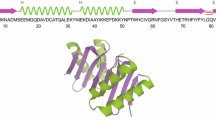
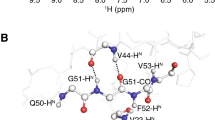
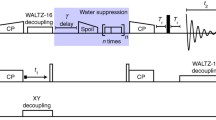
Abstract
Proton detection in solid-state NMR has seen a tremendous increase in popularity in the last years. New experimental techniques allow to exploit protons as an additional source of information on structure, dynamics, and protein interactions with their surroundings. In addition, sensitivity is mostly improved and ambiguity in assignment experiments reduced. We show here that, in the solid state, sequential amide-to-amide correlations turn out to be an excellent, complementary way to exploit amide shifts for unambiguous backbone assignment. For a general assessment, we compare amide-to-amide experiments with the more common 13C-shift-based methods. Exploiting efficient CP magnetization transfers rather than less efficient INEPT periods, our results suggest that the approach is very feasible for solid-state NMR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal V, Diehl A, Skrynnikov N, Reif B (2006) High resolution 1H detected 1H, 13C correlation spectra in MAS solid-state NMR using deuterated proteins with selective 1H, 2H isotopic labeling of methyl groups. J Am Chem Soc 128:12620–12621
Agarwal V et al (2014) De novo 3D structure determination from sub-milligram protein samples by solid-state 100 kHz MAS NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:12253–12256
Baldus M, Petkova AT, Herzfeld J, Griffin RG (1998) Cross polarization in the tilted frame: assignment and spectral simplification in heteronuclear spin systems. Mol Phys 95:1197–1207
Barbet-Massin E et al (2013) Out-and-back 13C–13C scalar transfers in protein resonance assignment by proton-detected solid-state NMR under ultra-fast MAS. J Biomol NMR 56:379–386
Barbet-Massin E et al (2014) Rapid proton-detected NMR assignment for proteins with fast magic angle spinning. J Am Chem Soc 136:12489–12497
Bellstedt P, Herbst C, Häfner S, Leppert J, Görlach M, Ramachandran R (2012) Solid state NMR of proteins at high MAS frequencies: symmetry-based mixing and simultaneous acquisition of chemical shift correlation spectra. J Biomol NMR 54:325–335
Brown SP (2012) Applications of high-resolution 1H solid-state NMR. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 41:1–27
Chevelkov V, Rehbein K, Diel A, Reif B (2006) Ultra-high resolution in proton solid-state NMR spectroscopy at high levels of deuteration. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:3878–3881
Chevelkov V, Faelber K, Schrey A, Rehbein K, Diehl A, Reif B (2007) Differential line broadening in MAS solid-state NMR due to dynamic interference. J Am Chem Soc 129:10195–10200
Chevelkov V, Fink U, Reif B (2009) Accurate determination of order parameters from 1H, 15N dipolar couplings in MAS solid-state NMR experiments. J Am Chem Soc 131:14018–14022
Chevelkov V, Giller K, Becker S, Lange A (2013) Efficient CO–CA transfer in highly deuterated proteins by band-selective homonuclear cross-polarization. J Magn Reson 230:205–211
Emsley L, Bodenhausen G (1990) Gaussian pulse cascades: new analytical functions for rectangular selective inversion and in-phase excitation in NMR. Chem Phys Lett 165:469–476
Ernst M, Samoson A, Meier BH (2003) Low-power XiX decoupling in MAS NMR experiments. J Magn Reson 163:332–339
Gardner KH, Rosen MK, Kay LE (1997) Global folds of highly deuterated, methyl-protonated proteins by multidimensional NMR. Biochemistry 36:1389–1401
Goddard TD, Kneller DG (2004) SPARKY 3. University of California, San Francisco
Grzesiek S, Anglister J, Ren H, Bax A (1993) 13C line narrowing by deuterium decoupling in 2D/13C/15N enriched proteins. Application to triple resonance 4D J connectivity of sequential amides. J Am Chem Soc 115:4369–4370
Harbison NW, Bhattacharya S, Eliezer D (2012) Assigning backbone NMR resonances for full length tau isoforms: efficient compromise between manual assignments and reduced dimensionality. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034679
Huber M, Hiller S, Schanda P, Ernst M, Böckmann A, Verel R, Meier BH (2011) A proton-detected 4D solid-state NMR experiment for protein structure determination. ChemPhysChem 12:915–918
