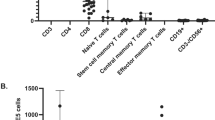
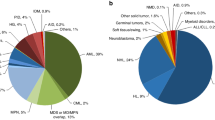
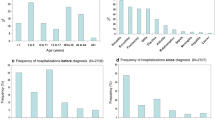
Natural killer (NK) cell alloreactions against recipient cells in the setting of bone marrow transplantation have been associated with decreased rates of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and improved survival in transplant recipients with myeloid leukemia. These alloreactions are predicted by the absence of recipient HLA class I ligands for donor inhibitory killer Ig-like receptors (KIR). We hypothesized that donor NK cell alloreactions against recipient cells may affect the development of T and B-cell functions and incidence of GVHD in infants with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Of the 156 patients with SCID who had received related bone marrow transplants without pretransplant chemotherapy or posttransplant GVHD prophylaxis, 137 patient–donor pairs were evaluated for the absence of recipient HLA class I ligands for donor inhibitory KIR. Analysis showed that the absence of a KIR ligand had no effect on the incidence or severity of GVHD (R 2 = 0.95, p = 0.84), development of T-cell function (R 2 = 1.05, p = 0.69), production of IgA (p = 0.46) or IgM (p = 0.33), or on 5-year survival (R 2 = 1.21, p = 0.10). Further, in patients possessing native NK cells, the absence of KIR ligands in donors for recipient-inhibitory KIR did not alter transplantation outcomes. This study suggests that inhibitory KIR/HLA interactions do not play a significant role in bone marrow transplantation for SCID.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckley RH: Molecular defects in human severe combined immunodeficiency and approaches to immune reconstitution. Annu Rev Immunol 22:625–655, 2004
Ryser O, Morell A, Hitzig W: Primary immunodeficiencies in Switzerland: First report of the national registry in adults and children. J Clin Immunol 8:479–488, 1988
Myers L, Patel DD, Buck JM, Buckley RH: Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe combined immunodeficiency in the neonatal period leads to superior thymic output and improved survival. Blood 99:872–878, 2002
Buckley RH, Schiff SE, Schiff RI, Markert ML, Williams LW, Roberts JL, Myers LA, Ward FE: Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for the treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med 340(7):508–516, 1999
Barao I, Murphy WJ: The immunobiology of natural killer cells and bone marrow allograft rejection. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 9(12):727–741, 2003
Farag S, Fehniger TA, Ruggeri L, Velardi A, Caligiuri MA: Natural killer cell receptors: New biology and insights into the graft-versus-leukemia effect. Blood 100:1935–1947, 2002
Parham P, McQueen K: Alloreactive killer cells: Hindrance and help for haematopoietic transplants. Nat Rev Immunol 3(2):108–122, 2003
Raulet D, Vance R, McMahon C: Regulation of the natural killer cell receptor repertoire. Annu Rev Immunol 19:291–330, 2001
Lanier LL: NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 23:225–274, 2005
Gumperz J, Litwin V, Phillips JH, Lanier LL, Parham P: The Bw4 public epitope of HLA-B molecules confers reactivity with natural killer cell clones that express NKB1, a putative HLA receptor. J Exp Med 181(3):1133–1144, 1995
Parham P: MHC class I molecules and KIRs in human history, health, and survival. Nat Rev Immunol 5:201–214, 2005
Leonard W: Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 1(3):200–208, 2001
Orange JS: Human natural killer cell deficiencies and susceptibility to infection. Microbes Infect 4(15):1545–1558, 2002
Murphy WJ, Bennett M, Kumar V, Longo DL: Donor-type activated natural killer cells promote marrow engraftment and B cell development during allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Immunol 148(9):2953–2960, 1992
Gaines AD, Schiff S, Buckley RH: Donor type natural killer cells after haploidentical T-cell depleted bone marrow stem cell transplantation in a patient with adenosine deaminase-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 60(2):299–304, 1991
Cooley S, McCullar V, Wangen R, Bergemann TL, Spellman S, Weisdorf DJ, Miller JS: KIR reconstitution is altered by T-cells in the graft and correlates with clinical outcomes after unrelated donor transplantation. Blood 106(13):4370–4376, 2005
Leung W, Iyengar R, Turner V, Lang P, Bader P, Conn P, Niethammer D, Handgretinger R: Determinants of antileukemia effects of allogeneic NK cells. J Immunol 172(1):644–650, 2004
Yawata M, Yawata N, Draghi M, Little AM, Partheniou F, Parham P: Roles for HLA and KIR polymorphisms in natural killer cell repetoire selection and modulation of effector function. J Exp Med 203(3):633–645, 2006
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Casucci M, Volpi I, Tosti A, Perruccio K, Urbani E, Negrin R, Martelli MF, Velardi A: Role of natural killer cell alloreactivity in HLA-mismatched hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 94(1):333–339, 1995
