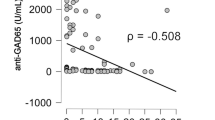
Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to determine the frequencies of autoantibodies to heterogeneous islet-cell cytoplasmic antigens (ICA), glutamic acid decarboxylase65 (GAD65A), insulinoma-associated antigen-2 (IA-2A) and insulin (IAA)–and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II markers (HLA-DR and -DQ) in first degree relatives of heterogeneous Brazilian patients with type I diabetes(T1DM). A major focus of this study was to determine the influence of age, gender, proband characteristics and ancestry on the prevalence of autoantibodies and HLA-DR and -DQ alleles on disease progression and genetic predisposition to T1DM among the first-degree relatives.
Methods
IAA, ICA, GAD65A, IA-2A and HLA- class II alleles were determined in 546 first-degree-relatives, 244 siblings, 55 offspring and 233 parents of 178 Brazilian patients with T1DM.
Results
Overall, 8.9% of the relatives were positive for one or more autoantibodies. IAA was the only antibody detected in parents. GAD65 was the most prevalent antibody in offspring and siblings as compared to parents and it was the sole antibody detected in offspring. Five siblings were positive for the IA-2 antibody. A significant number (62.1%) of siblings had 1 or 2 high risk HLA haplotypes. During a 4-year follow-up study, 5 siblings (expressing HLA-DR3 or –DR4 alleles) and 1 offspring positive for GAD65A progressed to diabetes.
Conclusions
The data indicated that the GAD65 and IA-2 antibodies were the strongest predictors of T1DM in our study population. The high risk HLA haplotypes alone were not predictive of progression to overt diabetes.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GAD65A:
-
Anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 autoantibodies
- IAA:
-
Anti-insulin autoantibodies
- ICA:
-
Anti-Islet cell autoantibodies
- IA-2A:
-
Anti-protein tyrosine phosphatase-like IA-2 (IA-2A) autoantibodies
- HLA:
-
Human leukocyte antigen
- TIDM:
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
References
Eisenbarth GS. Diabetes: a chronic autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:1360–8.
Atkinson MA, Maclaren NK. The pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:1428–36.
Gillespie KM. Type 1 pathogenesis and prevention. CMAJ. 2006;175:165–70.
Zhang L, Gianani R, Nakayama M, Liu E, Kobayashi M, Baschal E, Yu L, Babu S, Dawson A, Johnson K, Jahromi M, Aly T, Fain P, Barker J, Rewers M, Eisenbarth GS. Type 1 diabetes: chronic progressive autoimmune disease. Novartis Found Symp. 2008;292:85–94.
Spielman RS, Baker L, Zmijewski CM. Gene dosage and susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes. Ann Hum Genet. 1980;2:135–50.
Kumar D, Gemayel NS, Deapen D, Kapadia D, Yamashita PH, Lee M, Dwyer JH, Roy-Burman P, Bray GA, Mack TM. North-American twins with IDDM, genetic, etiological, and clinical significance of disease concordance according to age, zygosity, and the interval after diagnosis in first twin. Diabetes. 1993;42:1351–63.
Sheehly MJ. Prospective in diabetes. HLA and insulin-dependent diabetes. A protective perspective. Diabetes. 1992;41:123–9.
Davies JL, Kawaguchi Y, Bennett ST, Copeman JB, Cordell HJ, Pritchard LE, Reed PW, Gough SC, Jenkins SC, Palmer SM, et al. A genome-wide search for human type I diabetes susceptibility genes. Nature. 1994;371:130.
Todd JA, Bell JJ, McDevitt HO. HLA-DQ/β gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987;329:599–604.
Erlich H, Valdes AM, Noble J, Carlson JA, Varney M, Concannon P, Mychaleckyj JC, Todd JA, Bonella P, Fear AL, Lavant E, Louey A, Moonsamy P. HLA DR-DQ halotypes and genotypes and type 1 diabetes risk: analysis of the type 1 diabetes genetics consortium families. Diabetes. 2008;57:1084–92.
Zhang L, Eisenbarth GS. Prediction and prevention of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes. 2011;3:48–57.
Bonifacio E, Bingley PJ, Shattock M, Dean BM, Dunger D, Gale EA, Bottazzo GF. Quantification of islet-cell antibodies and prediction of insulin dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990;335:147–9.
Greenbaum CJ, Seras KL, Kahn SE, Palmer JP. Relationship of b-cells function and autoantibodies to progression and nonprogression of subclinical type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 1999;48:170–5.
