ABSTRACT
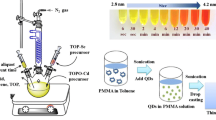
Polymer-CdTe quantum dots (QDs) nanocomposites were developed via solvent casting. Colloidal CdTe QDs, synthesized in aqueous solution, were transferred to organic media by exchanging of the original capping ligands by a long-chain thiol. Different commercial polymers (PMMA, OPS, PS, and PC), transparent in the visible spectral range, were chosen as matrices. Stock solutions of the polymers were prepared in suitable concentration (2 wt%) for the production of thin films with good quality, able to maximize the solubility of QDs, without phase separation. Studies on the morphological and optical properties were performed. The results showed that the polymer matrix has a considerable effect on QDs’ morphology, size, and electric conductivity. PMMA demonstrated to be the most promising embedding matrix, offering new possibilities for optoelectronic applications of polymer-QD nanocomposites.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seo Y-S, Raj CJ, Kim D-J, Kim BC, Yu K-H (2014) Effect of CdS/ZnS quantum dots dispersion in silicone based polymeric Fluids. Mater Lett 130:43–47
Bardajee GR, Hooshyar Z (2013) CdTe quantum dots embedded in a multidentate biopolymer based on salep: characterization and optical properties. J Chem. Article ID 202061
Suárez I, Gordillo H, Abargues R, Albert S, Martínez-Pastor J (2011) Photoluminescence waveguiding in CdSe and CdTe QDs–PMMA nanocomposite films. Nanotechnology 22:435202–435209
Zhu L, Yang S, Wang J, Wang C-F, Chen L, Chen S (2013) Quantum-dot-embedded polymeric fiber films with photoluminescence and superhydrophobicity. Mater Lett 99:54–56
Tomczak N, Janczewski D, Han M, Vancso GJ (2009) Designer polymer–quantum dot architectures. Prog Polym Sci 34(5):393–430
Kim HC, Hong HG, Yoon C, Choi H, Ahn IS, Lee DC, Kim YJ, Lee K (2013) Fabrication of high quantum yield quantum dot/polymer films by enhancing dispersion of quantum dots using silica particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 393:74–79
Ullah MH, Kim J-H, Ha C-S (2008) Highly transparent o-PDA functionalized ZnS-polymer nanocomposite thin films with high refractive index. Mater Lett 62(15):2249–2252
Lawrence WG, Thacker S, Palamakumbura S, Riley KJ, Nagarkar VV (2012) Quantum dot-organic polymer composite materials for radiation detection and imaging. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 59(1):215–221
Zhang H, Tang Y, Zhang J, Li M, Yao X, Li X, Yang B (2009) Manipulation of semiconductor nanocrystals growth in polymer soft materials. Soft Matter 5:4113–4117
Silva FO, Carvalho MS, Mendonça R, Macedo WAA, Balzuweit K, Reiss P, Schiavon MA (2012) Effect of surface ligands on the optical properties of aqueous soluble CdTe Quantum dots. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:536–545
Mansurand HS, Mansur AAP (2011) CdSe quantum dots stabilized by carboxylic-functionalized PVA: synthesis and UV–Vis spectroscopy characterization. Mater Chem Phys 125(3):709–717
Shavel A, Gaponik N, Eychmüller A (2006) Factors governing the quality of aqueous CdTe nanocrystals: calculations and experiment. J Phys Chem B 110(39):19280–19284
Zhang H, Zhou Z, Yang B, Gao M (2003) The influence of carboxyl groups on the photoluminescence of mercaptocarboxylic acid-stabilized CdTe nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 107(1):8–13
Gaponik N, Talapin DV, Rogach AL, Eychmuller A, Weller H (2002) Efficient phase transfer of luminescent thiol-capped nanocrystals: from water to nonpolar organic solvents. Nanolleters 2(8):803–806
Zhang H, Cui Z, Wang Y, Zhang K, Ji X, Lü C, Yang B, Gao M (2003) From water-soluble cdte nanocrystals to fluorescent nanocrystal-polymer transparent composites using polymerizable surfactants. Adv Mater 15:777–780
Zhang H, Wang C, Li M, Zhang J, Lu G, Yang B (2005) Fluorescent nanocrystal-polymer complexes with flexible processability. Adv Mater 17:853–857
Pang L, Shen Y, Tetz K, Fainma Y (2005) PMMA quantum dots composites fabricated via use of pre-polymerization. Opt Express 13(1):44–49
Ananthakumar S, Ramkumar J, Moorthy Babu S (2013) Enhanced light absorption in CdTe nanoparticles/P3HT nanofiber blends. AIP Conf Proc 1536:167–168
