Abstract
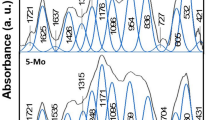
In this study, we have synthesized multi-component 10Li2O–(30 − x)Sb2O3–40GeO2–20PbO:x MoO3 (with five values of x ranging from 1.0 to 9.0) and investigated dielectric properties over a frequency range of 102–106 Hz and in the temperature range 30–300 °C of these samples. The evaluated dielectric parameters include dielectric constant, ε′(ω); ac conductivity, σ ac; and electric modulus, M(ω). The results were interpreted with the aid of the experimental data on optical absorption, IR, Raman, and ESR spectroscopy. The analysis of the results of spectroscopic studies have indicated that a considerable proportion of molybdenum ions reduce to Mo5+ state, form molybdenyl complexes, occupy octahedral positions, act as modifiers, and create dangling bonds in the glass network. The concentration of such molybdenyl complexes seemed to be increasing with increase in the concentration of MoO3. The temperature dispersion of real part of dielectric constant, ε′(ω), has been analyzed using space charge polarization model. The frequency and temperature dependence of the dielectric loss parameters have exhibited relaxation character. The relaxation effects have been attributed to molybdenyl complexes and to the divalent lead ions. Electrical conductivity exhibited an increasing trend and the activation energy showed a decreasing trend with increase in the concentration of MoO3. The increase of conductivity is attributed to (i) the increasing concentration of polaron Mo5+–Mo6+ pairs and (ii) increase in the concentration of dangling bonds in the glass network that causes the substantial decrement in jump distance for Li+ ions, which contribute to ionic conductivity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rada S, Culea E, Chelcea R, Rada M, Bot A, Aldea N, Rednic V (2013) Physical properties and electrochemical performance of molybdenum–lead–germanate glasses and glass ceramics. Ceram Int 39:1403–1411
El Batal FH, Abdelghany AM, Elwan RL (2011) Structural characterization of gamma irradiated lithium phosphate glasses containing variable amounts of molybdenum. J Mol Struct 1000:103–108
Padmanabham A, Ravi Kumar V, Satyanarayana T, Veeraiah N (2009) Induced crystallization and the physical properties of PbO–Sb2O3–As2O3: MoO3 glass system. J Phys Chem Solids 70:669–679
Hussain Z (2002) Optical and electrochromic properties of annealed lithium–molybdenum–bronze thin films. J Electron Mater 31:615–630
Doweidar H (2011) Considerations on the structure and physical properties of B2O3–SiO2 and GeO2–SiO2 glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 357:1665–1670
Nalin M, Poulain M, Ribeiro JL, Messaddeq Y (2001) Antimony oxide based glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 284:110–116
Satyanarayana T, Kityk IV, Gandhi Y, Ravi Kumar V, Kuznik W, Piasecki M, Valentie MA, Veeraiah N (2010) Optically induced effects in nano-crystallized PbO–Sb2O3–B2O3:Pr2O3 glasses. J Alloy Compd 500:9–15
Raghavaiah BV, Laxmikanth C, Veeraiah N (2004) Spectroscopic studies of titanium ions in PbO–Sb2O3:As2O3 glass system. Opt Commun 235:341–349
Irimpan L, Krishnan B, Nampoori VPN, Radhakrishnan P (2008) Nonlinear optical characteristics of nanocomposites of ZnO–TiO2–SiO2. Opt Mater 31:361–365
Zelniok D, Cramer C, Eckert H (2007) Structure/property correlations in ion-conducting mixed-network former glasses: solid-state NMR studies of the system Na2O–B2O3–P2O5. Chem Mater 19:3162–3170