Maclaren N, Lan M, Coutant R, Schatz D, Silverstein J, Muir A, Clare-Salzer M, She JX, Malone J, Crockett S, Schwartz S, Quattrin T, DeSilva M, Vander Vegt P, Notkins A, Krischer J. Only multiple autoantibodies to islet cells (ICA), insulin, GAD65, IA-2, and IA-2b predict immune-mediated (type 1) diabetes relatives. J Autoimmun. 1999;12:279–87.
Achenbach P, Bonifacio E, Koczwara K, Ziegler AG. Natural history of type I diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54 Suppl 2:S25–31.
Bottazo GF, Florin-Christensen A, Doniach D. Islet cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet. 1974;2:1279–82.
Lendrum R, Walker G, Cudworth AG, Theophanides C, Pyke DA, Bloom A, Gamble DR, et al. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1976;2:1273–6.
Baekkeskov S, Aanstoot H-J, Christgau S, Reetz A, Solimena M, Cascalho M, Folli F, Richter-Olesen H, De Camilli P. et al. Identification of the 64 K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decorboxylase [published erratum appears in (1990) Nature. 1990;347:782]. Nature.1990; 347151–156.
Payton MA, Hawkes CJ, Christie MR. Relationship of 37,000 and 40,000-Mr tryptic fragment of islet antigens in insulin dependent diabetes to the protein tyrosine phosphatase-like molecule IA-2 (ICA 512). J Clin Invest. 1995;96:1506–11.
Palmer JP, Asplin CM, Clemons P, Lyen K, Tatpati O, Raghu PK, Paquette TL. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science. 1983;222:1337–9.
Pihoker C, Gilliam LK, Hampe CS, Lenmark Å. Autoantibodies in diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54 Suppl 2:S52–61.
Serrano-Rios M, Gutierrez-López MD, Pérez-Bravo F, Martínez MT, Antona J, Rowley M, Mackay I, Zimmet P. HLA-DR, DQ and anti-GAD antibodies in first degree relatives of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1994;34 Suppl 34:S133–9.
Zeidler A, Raffel LJ, Costin G, Shaw SJ, Buchanan TA, Noble J, Rotter JI, Palmer J, Krischer JP, Wait C, Maclaren NK. Autoantibodies and human leucocyte antigen class II in first-degree family members of Mexican-American type 1 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:4957–62.
Wang J-P, Zhou Z-G, Lin J, Li X, Huang G, Zhou WD, Lin J, Zhou ZG, et al. Islet autoantibodies are associated with HLA-DQ genotypes in Han Chinese patients with type 1 diabetes and their relatives. Tissue Antigens. 2007;70:369–75.
Williams AJ, Aitken RJ, Chandler MA, Gillespie KM, Lampsona V, Bingley PJ. Autoantibodies to islet antigen-2 are associated with KLA-DRBI*07, and DRBI*09 haplotypes as well as DRBI*04 at onset of type 1 diabetes: the possible role of HLA-DQA in autoimmunity to IA-2. Diabetologia. 2008;51:1444–8.
Qu HQ, Polychronakos C. The effect of the MHC locus on autoantibodies in type 1 diabetes. J Med Genet. 2009;46:469–71.
Howson JM, Stevens H, Smyth DJ, et al. Evidence that HLA class I and II associations with type 1 diabetes, autoantibodies to GAD and autoantibodies to 1A-2 are distinct. Diabetes. 2011;60:2635–44.
van Belle TL, Coppieters KT, von Herrath MG. Type 1 diabetes: etiology, immunology, and therapeutic strategies. Physiol Rev. 2011;91:79–118.
Lins TC, Vieira RG, Abreu BS, Grattapaglia D, Pereira RW. Genetic composition of Brazilian population samples based on a set of twenty-eight ancestry informative SNPs. Am J Hum Biol. 2010;22:187–92.
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes. Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–53.
Ferreira SR, Franco LJ, Vivolo MA, Negrato CA, Simoes AC, Ventureli CR. Population based incidence of IDDM in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:701–4.
Lisboa HR, Graebin R, Butzke L, Rodrigues CS. Incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Passo Fundo, RS Brazil. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1998;31:553–6.
Alves C, Meyer I, Vieira N, Toralles MBP, LeMaire D. Distribuiçã e freqüência de alelos e haplptipos HLA em Brasileiros com diabetes melito tipo 1. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2006;50:436–44.
