Abstract
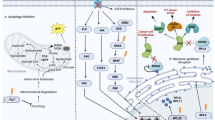
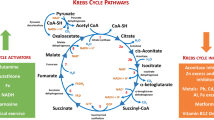
The concept that invasive cancer is associated with increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by mitochondria is consistent with an ROS-mediated signaling mechanism. As a tumor grows, it encounters adverse microenvironments, one of which is low oxygen (hypoxia), which selects tumor cells with characteristics of increased invasiveness. Hypoxic environments select for tumor cells with stabilized HIF1 apha, a transcription factor that regulates genes coding for pro-tumor cytokines that signal stromal cells such as macrophages and fibroblasts to support an invasive tumor cell phenotype. HIF1 alpha-mediated switches in the energy production of tumor cells from OXPHOS to glycolysis, as well as age-associated decreases in the metabolic rate of the host, enhance invasive qualities of tumor cells. An increase in environmental oxygen in combination with a mitochondrial targeted catalase mimetic and a metabolism booster may be of interest to investigate as a treatment strategy for invasive cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brizel DM, Sibley GS, Prosnitz LR, Scher RL, Dewhirst MW (1997) Tumor hypoxia adversely affects the prognosis of carcinoma of the head and neck. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 38:285
Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE, Wood TM, Melendez JA, Rodriguez AM, Schumacker PT (2000) Reactive oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex III stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha during hypoxia: a mechanism of O2 sensing. J Biol Chem 275(33):25130–8
Chi JT, Wang Z, Nuyten DS, Rodriguez EH, Schaner ME, Salim A, Wang Y et al (2006) Gene expression programs in response to hypoxia: cell type specificity and prognostic significance in human cancers. PLoS Med 3:e47
Dang CD, Semenza GL (1999) Oncogenic alterations of metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 24:68
Fukuda R, Zhang H, Kim JW, Shimoda L, Semenza GL, Dang CV (2007) HIF-1 regulatescytochrome oxidase subunits to optimize efficiency of respiration in hypoxic cells. Cell 129:111
Goh J, Enns L, Fatemie S, Hopkins H, Morton J, Pettan-Brewer C, Ladiges W (2011) Mitochondrial targeted catalase suppresses invasive breast cancer in mice. BMC Cancer 11:191
Hardie DG (2007) AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:774
Hockel M, Schlenger K, Aral B, Mitze M, Schaffer U, Vaupel P (1996) Association between tumor hypoxia and malignant progression in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix Cancer
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL, Dang CV (2006) HIF-1 -mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Meta
Luo Z, Saha AK, Xiang X, Ruderman NB (2005) AMPK, the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26:69
Murphy MP (2009) How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem J 417(1):1–13, Review
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL, Denko NC (2006) HIF-1 mediates adaptati to hypoxia by actively downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metab 3:187
Schriner SE, Linford NJ, Martin GM, Treuting P, Ogburn CE et al (2005) Extension of murine life span by overexpression of catalase targeted to mitochondria. Science 308:1909
Svensson S, Jirström K, Rydén L, Roos G, Emdin S, Ostrowski MC, Landberg G (2005) ERK phosphorylation is linked to VEGRF2 expression and Ets-2 phosphorylation in breast cancer a tumours with good prognosis. Oncogene 24:4370
Treuting PM, Linford NJ, Knoblaugh SE, Emond MJ, Morton JF, Ladiges WC (2008) Reduction of age-associated pathology in old mice by overexpression of catalase in mitochondria. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 63:813
Zhang H, Bosch-Marce M, Shimoda LA, Tan YS, Baek JH, Wesley JB, Gonzalez FJ, Semenza GL (2008) Mitochondrial autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem 283:10892
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enns, L., Ladiges, W. Mitochondrial redox signaling and cancer invasiveness. J Bioenerg Biomembr 44, 635–638 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-012-9467-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-012-9467-7