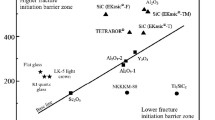
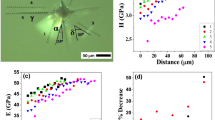
Abstract
In this paper, the mechanical properties of electronic glass are tested using a combination of the Vickers indentation test and a multiple-loading nanoindentation test to obtain the elastic modulus, Poisson’s ratio and hardness values. The basic mechanical property parameters of the electronic glass and its stress–strain curve are found using atomic force microscopy analysis of the indentation morphology. The critical pressure and depth for crack initiation and the corresponding load and depth can be obtained during vertical loading on the electronic glass. When cracks extend to the surface, the results show that the electronic glass is isotropic. Several loading cycles causes a fatigue effect on the surface of the electronic glass, which decreases its elastic–plastic response. While the loadings are increasing, the elastic–plastic response rates are decreasing bur it rends stability finally. These results can provide a reference and guide for micro machining and surface microstructure machining of electronic glass.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Kohsaka, C. Taylor, K. Fujita, A. Schmidt, C. Lupien, T. Hanaguri, M. Azuma, M. Takano, H. Eisaki, H. Takagi, S. Uchida, J.C. Davis, Science 315(5817), 1380–1385 (2007)
D.Z. Zhu, X.Z. Feng, J. Eng. Thermophys-rus. 18(4), 479–483 (1997)
J.H. Jean, C.R. Chang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80(12), 3084–3092 (1997)
K. Kese, M. Tehler, B. Bergm, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26(6), 1003–1011 (2006)
M. Suszynska, M. Szmida, Opt. Appl. 38(1), 245–250 (2008)
M. Arif, M. Rahman, Y.S. Wong, J. Manuf. Process. 13(1), 50–59 (2011)
T. Matsumura, P. Aristimuno, E. Gandarias, J.A. Pedro, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 213, 1523–1531 (2013)
H.T. Liu, Y.Z. Sun, D.B. Shan, C.X. Zhang, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 68, 1901–1909 (2013)
C.A. Schuh, Nanoindentation studies of materials. Mater. Today 9(5), 32–40 (2006)
M.F. Doerner, W.D. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 1(4), 601–609 (1986)
W.C. Oliver, G.M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7(6), 1564–1583 (1992)
J. W. Yan, H. W. Zhao, T. Kuriyagawa, T. Tamaki, in Proceedings 6th Euspen Int. Conf., Baden bei Wien, Austria, May, 276–279 (2006)
S. Shin, H. Bei, E.P. Georgea, G.M. Pharra, Scr. Mater. 59(10), 1095–1098 (2008)
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, S.R. Mahmoodi, A. Khalatbari, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18(10), 1071–1078 (2007)
S. Celik, O. Ozturk, E. Coşkun, M. Sarıhan, E. Asikuzun, K. Ozturk, C. Terzioglu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24(7), 2218–2227 (2013)
W.J. Plumbridge, C.R. Gagg, Effects of strain rate and temperature on the stress–strain response of solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 10(5–6), 461–468 (1999)
Z.G. Wang, X.T. Zu, L. Yang, F. Gao, J.W. William, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19(8–9), 863–867 (2008)
E. Horváth, G. Hénap, Á.G. Török, Harsányi, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23(12), 2123–2129 (2012)
H.W. Zhao, H.J. Zhao, J.J. Yao, H. Huang, Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 3(7), 205–210 (2009)
J.H. Wang, S.Z. Li, X.L. Song, W. Song, H.X. Wang, S.P. Li, Acta. Opt. Sin. 33(9), 243–248 (2013)
M.J. Chen, S. Dong, D. Li, F.H. Zhang, High Technol. Lett. 2, 64–67 (2000)
C.C. Lee, C.C. Lee, Y.W. Yang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21(8), 787–795 (2010)
M.J. Chen, Q.L. Zhao, S. Dong, D. Li, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 168, 75–82 (2005)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51205087) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. HIT. NSRIF.2009017) for providing financial support for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y.Z., Zhang, J. & Liu, H.T. Mechanical properties of and critical conditions for crack initiation in electronic glass. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 4466–4475 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2189-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2189-3