Davini E, Silva MER, Alves LI, Correia MRS, Fukui RT, Latronico AC. O genótipo I/I do locus VNTR do gene da insulina confere risco independente para diabetes mellitus tipo 1 nos pacientes sem os genótipos DRB1 e DQB1 de susceptibilidade. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2005;49 Suppl 2:S876.
Bingley PJ, Colman P, Eisenbarth GS, Jackson RA, McCulloch DK, Riley WJ, Gale EA. Standardization of IVGTT to predict IDDM. Diabetes Care. 1992;15:1313–6.
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2008;31 Suppl 1:S55–60.
Vardi P, Ziegler AG, Mattews JH, Dib S, Keller RJ, Richer AT. Concentration of insulin autoantibodies at onset of type 1 diabetes. Inverse log-linear correlation with age. Diabetes Care. 1998;11:736–9.
Dib SA, Colman PG, Dotta F, Tautkus M, Rabizadeh A, Eisenbarth GS. Expression of cytoplasmic islet cell antigens by rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1987;36:982–5.
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16:1215.
Eisenbarth GS, Lafferty K. Type 1 diabetes: cellular, molecular and clinical immunology. 2009. http://www.uchsc.edu/misc/diabetes/books.html.
Park Y. Why is type 1 diabetes uncommon in Asia? Ann NY Acad Sci. 2006;1079:31–40.
Zeidler A, Frasier SD, Penny R, Stein RB, Nicoloff JT. Pancreatic islet cell and thyroid antibodies, and islet cell function in diabetic patients of Mexican-American origin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982;54:949–54.
Shaw SJ, Vagheim CM, Rotter JI, Costin G, Beshkov Y, Zeidler A. Ancestral origin of insulin-dependent diabetes in Mexican-Americans. Intern J Epidemiol. 1992;21:725–9.
Baker JM. Clinical review: type 1 diabetes-associated autoimmunity: natural history, genetic associations, and screening. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1210–7.
Bingley PJ. Interaction of age, islet cell antibodies, insulin antibodies, and first-phase insulin response in predicting risk of progression to IDDM in ICA + relatives. The ICARUS data. Islet Cell Antibody Register Users Study. Diabetes. 1996;45:1720–8.
Verge CF, Gianani R, Kawasaki E, Yu L, Pietropolo M, Jackson RA, Chase HP, Eisenbarth GS. Prediction of type I diabetes in first-degree relatives using a combination of insulin, GAD, ICA512bdc/IA-2 autoantibodies. Diabetes. 1996;45:926–33.
Cantor AB, Krischer JP, Cuthbertson DD, Schatz DA, Riley WJ, Malone J, Schwartz S, Quattrin T, Maclaren NK. Age and family relationship accentuate the risk of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) in relatives of patients with IDDM. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80:3739–43.
Vandewalle CL, Falorni A, Svanholm S, Lernmark A, Pipeleers DG, Gorus FK. High diagnostic sensitivity of glutamate decarboxylase autoantibodies in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus with clinical onset between age 20 and 40 years. The Belgian Diabetes Registry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80:846–51.
Pugliese A, Gianani R, Moromissato R, Awdeh ZL, Alper CA, Erlich HA, Jackson RA, Eisenbath GS. HLA-DQB1*0602 is associated with dominant protection from diabetes even among islet cell antibody-positive first-degree relatives of patients with IDDM. Diabetes. 1995;44:608–13.
Redondo MJ, Babu S, Zeidler A, Orban T, Yu L, Greenbaum C, Palmer JP, Cuthbertson D, Eisenbarth GS, Krischer JP, Schatz D. Diabetes Prevention Trial Type 1 StudyGroup. Specific human leukocyte antigen DQ influence on expression of antiislet autoantibodies and progression to type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:1705–13.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Professor Salman Azhar for the outstanding scientific suggestions and careful revision of the manuscript. We acknowledge Ms. Greci S Paula for his excellent technical assistance. We are grateful to all first-degree relatives of patients with T1DM who participated in our study. This study was supported in part by grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP)
Contribution statement
LA, ED, MC, RF, MC, RS, WV and MS all participated in designing the studies and in carrying out Clinical and Experimental Procedures. MS wrote, edited and finalized the manuscript for publication.
Duality of interest
The authors declare no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alves, L.I., Davini, E., Correia, M.R. et al. Autoantibodies and High-Risk HLA Susceptibility Markers in First-Degree Relatives of Brazilian Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Progression to Disease Based Study. J Clin Immunol 32, 778–785 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9673-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9673-4