Abstract
It is now well established that processing by equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) leads to grain refinement and produces materials having the potential for exhibiting extensive superplastic flow at elevated temperatures. High-pressure torsion (HPT) is also an effective procedure for refining the grain sizes of polycrystalline metals to the submicrometer or even the nanometer level, and recent results show that this processing method also gives materials that exhibit excellent superplastic characteristics. This report examines the various publications describing superplasticity in metallic alloys processed by HPT. A comprehensive tabulation is presented listing all of the results to date showing true superplastic elongations of at least 400 % after processing by HPT. Examples of superplastic elongations are described for tensile tests conducted using specimens cut from either disk or ring samples. An analysis shows that the flow behavior of various Al and Mg alloys is in good agreement with the predicted flow behavior for conventional superplastic materials.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langdon TG (2009) Seventy-five years of superplasticity: historic developments and new opportunities. J Mater Sci 44:5998–6010
Barnes AJ (2007) Superplastic forming 40 years and still growing. J Mater Eng Perform 16:440–454
Langdon TG (1982) The mechanical properties of superplastic materials. Metall Trans A 13A:689–701
Langdon TG (1994) An evaluation of the strain contributed by grain boundary sliding in superplasticity. Mater Sci Eng A 174:225–230
Falk LKL, Howell PR, Dunlop GL, Langdon TG (1986) The role of matrix dislocations in the superplastic deformation of a copper alloy. Acta Metall 34:1203–1214
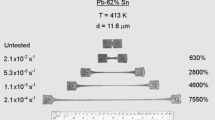
Valiev RZ, Langdon TG (1993) An investigation of the role of intragranular dislocation strain in the superplastic Pb–62 % Sn eutectic alloy. Acta Metall Mater 41:949–954
Xun Y, Mohamed FA (2003) Slip-accommodated superplastic flow in Zn–22 wt% Al. Phil Mag 83:2247–2266
Langdon TG (1994) A unified approach to grain boundary sliding in creep and superplasticity. Acta Metall Mater 42:2437–2443
Valiev RZ, Estrin Y, Horita Z, Langdon TG, Zehetbauer MJ, Zhu YT (2006) Producing bulk ultrafine-grained materials by severe plastic deformation. JOM 58(4):33–39
Valiev RZ, Langdon TG (2006) Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog Mater Sci 51:881–981
Zhilyaev AP, Langdon TG (2008) Using high-pressure torsion for metal processing: fundamentals and applications. Prog Mater Sci 53:893–979
Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2007) Principles of superplasticity in ultrafine-grained materials. J Mater Sci 42:1782–1796
Valiev RZ, Kaibyshev OA, Kuznetsov RI, Musalimov RSh, Tsenev NK (1988) Low-temperature superplasticity of metallic materials. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR (Proc USSR Acad Sci) 301:864–866
Langdon TG (2007) Ultrafine-grained materials: a personal perspective. Int J Mater Res 98:251–254
Wang J, Horita Z, Furukawa M, Nemoto M, Tsenev NK, Valiev RZ, Ma Y, Langdon TG (1993) An investigation of ductility and microstructural evolution in an Al–3 % Mg alloy with submicron grain size. J Mater Res 8:2810–2818
Valiev RZ, Krasilnikov NA, Tsenev NK (1991) Plastic deformation of alloys with submicron-grained structure. Mater Sci Eng A 137:35–40
Valiev RZ, Korznikov AV, Mulyukov RR (1993) Structure and properties of ultrafine-grained materials produced by severe plastic deformation. Mater Sci Eng A 168:141–148
Ma Y, Furukawa M, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Valiev RZ, Langdon TG (1996) Significance of microstructural control for superplastic deformation and forming. Mater Trans JIM 37:336–339
Valiev RZ, Salimonenko DA, Tsenev NK, Berbon PB, Langdon TG (1997) Observations of high strain rate superplasticity in commercial aluminum alloys with ultrafine grain sizes. Scripta Mater 37:1945–1950
Higashi K, Mabuchi M, Langdon TG (1996) High-strain-rate superplasticity in metallic materials and the potential for ceramic materials. ISIJ Intl 36:1423–1438
Zhilyaev AP, Lee S, Nurislamova GV, Valiev RZ, Langdon TG (2001) Microhardness and microstructural evolution in pure nickel during high-pressure torsion. Scripta Mater 44:2753–2758