Vladimír L, Marcel P, Marian K, Viera T, Fayçal G (2013) Electrical, dielectric and optical properties of Sb2O3–PbCl2–MoO3 glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 377:66–69
Song J, Chen G, Yuan C, Yang Y (2014) Effect of the Sr/Ba ratio on the microstructures and dielectric properties of SrO–BaO–Nb2O5–B2O3 glass–ceramics. Mater Lett 117:7–9
Pavić L, Narasimha Rao N, Moguš-Milanković A, Šantić A, Ravi Kumar V, Piasecki M, Kityk IV, Veeraiah N (2014) Physical properties of ZnF2–PbO–TeO2:TiO2 glass ceramics—Part III dielectric dispersion and ac conduction phenomena. Ceram Int 40:5989–5996
Balaji Rao R, Gopal NO, Veeraiah N (2004) Studies on the influence of V2O5 on dielectric relaxation and ac conduction phenomena of Li2O–MgO–B2O3 glass system. J Alloy Compd 368:25–37
Vijay R, Ramesh Babu P, Raghavaiah BV, Vinaya Teja PM, Piasecki M, Veeraiah N, Krishna Rao D (2014) Influence of modifier oxide on dielectric dispersion and a.c. conduction phenomena of Li2O–Sb2O3–GeO2 glass system. J Non-Cryst Solids 386:67–75
Umesaki N, Brunier TM, Wright AC, Hannon AC, Sinclair RN (1995) Neutron scattering from PbO–GeO2 glasses. Physica B 213:490–492
Alderman OLG, Hannon AC, Holland D, Umesaki N (2014) On the germanium–oxygen coordination number in lead germanate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 386:56–60
Nanba T, Miyaji T, Takada J, Osaka A, Miura Y, Yasui I (1994) Computer simulation on the structure and vibrational spectra in GePbOF glass. J Non-Cryst Solids 177:131–136
Ghigna P, Mustarelli P, Tomasi C, Quartarone E, Scavini M, Speghini A, Bettinelli M (2002) A combined nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray absorption fine structure study on the local structures of Ge and Pb in PbO–GeO2 glasses and their relationships with thermal properties and devitrification products. Phys Chem B 106:9802–9809
Ribeiro SJL, Dexpertghys J, Piriou B, Mastelaro VR (1993) Structural studies in lead germanate glasses: EXAFS and vibrational spectroscopy. J Non-Cryst Solids 159:213–221
Rada S, Culea E (2011) Structural and optical properties in gadolinium–aluminum–lead–germanate quaternary glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 357:1724–1728
Rada S, Chelcea R, Culea E (2011) Experimental and theoretical investigations on the structure-properties interrelationship of the gadolinium–vanadate–germanate glasses. J Mol Model 17:165–171
Rada M, Maties V, Culea M, Rada S, Culea E (2010) Dual role of the six-coordinated molybdenum and lead ions in novel of photochromic properties of the molybdenum–lead–borate glasses. Spectrochim Acta A 75:507–510
Böttcher CJF, Bordewijk P (1978) Theory of electrical polarization. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Krishna Mohan N, Rami Reddy M, Veeraiah N (2008) Spectroscopic and dielectric studies on MnO doped PbO–Nb2O5–P2O5 glass system. J Alloy Compd 458:66–76
Filipič C, Moguš-Milanković A, Pavić L, Srilatha K, Veeraiah N, Levstik A (2012) Polaronic behavior of MnO doped LiI–AgI–B2O3 glass. J Appl Phys 112:073705–073709
Srinivasa Reddy M, Prasad SVGVA, Veeraiah N (2007) Valence and coordination of chromium ions in ZnO–Sb2O3–B2O3 glass system by means of spectroscopic and dielectric relaxation studies. Phys Status Solidi A 204:816–832
Vinaya Teja PM, Rajyasree Ch, Murali Krishna SB, Tirupataiah Ch, Krishna Rao D (2012) Effect of some VA group modifiers on R2O3 (R = Sb, Bi)–ZnF2–GeO2 glasses doped with CuO by means of spectroscopic and dielectric investigations. Mater Chem Phys 133:239–248
