Abstract
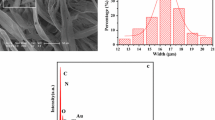
Novel magnetic–photoluminescent bifunctional [Fe3O4@Y2O3:Eu3+]/polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) flexible composite nanobelts were successfully prepared by electrospinning via dispersing Fe3O4@Y2O3:Eu3+ core–shell structured nanoparticles (NPs) into the PMMA matrix. The morphology, structure and properties of the flexible composite nanobelts were investigated by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry and fluorescence spectroscopy. The width and thickness of [Fe3O4@Y2O3:Eu3+]/PMMA composite nanobelts are 3.58 ± 0.29 and 1.2 μm, respectively. Fluorescence emission peaks of Eu3+ in [Fe3O4@Y2O3:Eu3+]/PMMA flexible composite nanobelts are observed and assigned to the energy levels transitions of 5D0 → 7F0 (580 nm), 5D0 → 7F1 (533, 586, 592, 599 nm), 5D0 → 7F2 (612 nm) and 5D0 → 7F3 (629 nm) of Eu3+ ions. Compared with Fe3O4/Y2O3:Eu3+/PMMA nanobelts, [Fe3O4@Y2O3:Eu3+]/PMMA flexible composite nanobelts possess much stronger luminescent intensity. The as-prepared flexible composite nanobelts exhibit excellent magnetism and photoluminescent performance. The intensities of magnetism and luminescence of the flexible composite nanobelts can be simultaneously tuned by adjusting the amount of Fe3O4@Y2O3:Eu3+ NPs introduced into the nanobelts. The high performance [Fe3O4@Y2O3:Eu3+]/PMMA flexible composite nanobelts have potential applications in the fields of cell separation, magnetic resonance imaging, drug deliver and future nanodevices.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.Y. Zhang, C.L. Shao, X.H. Li, L. Zhang, H.M. Xue, C.H. Wnag, Y.C. Liu, J. Phys. Chem. C 114(17), 7920–7925 (2010)
Y.C. Chou, C.L. Shao, X.H. Li, C.Y. Su, H.C. Xu, M.Y. Zhang, P. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y.C. Liu, Appl. Surf. Sci. Part B 285, 509–516 (2013)
L. Nicolas, H. Anne, S. Guy, T.M. Linda, R. RenéM, P. Ana-Maria, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 10090–10097 (2013)
K. Akash, S.K. Sang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95(2), 553–556 (2012)
X.F. Lu, W.J. Zhang, C. Wang, T.C. Wen, Y. Wei, Prog. Polym. Sci. 36, 671–712 (2011)
Z. Eduard, C. Daehwan, L.J. Yong, Phys. Fluids 23(073102), 1–3 (2011)
W.Y. Liu, J.C. Wei, Y.W. Chen, P. Huo, Y. Wei, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 680–685 (2013)
B.S. Kim, I.S. Kim, Polym. Rev. 51, 235–238 (2011)
B. Cedric, G. Thierry, A. Antigoni, ACS Nano 5(11), 8488–8505 (2011)
M. Thandar, G. Ray, E. Hergen, J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 1687–1693 (2012)
A.L. Morel, S.I. Nikitenko, K. Gionnet, A. Wattiaux, M. Simonoff, ACS Nano 2(5), 847–856 (2008)
M.J. Li, Z.F. Chen, V.W.W. Yam, Y.B. Zu, ACS Nano 2(5), 905–912 (2008)
J.H. Wang, S.R. Zheng, Y. Shao, J.L. Liu, Z.Y. Xu, D.Q. Zhu, J. Colloid Interface Sci 349, 293–299 (2010)
M. Runowski, T. Gizyb, S. Lis, J. Rare Earths 29(12), 1117–1121 (2011)
Z.Y. Ma, D. Dosi, N. Mikaela, J.G. Shirley, D.H. Bruce, M.K. Ian, J. Mater. Chem. 19, 4695–4700 (2009)
Q. Wang, X.W. Yang, L.X. Yu, H. Yang, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 9098–9104 (2011)
D.M. Liu, L.Z. Tong, J.H. Shi, X.W. Yang, H. Yang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 464–467 (2012)
Y. Xu, A. Karmakar, D.Y. Wang, M. Mahmood, F. Watanabe, Y.B. Zhang, A. Fejleh, P. Fejleh, Z.R. Li, G. Kannarpady, S. Ali, A. Biris, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 5020–5026 (2010)
Z.S. Yang, Adv. Mater. Lett. 2(3), 195–199 (2011)
H.T. Wong, H.L. Chan, J.H. Hao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 510–512 (2009)
M. Runowski, T. Grzyb, S. Lis, J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1188–1195 (2012)
P. Lu, J.L. Zhang, Y.L. Liu, D.H. Sun, G.X. Liu, G.Y. Hong, N.J. Zuan, Talanta 83, 450–457 (2010)
H.X. Peng, G.X. Liu, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, J. Xu, W.S. Yu, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6930–6934 (2011)
W. Wang, M. Zou, K.Z. Chen, Chem. Commun. 46, 5100–5102 (2010)
J. Feng, S.Y. Song, R.P. Deng, W.Q. Fan, H.J. Zhang, Langmuir 26, 3596–3600 (2010)
L.Z. Tong, J.H. Shi, D.M. Liu, Q.H. Li, X.Z. Ren, H. Yang, J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 7153–7157 (2012)
X.G. Yu, Y. Shan, G.C. Li, K.Z. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. 21, 8104–8108 (2011)
H.G. Wang, Y.X. Li, L. Sun, Y. Li, W. Wang, S. Wang, S.F. Xu, Q.B. Yang, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 350, 396–401 (2010)
Q.L. Ma, J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, J. Xu, J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1203–1209 (2012)
Q.L. Ma, W.S. Yu, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, Opt. Mater. 35, 526–530 (2013)
Q.L. Ma, J.X. Wang, X.T. Dong, W.S. Yu, G.X. Liu, J. Xu, J. Mater. Chem. 22, 14438–14442 (2012)
Q.L. Ma, W.S. Yu, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, ChemPlusChem. 79, 290–297 (2014)
Q.L. Ma, W.S. Yu, X.T. Dong, J.X. Wang, G.X. Liu, Nanoscale 6(5), 2945–2952 (2014)
G.Q. Gai, L.Y. Wang, X.T. Dong, C.M. Zheng, W.S. Yu, X.J. Wang, X.F. Xiao, J. Nanopart. Res. 15(4), 1539–1547 (2013)
Y.Y. Zheng, X.B. Wang, L. Shang, C.R. Li, C. Cui, W.J. Dong, W.H. Tang, B.Y. Chen, Mater. Charact. 61, 489–492 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 50972020, 51072026), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20102216110002, 20112216120003), the Science and Technology Development Planning Project of Jilin Province (Grant Nos. 20130101001JC, 20070402, 20060504), the Science and Technology Research Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province during the eleventh five-year plan period (Under Grant No. 2010JYT01), Key Research Project of Science and Technology of Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. 207026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, R., Wang, J., Dong, X. et al. A new tactics to fabricate flexible nanobelts with enhanced magnetic–luminescent bifunction. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 25, 2561–2568 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-1910-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-1910-6