Zhilyaev AP, Nurislamova GV, Kim BK, Baró MD, Szpunar JA, Langdon TG (2003) Experimental parameters influencing grain refinement and microstructural evolution during high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 51:753–765
Wongsa-Ngam J, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2013) A comparison of microstructures and mechanical properties in a Cu–Zr alloy processed using different SPD techniques. J Mater Sci 48:4653–4660
Valiev RZ, Ivanisenko YuV, Rauch EF, Baudelet B (1996) Structure and deformation behaviour of Armco iron subjected to severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater 44:4705–4712
Wetscher F, Vorhauer A, Stock R, Pippan R (2004) Structural refinement of low alloyed steels during severe plastic deformation. Mater Sci Eng A 387–389:809–816
Wetscher F, Pippan R, Sturm S, Kauffmann F, Scheu C, Dehm G (2006) TEM investigations of the structural evolution in a pearlitic steel deformed by high-pressure torsion. Metall Mater Trans A 37A:1963–1968
Langdon TG (2013) Twenty-five years of ultrafine-grained materials: achieving exceptional properties through grain refinement. Acta Mater 61:7035–7059
Kawasaki M (2014) Different models of hardness evolution in ultrafine-grained materials processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 49:18–34
Loucif A, Figueiredo RB, Kawasaki M, Baudin T, Brisset F, Chemam R, Langdon TG (2012) Effect of aging on microstructural development in an Al–Mg–Si alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 47:7815–7820
An XH, Lin QY, Wu SD, Zhang ZF, Figueiredo RB, Gao N, Langdon TG (2011) The influence of stacking fault energy on the mechanical properties of nanostructured Cu and Cu–Al alloys processed by high-pressure torsion. Scripta Mater 64:954–957
An XH, Wu SD, Zhang ZF, Figueiredo RB, Gao N, Langdon TG (2012) Enhanced strength-ductility synergy in nanostructured Cu and Cu–Al alloys processed by high-pressure torsion and subsequent annealing. Scripta Mater 66:227–230
Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2011) Developing superplasticity and a deformation mechanism map for the Zn–Al eutectoid alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 528:6140–6145
Ishikawa H, Mohamed FA, Langdon TG (1975) The influence of strain rate on ductility in the superplastic Zn–22 % Al eutectoid. Phil Mag 32:1269–1271
Langdon TG (1991) The physics of superplastic deformation. Mater Sci Eng A 137:1–11
Langdon TG (1982) Fracture processes in superplastic flow. Metal Sci 16:175–183
Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2008) Grain boundary sliding in a superplastic zinc-aluminum alloy processed using severe plastic deformation. Mater Trans 49:84–89
Furukawa M, Iwahashi Y, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1998) The shearing characteristics associated with equal-channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A 257:328–332
Morrison WB (1968) Elongation of superplastic alloys. Trans TMS-AIME 242:2221–2227
Ahmed MMI, Langdon TG (1977) Exceptional ductility in the superplastic Pb–62 pct Sn eutectic. Metall Trans A 8A:1832–1833
Ma Y, Langdon TG (1994) Factors influencing the exceptional ductility of a superplastic Pb–62 Sn alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 25A:2309–2311
Zhao YH, Guo YZ, Wei Q, Dangelewicz AM, Xu C, Zhu YT, Langdon TG, Zhou YZ, Lavernia EJ (2008) Influence of specimens dimensions on the tensile behavior of ultrafine-grained Cu. Scripta Mater 59:627–630
Zhao YH, Guo YZ, Wei Q, Topping TD, Dangelewicz AM, Zhu YT, Langdon TG, Lavernia EJ (2009) Influence of specimen dimensions and strain measurement methods on tensile stress-strain curves. Mater Sci Eng A 525:68–77
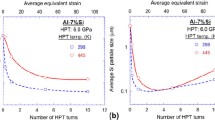
Kawasaki M, Foissey J, Langdon TG (2013) Development of hardness homogeneity and superplastic behavior in an aluminum-copper eutectic alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 561:118–125
Harai Y, Kai M, Kaneko K, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2008) Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of AZ61 magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Trans 49:76–83
Erbel S (1979) Mechanical properties and structure of extremely strain-hardened copper. Metals Technol 6:482–486
Saunders I, Nutting J (1984) Deformation of metals to high strains using combination of torsion and compression. Metal Sci 18:571–575
Harai Y, Edalati K, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2009) Using ring samples to evaluate the processing characteristics in high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 57:1147–1153