Galeener FL, Geissberger AE, Ogar GW Jr, Loehman RE (1983) Vibrational dynamics in isotopically substituted vitreous GeO2. Phys Rev B 28:4768–4773
Beattie IR, Livingston KMS, Renolds DJ (1970) Single-crystal Raman spectra of arsenolite (As4O6) and senarmonite (Sb4O6). The gas-phase Raman spectra of P4O6, P4O10, and As4O6. J Chem Soc A:449–451
Baia L, Iliescu T, Simonb S, Kiefer W (2001) Raman and IR spectroscopic studies of manganese doped GeO2–Bi2O3 glasses. J Mol Struct 599:9–13
Srinivasa Reddy M, Sridhar Raja VLN, Veeraiah N (2007) Molybdenum ion as a structural probe in PbO–Sb2O3–B2O3 glass system by means of dielectric and spectroscopic investigations. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 37:203–211
Mogus-Milankovic A, Santic A, Gajovic A, Day DE (2003) Spectroscopic investigation of MoO3–Fe2O3–P2O5 and SrO–Fe2O3–P2O5 glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 325:76–84
Rada S, Chelcea R, Rada M, Bot A, Aldea N, Rednic V, Culea E (2013) Electrochemical characterization and structure of tungsten–lead–germanate glasses and glass ceramics. Electrochim Acta 109:82–88
Dubois B, Videau JJ, Portier J (1986) Structural approach of the (xPbCl2–(1 − x)Sb2O3) glass system. J Non-Cryst Solids 88:355–365
Miller PJ, Cody CA (1982) Infrared and Raman investigation of vitreous antimony trioxide. Spectrochim Acta A 38:555–559
Raghavaiah BV, Veeraiah N (2003) The improved glass forming ability and some physical properties of PbO–Sb2O3:Cr2O3 glasses with As2O3 as additive. Phys Status Solidi A 199:389–402
Syam Prasad P, Srinivasa Reddy M, Ravi Kumar V, Veeraiah N (2007) Spectroscopic and dielectric studies on PbO–MoO3–B2O3 glasses incorporating small concentrations of TiO2. Philos Mag 87:5763–5787
Morinaga K, Yoshida H, Takebe H (1994) Compositional dependence of absorption spectra of Ti3+ in silicate, borate, and phosphate glasses. J Am Ceram Soc 77:3113–3118
Iordanova R, Dimitriev Y, Dimitrov V, Kassabov S, Klissurski D (1998) Glass formation and structure in the system MoO3–Bi2O3–Fe2O3. J Non-Cryst Solids 231:227–233
Rada M, Chelcea R, Rada S, Rus L, Dura N, Ristoiu T, Rusu T, Culea E (2013) Effect of aluminum oxide codoping on copper–lead–germanate glasses. Spectrochim Acta A 102:414–418
Calas G, Le Grand M, Galoisy L, Ghaleb D (2003) Structural role of molybdenum in nuclear glasses: an EXAFS study. J Nucl Mater 322:15–20
Cozar O, Magdas DA, Ardelean I (2008) EPR study of molybdenum–lead–phosphate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 354:1032–1035
Chowdari BVR, Radha Krishnan K (1989) Ionic conductivity studies of the vitreous Li2O:P2O5:Ta2O5 system. J Non-Cryst Solids 108:323–332
Selvaraj U, Rao KJ (1988) ESR and optical studies of Mo5+ and W5+ ions in phosphomolybdate and phosphotungstate glasses. Chem Phys 123:141–150
Cozar O, Ardelean I, Simon S, David L (1993) ESR studies of Mo5+ ions in potassium–borate and soda–phosphate glasses. Solid State Commun 85:461–465
Boudlich D, Haddad M, Nadiri A, Berger R, Kliava J (1998) Mo5+ ions as EPR structural probes in molybdenum phosphate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 224:135–142
Bals A, Kliava J (1983) Simulations of EPR spectra for d1 ions with distributed spin Hamiltonian parameters. J Magn Reson 53:243–258
Nagarjuna M, Satyanarayana T, Ravi Kumar V, Veeraiah N (2009) Ag concentration dependent transport properties of LiF–MoO3–P2O5 glasses. Physica B 404:3748–3755