Hyberts SG, Milbradt AG, Wagner AB, Arthanari H, Wagner G (2012) Application of iterative soft thresholding for fast reconstruction of NMR data non-uniformly sampled with multidimensional poisson gap scheduling. J Biomol NMR 52:315–327
Keller RLJ (2005) Optimizing the process of nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum analysis and computer aided resonance assignment. Doctoral and habilitation theses ETH
Knight MJ et al (2011) Fast resonance assignment and fold determination of human superoxide dismutase by high-resolution proton-detected solid-state MAS NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:11697–11701
Knight MJ et al (2012) Structure and backbone dynamics of a microcrystalline metalloprotein by solid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:11095–11100
Krushelnitsky A, deAzevedo E, Linser R, Reif B, Saalwächter K, Reichert D (2009) Direct observation of millisecond to second motions in proteins by dipolar CODEX NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 131:12097–12099
Lamley JM et al (2014) Solid-state NMR of a protein in a precipitated complex with a full-length antibody. J Am Chem Soc 136:16800–16806
Lewandowski JR, Dumez J-N, Akbey U, Lange S, Emsley L, Oschkinat H (2011) Enhanced resolution and coherence lifetimes in the solid-state NMR spectroscopy of perdeuterated proteins under ultrafast magic-angle spinning. J Phys Chem Lett 2:2205–2211
Linser R (2012) Backbone assignment of perdeuterated proteins using long-range H/C-dipolar transfers. J Biomol NMR 52:151–158
Linser R, Chevelkov V, Diehl A, Reif B (2007) Sensitivity enhancement using paramagnetic relaxation in MAS solid-state NMR of perdeuterated proteins. J Magn Reson 189:209–216
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2008) Proton-detected scalar coupling based assignment strategies in MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy applied to perdeuterated proteins. J Magn Reson 193:89–93
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2009) Probing surface accessibility of proteins using paramagnetic relaxation in solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 131:13703–13708
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2010a) Assignment of dynamic regions in biological solids enabled by spin-state selective NMR experiments. J Am Chem Soc 132:8891–8893
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2010b) Narrow carbonyl resonances in proton-diluted proteins facilitate NMR assignments in the solid state. J Biomol NMR 47:1–6
Linser R, Bardiaux B, Higman V, Fink U, Reif B (2011a) Structure calculation from unambiguous long-range amide and methyl 1H–1H distance restraints for a micro-crystalline protein with MAS solid state NMR. J Am Chem Soc 133:5905–5912
Linser R et al (2011b) Proton detected solid-state NMR of fibrillar and membrane proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:4508–4512
Linser R, Bardiaux B, Hyberts SG, Kwan AH, Morris VK, Sunde M, Wagner G (2014) Solid-state NMR structure determination from diagonal-compensated, sparsely nonuniform-sampled 4D proton–proton restraints. J Am Chem Soc 136:11002–11010
Ma P et al (2014) Probing transient conformational states of proteins by solid-state R(1ρ) relaxation-dispersion NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:4312–4317
Mainz A, Religa T, Sprangers R, Linser R, Kay LE, Reif B (2013) Solution-state NMR spectroscopy at 1 MDa and beyond. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:8746–8751
Marchetti A et al (2012) Backbone assignment of fully protonated solid proteins by 1H detection and ultrafast magic-angle-spinning NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:10756–10759
Morris GA, Freeman R (1979) Enhancement of nuclear magnetic resonance signals by polarization transfer. J Am Chem Soc 101:760–762
Nielsen NC, Bildsoe H, Jakobsen HJ, Levitt MH (1994) Double-quantum homonuclear rotary resonance: efficient dipolar recovery in magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance. J Chem Phys 101:1805–1812
Nishiyama Y, Malon M, Ishii Y, Ramamoorthy A (2014) 3D 15N/15N/1H chemical shift correlation experiment utilizing an RFDR-based 1H/1H mixing period at 100 kHz MAS. J Magn Reson 244:1–5