Mishra RS, Valiev RZ, McFadden SX, Islamgaliev RK, Mukherjee AK (2001) High-strain-rate superplasticity from nanocrystalline Al alloy 1420 at low temperatures. Phil Mag A 81:37–48
Islamgaliev RK, Yunusova NF, Valiev RV (2006) The influence of the SPD temperature on superplasticity of aluminium alloys. Mater Sci Forum 503–504:585–590
Perevezentsev VN, Shcherban MYu, Murashkin MYu, Valiev RZ (2007) High-strain-rate superplasticity of nanocrystalline aluminum alloy 1570. Tech Phys Lett 33:648–650
Dobatkin SV, Bastarache EN, Sakai G, Fujita T, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2005) Grain refinement and superplastic flow in an aluminum alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 408:141–146
Xu C, Dobatkin SV, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2009) Superplastic flow in a nanostructured aluminum alloy produced using high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 500:170–175
Sabbaghianrad S, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2012) Microstructural evolution and the mechanical properties of an aluminum alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 47:7789–7795
Sakai G, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2005) Grain refinement and superplasticity in an aluminum alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 393:344–351
Horita Z, Langdon TG (2008) Achieving exceptional superplasticity in a bulk aluminum alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Scripta Mater 58:1029–1032
Torbati-Sarraf SA, Langdon TG (2014) Mechanical properties of ZK60 magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Adv Mater Research (in press)
Kai M, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2008) Developing grain refinement and superplasticity in a magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A 488:117–124
Kulyasova OB, Islamgaliev RK, Kil’mametov AR, Valiev RZ (2006) Superplastic behavior of magnesium-based Mg–10 wt% Gd alloy after severe plastic deformation by torsion. Phys Met Metall 101:585–590
Mishra RS, Valiev RZ, McFadden SX, Mukherjee AK (1998) Tensile superplasticity in a nanocrystalline nickel aluminide. Mater Sci Eng A 252:174–178
Valiev RZ, Song C, McFadden SX, Mukherjee AK, Mishra RS (2001) TEM/HREM observations of nanostructured superplastic Ni3Al. Phil Mag A 81:25–36
Sergueeva AV, Stolyarov VV, Valiev RZ, Mukherjee AK (2000) Enhanced superplasticity in a Ti–6Al–4V alloy processed by severe plastic deformation. Scripta Mater 43:819–824
Sergueeva AV, Stolyarov VV, Valiev RZ, Mukherjee AK (2002) Superplastic behaviour of ultrafine-grained Ti–6A1–4V alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 323:318–325
Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2014) Microstructure development and superplasticity in a Zn–22 % Al eutectoid alloy processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater Sci Forum (in press)
Cho T-S, Lee H-J, Ahn B, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2014) Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties in a Zn–Al eutectoid alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2014.03.026
Kawasaki M, Balasubramanian N, Langdon TG (2011) Flow mechanisms in ultrafine-grained metals with an emphasis on superplasticity. Mater Sci Eng A 528:6624–6629
Mohamed FA, Langdon TG (1974) Deformation mechanism maps based on grain size. Metall Trans 5:2339–2345
Mohamed FA, Langdon TG (1975) Creep at low stress levels in the superplastic Zn 22 % Al eutectoid. Acta Metall 23:117–124
Vagarali SS, Langdon TG (1982) Deformation mechanisms in h.c.p. metals at elevated temperatures—II. Creep behavior of a Mg–0.8 % Al solid solution alloy. Acta Metall 30:1157–1170
Frost HJ, Ashby MF (1982) Deformation-mechanism maps: the plasticity and creep of metals and ceramics. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation of the United States under Grant No. DMR-1160966 and in part by the European Research Council under ERC Grant Agreement No. 267464-SPDMETALS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawasaki, M., Langdon, T.G. Review: achieving superplasticity in metals processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 49, 6487–6496 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8204-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8204-5