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, Perruccio K, Schlomchik WD, Tosti A, Posati S, Rogaia D, Frassoni, F, Aversa F, Martelli MF, Velardi A: Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoeitic transplants. Science 295(5562):2097–2100, 2002
Bornhauser M, Schwerdtfeger R, Martin H, Frank KH, Theuser C, Ehninger G: Role of KIR ligand incompatibility in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using unrelated donors. Blood 103(7):2860–2861, 2004
Davies SM, Ruggieri L, DeFor T, Wagner JE, Weisdorf DJ, Miller JS, Velardi A, Blazar BR: Evaluation of KIR ligand incompatibility in mismatched unrelated donor hematopoietic transplants. Blood 100(10):3825–3827, 2002
Giebel S, Locatelli F, Lamparelli T, Velardi A, Davies S, Frumento G, Maccario R, Bonetti F, Wojnar J, Martinetti M, Frassoni F, Giorgiani G, Bacigalupo A, Holowiecki J: Survival advantage with KIR ligand incompatibility in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors. Blood 102(3):814–819, 2003
Hsu KC, Keever-Taylor CA, Wilton A, Pinto C, Heller G, Arkun K, O’Reilly RJ, Horowitz MM, Dupont B: Improved outcome in HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia predicted by KIR and HLA genotypes. Blood 105(12):4878–4884, 2005
Cudkowicz G, Bennett M: Peculiar immunobiology of bone marrow allografts. I. Graft rejection by heavily irradiated “responder” mice. J Exp Med 134(1):83–102, 1971
Cudkowicz G, Bennett M: Peculiar immunobiology of bone marrow allografts. II. Rejection of parental grafts by F1 hybrid mice. J Exp Med 134(6):1513–1528, 1971
Murphy WJ, Kumar V, Bennett M: Rejection of bone marrow allograft by mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Evidence that natural killer cells can mediate the specificity of marrow graft rejection. J Exp Med 165(4):1212–1217, 1987
O’Reilly RJ, Brochstein J, Collins N, Keever C, Kapoor N, Kirkpatrick D, Kernan N, Dupont B, Burns J, Reisner Y: Evaluation of HLA-haplotype disparate parental marrow grafts depleted of T lymphocytes by differential agglutination with a soybean lectin and E-rosette depletion for the treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency. Vox Sang 51:81–86, 1986
Dal-Cortivo L, Ouachee-Chardin M, Hirsch I, Blanche S, Fischer A, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Caillat-Zucman S: Does haploidentical transplantation in children with primary immunodeficiencies have the potential to exploit donor NK cell alloreactivity? Bone Marrow Transplant 34(11):945–947, 2004
Hershfield MS, Buckley RH, Greenberg ML, Melton AL, Schiff R, Hatem C, Kurtzberg J, Markert ML, Kobayashi RH, Kobayashi AL: Treatment of adenosine deaminase deficiency with polyethylene glycol-modified adenosine deaminase (PEG-ADA). N Engl J Med 316(10):589–596, 1987
Aiuti A, Vai S, Mortellaro A, Casorati G, Ficara F, Andolfi G, Ferrari G, Tabucchi A, Carlucci F, Ochs HD, Notarangelo LD, Roncarolo MG, Bordignon C: Immune reconstitution in ADA-SCID after PBL gene therapy and discontinuation of enzyme replacement. Nat Med 8(5):423–425, 2002
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA, Lerner KG, Thomas ED: Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HLA-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 18(4):295–304, 1974
Iwasaki T: Recent advances in the treatment of graft-versus-host disease. Clin Med Res 2(4):243–252, 2004
Couriel D, Caldera H, Champlin R, Komanduri K: Acute graft-versus-host disease: pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Cancer 101(9):1936–1946, 2004
Cooper M, Fehniger T, Caligiuri M. The biology of human natural killer cell subsets. Trends Immunol 22(11):633–640, 2001
Blanca IR, Bere EW, Young HA, Ortaldo JR: Human B cell activation by autologous NK cells is regulated by CD40-CD40 ligand interaction: Role of memory B cells and CD5+ B cells. J Immunol 167(11):6132–6139, 2001
Yuan D: Interactions between NK cells and B lymphocytes. Adv Immunol 84:1–84, 2004
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NIH Grant 5R01-AI/HD042951-07 and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute Research Fellows Program. The authors would like to thank Ms. Adella Clark, Ms. Myriah Cooney, Ms. Donna Oliver, Ms. Roberta Parrott, and Ms. Elisa Sajaroff, for their excellent technical assistance, and Ms. Lora DeRubeis for her administrative work. We would also like to thank Dr. Eric Long, Dr. Sumi Rajagopalan, and Dr. Andreas Velardi for kindly sharing their protocols and advice. We are also grateful to Dr. Peter Parham for his generosity in providing cell lines, and Steven Grambow for his expertise in our statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9116-9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KELLER, M.D., CHEN, DF., CONDRON, S.A. et al. The Effect of Natural Killer Cell Killer Ig-Like Receptor Alloreactivity on the Outcome of Bone Marrow Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID). J Clin Immunol 27, 109–116 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9058-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-006-9058-7