Abstract
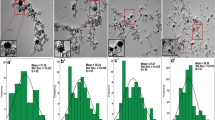
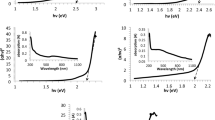
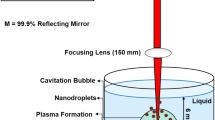
The paper explores the synthesis of oxide-free nanoparticles of Ag and Cu through laser ablation of pure targets under aqueous medium and tuning the quality and size through addition of Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in the medium. The size distribution of nanoparticles reduces from 37 ± 30 nm and 13 ± 5 nm to 32 ± 12 nm and 4 ± 1 nm for Ag and Cu with changes in PVP concentration from 0.00 to 0.02 M, respectively. Irregular shaped particles of Ag with Ag2O phase and a Cu–Cu2O core–shell particles form without the addition of PVP, while oxide layer is absent with 0.02 M of PVP. The recent understanding of the mechanism of particle formation during laser ablation under liquid medium allows us to rationalize our observation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shima PD, Philip J (2013) Role of thermal conductivity of dispersed nanoparticles on heat transfer properties of nanofluid. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(2):980–988
Singh D, Timofeeva EV, Moravek MR, Cingarapu S, Yu W, Fischer T, Mathur S (2014) Use of metallic nanoparticles to improve the thermophysical properties of organic heat transfer fluids used in concentrated solar power. Sol Energy 105:468–478
Sebti S, Mastiani M, Mirzaei H, Dadvand A, Kashani S, Hosseini S (2013) Numerical study of the melting of nano-enhanced phase change material in a square cavity. J Zhejiang Univ Sci A 14(5):307–316
Tamayo LA, Zapata PA, Vejar ND, Azócar MI, Gulppi MA, Zhou X, Thompson GE, Rabagliati FM, Páez MA (2014) Release of silver and copper nanoparticles from polyethylene nanocomposites and their penetration into Listeria monocytogenes. Mater Sci Eng C 40:24–31
Tauran Y, Brioude A, Coleman AW, Rhimi M, Kim B (2013) Molecular recognition by gold, silver and copper nanoparticles. World J Biol Chem 4(3):35–63
Devi JM, Umadevi M (2014) Synthesis and characterization of silver–PVA nanocomposite for sensor and antibacterial applications. J Clust Sci 25(2):639–650
Yang W, Liu C, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Nie S (2013) Preparation and conductive mechanism of copper nanoparticles ink. J Mater Sci 24(12):5175–5182. doi:10.1007/s10854-013-1541-3
Zhai D, Zhang T, Guo J, Fang X, Wei J (2013) Water-based ultraviolet curable conductive inkjet ink containing silver nano-colloids for flexible electronics. Colloid Surf A 424:1–9
Amendola V, Meneghetti M (2013) What controls the composition and the structure of nanomaterials generated by laser ablation in liquid solution? Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(9):3027–3046
Walter J, Petersen S, Stahl F, Scheper T, Barcikowski S (2010) Laser ablation-based one-step generation and bio-functionalization of gold nanoparticles conjugated with aptamers. J Nanobiotechnol 8(1):1–11
Malviya KD, Chattopadhyay K (2014) Synthesis and mechanism of composition and size dependent morphology selection in nanoparticles of Ag–Cu alloys processed by laser ablation under liquid medium. J Phys Chem C 118(24):13228–13237
Messina GC, Wagener P, Streubel R, De Giacomo A, Santagata A, Compagnini G, Barcikowski S (2013) Pulsed laser ablation of a continuously-fed wire in liquid flow for high-yield production of silver nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(9):3093–3098
Mafuné F, Kohno JY, Takeda Y, Kondow T, Sawabe H (2000) Formation and size control of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 104(39):9111–9117
He C, Sasaki T, Zhou Y, Shimizu Y, Masuda M, Koshizaki N (2007) Surfactant-assisted preparation of novel layered silver bromide-based inorganic/organic nanosheets by pulsed laser ablation in aqueous media. Adv Funct Mater 17(17):3554–3561
Bian F, Tian YC, Wang R, Yang HX, Xu H, Meng S, Zhao J (2011) Ultrasmall silver nanopores fabricated by femtosecond laser pulses. Nano Lett 11(8):3251–3257
