Abstract
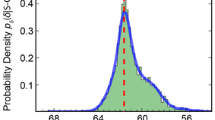
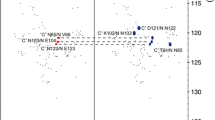
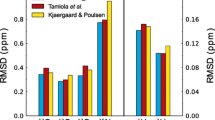
Side chain amide protons of asparagine and glutamine residues in random-coil peptides are characterized by large chemical shift differences and can be stereospecifically assigned on the basis of their chemical shift values only. The bimodal chemical shift distributions stored in the biological magnetic resonance data bank (BMRB) do not allow such an assignment. However, an analysis of the BMRB shows, that a substantial part of all stored stereospecific assignments is not correct. We show here that in most cases stereospecific assignment can also be done for folded proteins using an unbiased artificial chemical shift data base (UACSB). For a separation of the chemical shifts of the two amide resonance lines with differences ≥0.40 ppm for asparagine and differences ≥0.42 ppm for glutamine, the downfield shifted resonance lines can be assigned to Hδ21 and Hε21, respectively, at a confidence level >95%. A classifier derived from UASCB can also be used to correct the BMRB data. The program tool AssignmentChecker implemented in AUREMOL calculates the Bayesian probability for a given stereospecific assignment and automatically corrects the assignments for a given list of chemical shifts.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NOE:
-
Nuclear Overhauser effect
- NOESY:
-
Nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectroscopy
- UACSB:
-
Unbiased artificial chemical shift database
References
Berenden HJC, van der Spoerl D, van Dunen R (1995) GROMACS: a message-passing parallel dynamics impmementation. Comp Phys Comm 91:43–56
Bundi A, Wuthrich K (1979) 1H-nmr parameters of the common amino acid residues measured in aqueous solutions of the linear tetrapeptides H-Gly-Gly-X-L-Ala-OH. Biopolymers 18:285–297
Gronwald W, Kalbitzer HR (2004) Automated structure determination of proteins by NMR spectroscopy. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 44:33–96
Harsch T, Dasch C, Donaubauer H, Baskaran K, Kremer W, Kalbitzer HR (2013) Stereospecific assignment of the asparagine and glutamine side chain amide protons in random-coil peptides by combination of molecular dynamic simulations with relaxation matrix calculations. Appl Magn Reson 44(1–2):319–331
Hess B, Kutzner C, van der Spoel D, Lindahl E (2008) GROMACS 4: algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4(3):435–447
Markley JL, Bax A, Arata Y, Hilbers CW, Kaptein R, Sykes BD, Wright PE, Wüthrich K (1998) Recommendations for the presentation of nmr structures of proteins and nucleic acids. Pure Appl Chem 70:117–142
McIntosh LP, Brun E, Kay LE (1997) Stereospecific assignment of the NH2 resonances from the primary amides of asparagine and glutamine side chains in isotopically labeled proteins. J Biomol NMR 9:306–312
Nasser, A. (2006) Optimierung der Zuordnung mehrdeutiger NOESY-NMR-Signale unter Anwendung einer Datenbank nichtredundanter Proteinstrukturen. Doctoral thesis, University of Regensburg.
Neal S, Nip AM, Zhang H, Wishart DS (2003) Rapid and accurate calculation of protein 1H, 13C and 15N chemical shifts. J Biomol NMR 26:215–240
Osapay K, Case DA (1991) A new analysis of proton chemical shifts in proteins. J Am Chem Soc 113(25):9436–9444
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O et al (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J Machine Learn Res 12:2825–2830
Schölkopf B, Smola AJ (2002) Learning with kernels support vector machines, regularization, optimization, and beyond. Adaptive computation and machine learning. MIT Press, Cambridge
Sillitoe, I., Cuff, Alison L. (2013) New functional families (FunFams) in CATH to improve the mapping of conserved functional sites to 3D structures. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D490–D498
Silverman BW (1998) Density estimation for statistics and data analysis. Chapman & Hall, London
Ulrich EL, Akutsu H, Doreleijers JF, Harano Y, Ioannidi YE, Lin J, Livny M, Mading S, Maziuk D, Miller Z, Nakatani E, Schulte CF, Tolmie DE, Wenger RK, Yao H, Markley JL (2007) BioMagResBank. Nucl Acids Res 36:D402–D408
Word JM, Lovell SC, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (1999) Asparagine and glutamine: using hydrogen atom contacts in the choice of side-chain amide orientation. J Mol Biol 285(4):1735–1747
Wüthrich K (1986) NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. Wiley, New York
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the DFG (FOR1979 and KA 647), the Humboldt Society, the Fonds of the Chemical Industry (VCI), and the Human Frontier Science Program Organization (HFSPO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harsch, T., Schneider, P., Kieninger, B. et al. Stereospecific assignment of the asparagine and glutamine sidechain amide protons in proteins from chemical shift analysis. J Biomol NMR 67, 157–164 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-017-0093-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-017-0093-x