Abstract
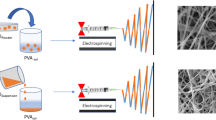
This investigation addresses the morphological, mechanical, and antibacterial evaluation of nanocomposite mats based on poly(d,l-lactide) nanofibers with different zinc oxide nanoparticles (nano-ZnO) concentration, that were elaborated by two techniques, i.e., electrospinning of polymer/ZnO solutions and the combination of electrospinning of polymer solutions with electrospraying of nano-ZnO dispersions. The analysis of the precursory solutions was carried out in order to understand the achieved morphology of nanofibers. The obtained poly(d,l-lactide)/ZnO fibrous mats showed a uniform morphology with an average porosity ca. 55 % and average pore size around 45 μm. The presence of ZnO nanoparticles increased the toughness of the mats, and an optimal nano-ZnO concentration (i.e., 3 wt%) was observed at which the tensile strength and Young’s modulus could be improved. Concerning to the antibacterial properties, a relatively low concentration of nanoparticles provoked a growth inhibition of the Gram-negative Escherichia coli and the Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. The mats have potential features for use as antimicrobial wound dressings.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Wendorff JH, Greiner A (2008) Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 49(26):5603–5621. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2008.09.014
Bhardwaj N, Kundu SC (2010) Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol Adv 28(3):325–347. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.01.004
Zahedi P, Rezaeian I, Ranaei-Siadat S-O, Jafari S-H, Supaphol P (2009) A review on wound dressings with an emphasis on electrospun nanofibrous polymeric bandages. Polym Adv Technol 21(2):77–95. doi:10.1002/pat.1625
Jaworek A, Krupa A, Lackowski M, Sobczyk AT, Czech T, Ramakrishna S, Sundarrajan S, Pliszka D (2009) Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques for nanocomposite non-woven fabric production. Fibres & Textiles in Eastern Europe 17(4):77–81
Martins A, Reis RL, Neves NM (2008) Electrospinning: processing technique for tissue engineering scaffolding. Int Mater Rev 53(5):257–274. doi:10.1179/174328008x353547
Espitia PJP, NdFF Soares, JSdR Coimbra, Andrade NJ, Cruz RS, Medeiros EAA (2012) Zinc Oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, antimicrobial activity and food packaging applications. Food Bioprocess Technol 5(5):1447–1464. doi:10.1007/s11947-012-0797-6
Huh AJ, Kwon YJ (2011) “Nanoantibiotics”: a new paradigm for treating infectious diseases using nanomaterials in the antibiotics resistant era. J Controlled Release 156(2):128–145. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.07.002
Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Ashkarran AA, DJd Aberasturi, IRd Larramendi, Rojo T, Serpooshan V, Parak WJ, Mahmoudi M (2012) Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol 30(10):499–511
Wang ZL (2004) Zinc Oxide Nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J Phys: Condens Matter 16:829–858. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/16/25/R01
Yu W, Lan C-H, Wang S-J, Fang P-F, Sun Y-M (2010) Influence of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the crystallization behavior of electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) nanofiber. Polymer 51:2403–2409. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2010.03.024
Ashrafi F, Babanejad SA (2012) Investigation on synthesis of zinc oxide-polyethylene composite nanofibers by electrospinning method. Res J Appl Sci, Eng Technol 4(18):3386–3390
Kayaci F, Ozgit-Akgun C, Donmez I, Biyikli N, Uyar T (2012) Polymer-inorganic core-shell nanofibers by electrospinning and atomic layer deposition: flexible nylon-ZnO core-shell nanofiber mats and their photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(11):6185–6194. doi:10.1021/am3017976
Vitchuli N, Shi Q, Nowak J, Kay K, Caldwell JM, Breidt F, Bourham M, McCord M, Zhang X (2011) Multifunctional ZnO/Nylon 6 nanofiber mats by an electrospinning–electrospraying hybrid process for use in protective applications. Sci Technol Adv Mater 12(5):055004. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/12/5/055004
Shalumon KT, Anulekha KH, Nair SV, Chennazhi KP, Jayakumar R (2011) Sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol)/nano ZnO composite nanofibers for antibacterial wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol 49(3):247–254. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.04.005
Son B, Yeom B-Y, Song SH, Lee C-S, Hwang TS (2009) Antibacterial electrospun chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers containing silver nitrate and titanium dioxide. J Appl Polym Sci 111(6):2892–2899. doi:10.1002/app.29233
Anitha S, Brabu B, Thiruvadigal DJ, Gopalakrishnan C, Natarajan TS (2012) Optical, bactericidal and water repellent properties of electrospun nano-composite membranes of cellulose acetate and ZnO. Carbohydr Polym 87(2):1065–1072. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.08.030
Augustine R, Malik HN, Singhal DK, Mukherjee A, Malakar D, Kalarikkal N, Thomas S (2014) Electrospun polycaprolactone/ZnO nanocomposite membranes as biomaterials with antibacterial and cell adhesion properties. J Polym Res 21(3):1–17. doi:10.1007/s10965-013-0347-6
Augustine R, Dominic EA, Reju I, Kaimal B, Kalarikkal N, Thomas S (2014) Electrospun polycaprolactone membranes incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles as skin substitutes with enhanced fibroblast proliferation and wound healing. RSC Advances 4(47):24777. doi:10.1039/c4ra02450h