Srinivasarao G, Veeraiah N (2002) Characterization and physical properties of PbO–As2O3 glasses containing molybdenum ions. J Solid State Chem 166:104–117
Durga DK, Veeraiah N (2001) Study on ZnF2–P2O5–TeO2 glass system by dielectric properties, IR spectra and differential thermal analysis. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 39:382–391
Veerabhadra Rao A, Laxmikanth C, Appa Rao B, Veeraiah N (2006) Dielectric relaxation and a.c. conduction phenomena of PbO–PbF2–B2O3 glasses doped with FeO. J Phys Chem Solids 67:2263–2274
Satyanarayana T, Kityk IV, Piasecki M, Bragiel P, Brik MG, Gandhi Y, Veeraiah N (2009) Structural investigations on PbO–Sb2O3–B2O3: CoO glass ceramics by means of spectroscopic and dielectric studies. J Phys Condens Matter 21:245104–245112
Langar A, Sdiri N, Elhouichet H, Ferid M (2014) Conductivity and dielectric behavior of NaPO3–ZnO–V2O5 glasses. J Alloy Compd 590:380–387
Xue S, Wang J, Liu S, Zhang W, Tang L, Shen B, Zhai J (2014) Effect of the Ba/Na ratio on the microstructure and dielectric properties of (BaO, Na2O)–Nb2O5–SiO2 glass–ceramics. Ceram Int 40:7495–7499
Szreder NA, Barczyński RJ, Karczewski J, Gazda M (2014) Electrical properties and structure of lead–borate glass containing iron ions. Solid State Ionics. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2014.01.042
Mukherjee S, Pal AK (2008) Size-dependent magnetic properties of VO2 nanocrystals dispersed in a silica matrix. J Phys Condens Matter 20:255202–255211
Gajovic A, Santic A, Djerdj I, Tomasic N, Mogus-Milankovic A, Sheng SuD (2009) Structure and electrical conductivity of porous zirconium titanate ceramics produced by mechanochemical treatment and sintering. J Alloy Compd 479:525–531
Srikumar T, Srinvasa Rao Ch, Gandhi Y, Venkatramaiah N, Ravikumar V, Veeraiah N (2011) Dielectric and spectroscopic properties of Li2O–Nb2O5–ZrO2–SiO2 glass system crystallized with V2O5. J Phys Chem Solids 72:190–200
Naresh P, Naga Raju G, Ravi Kumar V, Piasecki M, Kiytyk IV, Veeraiah N (2014) Optical and dielectric features of zinc oxy fluoro borate glass ceramics with TiO2 as crystallizing agent. Ceram Int 40:2249–2260
Ting W, Yongping P, Chen K (2013) Dielectric relaxation behavior and energy storage properties in Ba0.4Sr0.6Zr0.15Ti0.85O3 ceramics with glass additives. Ceram Int 39:6787–6793
Elliott SR (1987) Physics of amorphous materials. Adv Phys 36:135
Cramer C, Funke K, Roling B, Saatkamp T, Wilmer D, Ingram MD, Pradel A, Ribes M, Taillades G (1996) Ionic and polaronic hopping in glass. Solid State Ionics 86:481–486
Austin IG, Mott NF (1969) Polarons in crystalline and non-crystalline materials. Adv Phys 18:41–102
Acknowledgements
The authors namely R. Vijay and P. Ramesh Babu are thankful to the University Grants Commission (U.G.C), New Delhi, India for awarding research fellowship under meritorious student scheme. The authors are also grateful to Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. India, for the financial support through FIST programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vijay, R., Ramesh Babu, P., Gandhi, Y. et al. Molybdenum ion: a structural probe in lithium–antimony–germanate glass system by means of dielectric and spectroscopic studies. J Mater Sci 49, 6203–6216 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8345-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8345-6