Meli L, Green PF (2008) Aggregation and coarsening of ligand-stabilized gold nanoparticles in poly(methyl methacrylate) thin films. ACS Nano 2:1305–1312
Kane RS, Cohen RE, Silbey R (1999) Semiconductor nanocluster growth within polymer films. Langmuir 15:39–43
Moradian R, Elahi M, Hadizadeh A, Roshani M, Taghizadeh A, Sahraei R (2013) Structural, optical, and electrical properties of thioglycolic acid-capped CdTe quantum dots thin films. Int Nano Lett 3:56–61
Klayman DL, Griffin TS (1973) Reaction of selenium with sodium borohydride in protic solvents. A Facile Method for the introduction of selenium into organic molecules. J Am Chem Soc 95(1):197–199
Gao M, Kirstein S, Möhwald H, Rogach AL, Kornowski A, Eychmüller A, Weller H (1998) Strongly photoluminescent CdTe nanocrystals by proper surface modification. J Phys Chem B 102(43):8360–8363
López F, Ojeda P, Arbeloa I (1989) Fluorescence self-quenching of the molecular forms of Rhodamine B in aqueous and ethanolic solutions. J Luminesc 44:105–112
Stuart BH (2004) Infrared spectroscopy: fundamentals and applications. Wiley, New York
Yu WW, Qu L, Guo W, Peng X (2003) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater 15:2854–2860
Ananthakumar S, Ramkumar J, Moorthy Babu S (2013) Synthesis and efficient phase transfer of cdse nanoparticles for hybrid solar cell applications. In: Conference papers in energy, vol 2013, p 3
Gopi A, Vindhyasarumi A, Yoosaf K (2015) Electrostatically driven self-assembly of CdTe nanoparticles with organic chromophores probed via Ham effect. RSC Adv 5(59):47813–47819
Gregorio RJ, Ueno EM (1999) Effect of crystalline phase, orientation and temperature on the dielectric properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF). J Mater Sci 34(18):4489–4500
Rajabi HR, Khani O, Shamsipur M, Vatanpour V (2013) High-performance pure and Fe3+-ion doped ZnS quantum dots as green nanophotocatalysts for the removal of malachite green under UV-light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 250–251:370–378
Cao X, Li CM, Bao H, Bao Q, Dong H (2007) Fabrication of strongly fluorescent quantum dot—polymer composite in aqueous solution. Chem Mater 19(15):3773–3779
Yoon C, Hong H-G, Kim HC, Hwang D, Lee DC, Kim C-K, Kim Y-J, Lee K (2013) High luminescence efficiency white light emitting diodes based on surface functionalized quantum dots dispersed in polymer matrices. Colloids Surf A 428:86–91
Thuy UTD, Liem NQ (2013) Transition from type-I to type-II CdTe/CdS core/shell quantum dots synthesized in water at low temperature. Adv Nat Sci 4(4):045010–045015
Tang Z, Kotov NA, Giersig M (2002) Spontaneous organization of single CdTe nanoparticles into luminescent nanowires. Science 297(5579):237–240
Jakubiak R, Collison CJ, Wan WC, Rothberg LJ, Hsieh BR (1999) Aggregation quenching of luminescence in electroluminescent conjugated polymers. J Phys Chem A 103(14):2394–2398
Korala L, Wang Z, Liu Y, Maldonado S, Brock SL (2013) Uniform thin films of CdSe and CdSe(ZnS) core(shell) quantum dots by sol-gel assembly: enabling photoelectrochemical characterization and electronic applications. ACS Nano 7(2):1215–1223
Ranjbartoreh AR, Ghorbanpour A, Soltani B (2007) Double-walled carbon nanotube with surrounding elastic medium under axial pressure. Physica E 39(2):230–239
Ketenoğlu D, Ünal B (2013) Influence of surface roughness on the electrical conductivity of semiconducting thin films. Physica A 392(14):3008–3017
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the n-STeP—Nanostructured systems for Tailored Performance, with reference NORTE-07-0124-FEDER-000039, supported by the Programa Operacional Regional do Norte (ON.2), PEst-C/CTM/LA0025/2013 (Strategic Project - LA 25 - 2013-2014). The authors also acknowledge Agnieszka Tercjak from Dpto. Ingeniería Química y del Medio Ambiente, Escuela Politécnica Donostia-San Sebastián for the AFM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moura, I., de Sá, A., Abreu, A.S. et al. Morphology, optical, and electric properties of polymer-quantum dots nanocomposites: effect of polymeric matrix. J Mater Sci 51, 8699–8710 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0129-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0129-8