Garlotta D (2001) A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J Polym Environ 9(2):63–84
Gupta B, Revagade N, Hilborn J (2007) Poly(lactic acid) fiber: an overview. Prog Polym Sci 32(4):455–482. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.01.005
Lasprilla AJ, Martinez GA, Lunelli BH, Jardini AL, Filho RM (2012) Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices - a review. Biotechnol Adv 30(1):321–328. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.06.019
Rasal RM, Janorkar AV, Hirt DE (2010) Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci 35(3):338–356. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.12.003
Shameli K, Ahmad MB, Yunus WMZW, Ibrahim NA, Rahman RA, Jokar M, Darroudi M (2010) Silver/poly (lactic acid) nanocomposites: preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Int J Nanomed 5:573–579
Buzarovska A, Grozdanov A (2012) Biodegradable poly(L-lactic acid)/TiO2 nanocomposites: thermal properties and degradation. J Appl Polym Sci 123(4):2187–2193. doi:10.1002/app.34729
Fukushima K, Abbate C, Tabuani D, Gennari M, Camino G (2009) Biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) and its nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab 94(10):1646–1655. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2009.07.001
Song M, Pan C, Li J, Wang X, Gu Z (2006) Electrochemical Study on Synergistic Effect of the Blending of Nano TiO2 and PLA Polymer on the Interaction of Antitumor Drug with DNA. Electroanalysis 18(19–20):1995–2000. doi:10.1002/elan.200603613
Yang T, Wu D, Lu L, Zhou W, Zhang M (2011) Electrospinning of polylactide and its composites with carbon nanotubes. Polym Compos 32(8):1280–1288. doi:10.1002/pc.21149
Ji X, Wang D, Guo L, Jin L, Yang W, Wang T, He N Effect of ZnO on the mechanical properties of poly(L-lactide)/zinc oxide blends prepared by electrospinning. In: 243rd ACS National Meeting & Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA, 2012. American Chemical Society
Ramier J, Bouderlique T, Stoilova O, Manolova N, Rashkov I, Langlois V, Renard E, Albanese P, Grande D (2014) Biocomposite scaffolds based on electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) nanofibers and electrosprayed hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C 38 (0):161-169. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.01.046
Barreto G, Morales G, López-Quintanilla ML (2013) Microwave assisted synthesis of zno nanoparticles: effect of precursor reagents, temperature, irradiation time and additives on nano-zno morphology development. J Mater 478681:1–11. doi:10.1155/2013/478681
Zhou S, Zheng X, Yu X, Wang J, Weng J, Li X, Feng B, Yin M (2007) Hydrogen bonding interaction of poly(d, l-lactide)/hydroxyapatite nanocomposites. Chem Mater 19(2):247–253
Ortíz-Rodríguez E (2013) Polymer Rheology. In: Saldivar-Guerra E, Vivaldo-Lima E (eds) Handbook of polymer synthesis, characterization, and processing. Wiley, Hoboken
Tiwari SK, Venkatraman SS (2012) Importance of viscosity parameters in electrospinning: of monolithic and core–shell fibers. Mater Sci Eng, C 32(5):1037–1042. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2012.02.019
Ck Sen (2009) Wound healing essentials: let there be oxygen. Wound Repair Regen 17(1):1–18
Fu S-Y, Feng X-Q, Lauke B, Mai Y-W (2008) Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos B Eng 39(6):933–961. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2008.01.002
Jeong JS, Moon JS, Jeon SY, Park JH, Alegaonkar PS, Yoo JB (2007) Mechanical properties of electrospun PVA/MWNTs composite nanofibers. Thin Sol Films 515(12):5136–5141. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2006.10.058
Brayner R, Ferrari-Iliou R, Brivois N, Djediat S, Benedetti MF, Fiévet F (2006) Toxicological impact studies based on escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine zno nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett 6(4):866–870
Amna T, Hassan MS, Barakat NA, Pandeya DR, Hong ST, Khil MS, Kim HY (2012) Antibacterial activity and interaction mechanism of electrospun zinc-doped titania nanofibers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(2):743–751. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3459-0
Ts P, Lakshmanan VK, Raj M, Biswas R, Hiroshi T, Nair SV, Jayakumar R (2013) Evaluation of wound healing potential of beta-chitin hydrogel/nano zinc oxide composite bandage. Pharm Res 30(2):523–537. doi:10.1007/s11095-012-0898-y
Lee S (2009) Multifunctionality of layered fabric systems based on electrospun polyurethane/zinc oxide nanocomposite fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 114(6):3652–3658. doi:10.1002/app.30778
Acknowledgements
The authors thank CONACyT (México) for providing H. Rodríguez-Tobías with a Ph.D. Grant as well as a financial support for the research stay in the ICMPE (Thiais, France). The authors also thank Jesús Cepeda, Myriam Lozano, María Luisa López (CIQA, México), and Marie-France Trichet (ICMPE, France) for their technical assistance in issues related to electron microscopy characterization, as well as Enrique Jiménez and Arely Velazquez (CIQA, México) for the facilities concerning viscosity measurements, and finally Jesús Quiróz and Gabriela Padrón (CIQA, México) for their technical support in the evaluation of the mechanical and antibacterial properties, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Tobías, H., Morales, G., Ledezma, A. et al. Novel antibacterial electrospun mats based on poly(d,l-lactide) nanofibers and zinc oxide nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 49, 8373–8385 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8547-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8547-y