Tsuji T, Thang DH, Okazaki Y, Nakanishi M, Tsuboi Y, Tsuji M (2008) Preparation of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in polyvinylpyrrolidone solutions. Appl Surf Sci 254(16):5224–5230
Lin XZ, Liu P, Yu JM, Yang GW (2009) Synthesis of CuO nanocrystals and sequential assembly of nanostructures with shape-dependent optical absorption upon laser ablation in liquid. J Phys Chem C 113(40):17543–17547
Muniz-Miranda M, Gellini C, Giorgetti E (2011) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from copper nanoparticles obtained by laser ablation. J Phys Chem C 115(12):5021–5027
Wagener P, Ibrahimkutty S, Menzel A, Plech A, Barcikowski S (2013) Dynamics of silver nanoparticle formation and agglomeration inside the cavitation bubble after pulsed laser ablation in liquid. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(9):3068–3074
Ring TA (1996) Chapter 2 Ceramic powder characterization. In: Ring TA (ed) Fundamentals of ceramic powder processing and synthesis. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 43–79
McClary F, Gaye-Campbell S, Hai Ting A, Mitchell J (2013) Enhanced localized surface plasmon resonance dependence of silver nanoparticles on the stoichiometric ratio of citrate stabilizers. J Nanopart Res 15(2):1–13
Maleki A, Rahimi R, Maleki S (2014) Synthesis, characterization and morphology of new magnetic fluorochromate hybrid nanomaterials with triethylamine surface modified iron oxide nanoparticles. Synth Met 194:11–18
Yan Z, Bao R, Chrisey DB (2013) Generation of Ag-Ag2O complex nanostructures by excimer laser ablation of Ag in water. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(9):3052–3056
Muniz-Miranda M, Gellini C, Simonelli A, Tiberi M, Giammanco F, Giorgetti E (2013) Characterization of copper nanoparticles obtained by laser ablation in liquids. Appl Phys A 110(4):829–833
Goswami R, Chattopadhyay K (1994) Microstructural developments in rapidly soliified monotectic alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 179–180(Part 1):163–167
Uhlmann DR, Chalmers B, Jackson KA (1964) Interaction between particles and a solid-liquid interface. J Appl Phys 35(10):2986–2993
Surappa MK, Rohatgi PK (1981) Heat diffusivity criterion for the entrapment of particles by a moving solid-liquid interface. J Mater Sci 16(2):562–564. doi:10.1007/BF00738658
Shangguan D, Ahuja S, Stefanescu DM (1992) An analytical model for the interaction between an insoluble particle and an advancing solid/liquid interface. Metall Trans A 23(2):669–680
Sasikumar R, Ramamohan TR (1991) Distortion of the temperature and solute concentration fields due to the presence of particles at the solidification front—effects on particle pushing. Acta Metall 39(4):517–522
Luk’yanchuk BS, Marine W, Anisimov SI, Simakina GA (1999) Condensation of vapor and nanoclusters formation within the vapor plume produced by nanosecond laser ablation of Si, Ge, and C. In: Proceedings of SPIE 3618, Laser applications in microelectronic and optoelectronic manufacturing IV pp. 434–452
Yan Z, Chrisey DB (2012) Pulsed laser ablation in liquid for micro-/nanostructure generation. J Photochem Photobiol C 13(3):204–223
Wang CX, Liu P, Cui H, Yang GW (2005) Nucleation and growth kinetics of nanocrystals formed upon pulsed-laser ablation in liquid. Appl Phys Lett 87(20):201913–201914
Zheludkevich ML, Gusakov AG, Voropaev AG, Vecher AA, Kozyrski EN, Raspopov SA (2004) Oxidation of Silver by atomic Oxygen. Oxid Met 61(1–2):39–48
Fujita K, Ando D, Uchikoshi M, Mimura K, Isshiki M (2013) New model for low-temperature oxidation of copper single crystal. Appl Surf Sci 276:347–358
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the microscopy facilities available at Advanced Facility for Microscopy and Microanalysis (AFMM), Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malviya, K.D., Chattopadhyay, K. High quality oxide-free metallic nanoparticles: a strategy for synthesis through laser ablation in aqueous medium. J Mater Sci 50, 980–989 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8658-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8658-5