analg. 2007;104(1):51–8.
Alassar A, Soppa G, Edsell M, Rich P, Roy D, Chis Ster I, et al. Incidence and mechanisms of cerebral ischemia after transcatheter aortic valve implantation compared with surgical aortic valve replacement. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;99(3):802–8.
Fischer GW, Lin HM, Krol M, Galati MF, Di Luozzo G, Griepp RB, et al. Noninvasive cerebral oxygenation may predict outcome in patients undergoing aortic arch surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;141(3):815–21.
Meredith IT, Walters DL, Dumonteil N, Worthley SG, Tchetche D, Manoharan G, et al. 1-Year outcomes with the fully repositionable and retrievable lotus transcatheter aortic replacement valve in 120 high-risk surgical patients with severe aortic stenosis: results of the REPRISE II study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9(4):376–84.
Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack MJ, Makkar RR, Svensson LG, Kodali SK, et al. Transcatheter or surgical aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(17):1609–20.
Athappan G, Gajulapalli RD, Sengodan P, Bhardwaj A, Ellis SG, Svensson L, et al. Influence of transcatheter aortic valve replacement strategy and valve design on stroke after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a meta-analysis and systematic review of literature. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(20):2101–10.
Erdoes G, Basciani R, Huber C, Stortecky S, Wenaweser P, Windecker S, et al. Transcranial Doppler-detected cerebral embolic load during transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Eur J Cardio-Thorac Surg. 2012;41(4):778–83.
Ghanem A, Muller A, Nahle CP, Kocurek J, Werner N, Hammerstingl C, et al. Risk and fate of cerebral embolism after transfemoral aortic valve implantation: a prospective pilot study with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(14):1427–32.
Kahlert P, Knipp SC, Schlamann M, Thielmann M, Al-Rashid F, Weber M, et al. Silent and apparent cerebral ischemia after percutaneous transfemoral aortic valve implantation: a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. Circulation. 2010;121(7):870–8.
Funding
This work was supported by the Limburg Clinical Research Program (LCRP) UHasselt-ZOL- Jessa, supported by the foundation Limburg Sterk Merk, Hasselt University, Ziekenhuis Oost-Limburg and Jessa Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eertmans, W., Genbrugge, C., Fret, T. et al. Influence of continuously evolving transcatheter aortic valve implantation technology on cerebral oxygenation. J Clin Monit Comput 31, 1133–1141 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-016-9971-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-016-9971-0