Paulson EK, Morcombe CR, Gaponenko V, Dancheck B, Byrd RA, Zilm KW (2003) Sensitive high resolution inverse detection NMR spectroscopy of proteins in the solid state. J Am Chem Soc 125:15831–15836
Pervushin KV, Riek R, Wider G, Wüthrich K (1997) Attenuated T2 relaxation by mutual cancellation of dipole–dipole coupling and chemical shift anisotropy indicates an avenue to NMR structures of very large biological macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12366–12371
Pines A, Gibby MG, Waugh JS (1973) Proton-enhanced NMR of dilute spins in solids. J Chem Phys 59(2):569–590
Schanda P, Huber M, Verel R, Ernst M, Meier BH (2009) Direct detection of \( ^{{3{\text{h}}}} J_{{{\text{NC}}^{{\prime }} }} \) hydrogen-bond scalar couplings in proteins by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:9322–9325
Schanda P, Meier BH, Ernst M (2010) Quantitative analysis of protein backbone dynamics in microcrystalline ubiquitin by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 132:15957–15967
Shaka AJ, Keeler J, Frenkiel T, Freeman R (1983) An improved sequence for broad-band decoupling—WALTZ-16. J Magn Reson 52:335–338
Sinnige T, Daniëls M, Baldus M, Weingarth M (2014) Proton clouds to measure long-range contacts between nonexchangeable side chain protons in solid-state NMR. J Am Chem Soc 136:4452–4455
Sun Z-Y, Frueh D, Selenko P, Hoch J, Wagner G (2005) Fast assignment of 15N-HSQC peaks using high-resolution 3D HNcocaNH experiments with non-uniform sampling. J Biomol NMR 33:43–50
Ulrich EL et al (2008) BioMagResBank. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D402–D408
van Rossum BJ, Castellani F, Pauli J, Rehbein K, Hollander J, de Groot HJM, Oschkinat H (2003) Assignment of amide proton signals by combined evaluation of HN, NN and HNCA MAS–NMR correlation spectra. J Biomol NMR 25:217–223
Vranken WF et al (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59:687–696
Ward ME, Shi L, Lake E, Krishnamurthy S, Hutchins H, Brown LS, Ladizhansky V (2011) Proton-detected solid-state NMR reveals intramembrane polar networks in a seven-helical transmembrane protein proteorhodopsin. J Am Chem Soc 133:17434–17443
Weisemann R, Rüterjans H, Bermel W (1993) 3D triple-resonance NMR techniques for the sequential assignment of NH and 15N resonances in 15N- and 13C-labelled proteins. J Biomol NMR 3:113–120
Wittekind M, Mueller L (1993) HNCACB: a high sensitivity 3D NMR experiment to correlate amide proton and nitrogen resonances with the α-carbon and β-carbon resonances in proteins. J Magn Reson B 101:201–205
Xiang S, Chevelkov V, Becker S, Lange A (2014) Towards automatic protein backbone assignment using proton-detected 4D solid-state NMR data. J Biomol NMR 60:85–90
Zhou DH, Rienstra CM (2008) High-performance solvent suppression for proton-detected solid-state NMR. J Magn Reson 192:167–172
Zhou DH et al (2007) Solid-state protein structure determination with proton-detected triple resonance 3D magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:8380–8383
Zhou DH et al (2012) Solid-state NMR analysis of membrane proteins and protein aggregates by proton detected spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 54:291–305
Zinkevich T, Chevelkov V, Reif B, Saalwächter K, Krushelnitsky A (2013) Internal protein dynamics on ps to μs timescales as studied by multi-frequency 15N solid-state NMR relaxation. J Biomol NMR 57:219–235
Acknowledgments
R.L. acknowledges support from the Max-Planck Gesellschaft and the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie (FCI) in terms of a Liebig junior group fellowship. R.L. and S.X. acknowledge funding from the DFG Collaborative Research Center 803 (Project A4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ShengQi Xiang and Kristof Grohe have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, S., Grohe, K., Rovó, P. et al. Sequential backbone assignment based on dipolar amide-to-amide correlation experiments. J Biomol NMR 62, 303–311 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-015-9945-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-015-9945-4