Abstract
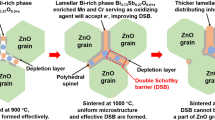
In ceramic materials, special boundaries play the key role in crystal growth. They introduce an abrupt structural and chemical anisotropy, which is readily reflected in an unusual microstructure evolution, whereas their local structure affects the physical properties of polycrystalline materials. These effects, however, can be exploited to tailor the electronic and optical properties of the materials, as demonstrated in this review. The presented topic is related to a preparatory stage of phase transformations, manifested through the evolution of chemically induced structural faults. In non-centrosymmetric structure of ZnO, inversion boundaries (IBs) are the most common type of planar faults that is triggered by the addition of the specific IB-forming dopants (Sb2O3, SnO2, TiO2). In addition to conventional TEM techniques, new methods were developed to resolve crystallography and atomic-scale chemistry of IBs. The absolute orientation of the polar c-axes on both sides of an IB was determined by micro-diffraction, providing the most reliable identification of crystal polarity in non-centrosymmetric crystals. To determine sub-monolayer quantities of dopants on the IB, we developed a special technique of analytical electron microscopy using concentric electron probe (CEP) in EDS or EELS mode, providing more accurate and precise results than any other technique. Knowing the local crystal chemistry of IBs, we were able to design experiments to identify their formation mechanism. IBs nucleate in the early stage of grain growth as a dopant-rich topotaxial 2D reaction product on Zn-terminated surfaces of ZnO grains. Soon after their nucleation, ZnO is epitaxially grown on the inherent 2D phase in an inverted orientation, which effectively starts to dictate anisotropic growth of the infected crystallite. In very short time, the grains with IBs dominate the entire microstructure via IB-induced exaggerated grain growth mechanism. This phenomenon was used to design physical properties of ZnO-based varistor ceramics, whereas the bottom-up approach demonstrated here provides the basic tool for microstructural engineering of functional materials in virtually any system that is prone to the formation of special boundaries.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsuoka M (1971) J Appl Phys 10:736
Inada M (1978) Jpn J Appl Phys 17:1
Gupta TK (1990) J Am Ceram Soc 73:1817
Clarke DR (1999) J Am Ceram Soc 82:485
Stucki F, Greuter F (1990) Appl Phys Lett 57:446
Ramírez MA, Simões AZ, Bueno PR, Márquez MA, Orlandi MO, Varela JA (2006) J Mater Sci 41:6221. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-0589-3
Ramírez MA, Simões AZ, Márquez MA, Maniette Y, Cavalheiro AA, Varela JA (2007) Mater Res Bull 42:1159
Kutty TRN, Ezhilvalavan S (1994) Mater Chem Phys 38:267
Rahaman MN, Lutgard CJ, James AV, Tuttle BA (1990) J Mater Sci 25:737. doi:10.1007/BF00714102
Kobayashi KI, Wada O, Kobayashi M, Takada Y (1998) J Am Ceram Soc 81:2071
Luo J, Wang H, Chiang YM (1999) J Am Ceram Soc 82:916
Kingery WD, Bowen HK, Uhlmann DR (1976) Introduction to ceramics. Wiley, New York, p 460
Kim J, Kimura T, Yamaguchi T (1989) J Mater Sci 24:2581. doi:10.1007/BF01174529
Senda T, Bradt RC (1991) J Am Ceram Soc 74:1296
Ito M, Tanahashi M, Uehara M, Iga A (1997) Jpn J Appl Phys 36:L1460
Hennings DFK, Hartung R, Reijnen PJL (1990) J Am Ceram Soc 73:645
Makovec D, Kolar D, Trontelj M (1993) Mater Res Bull 28:803
Zhang CC, Zhou DX, Lu WZ, Hu YX (2001) J Mater Sci 12:357. doi:10.1023/A:1011245624525
Bernik S, Daneu N, Rečnik A (2004) J Eur Ceram Soc 24:3703
Daneu N, Rečnik A, Bernik S, Kolar D (2000) J Am Ceram Soc 83:3165
Bernik S, Daneu N (2001) J Eur Ceram Soc 21:1879
Nunes SI, Bradt RC (1995) J Am Ceram Soc 78:2469
Bruley J, Bremer U, Kraševec V (1991) J Am Ceram Soc 75:3127
Makovec D, Trontelj M (1994) J Am Ceram Soc 77:1202
Rečnik A, Daneu N, Walther T, Mader W (2001) J Am Ceram Soc 84:2675
Mader W, Rečnik A (1998) Phys Stat Sol (a) 166:381
Haskell BA, Souri SJ, Helfand MA (1999) J Am Ceram Soc 82:2106
Walther T, Daneu N, Rečnik A (2004) Interface Sci 12:267
Walther T (2004) J Microsc 215:191
Yamazaki T, Nakanishi N, Rečnik A, Kawasaki M, Watanabe K, Čeh M, Shiojiri M (2004) Ultramicroscopy 98:305
Walther T, Wolf F, Rečnik A, Mader W (2006) Int J Mater Res 97:934
Pauling L (1940) The nature of the chemical bond. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Gehman WG, Austerman SB (1965) Acta Crystallogr 18:375
Rečnik A, Daneu N, Bernik S (2007) J Eur Ceram Soc 27:1999
Tomlins GW, Routbort JL, Mason TO (2000) J Appl Phys 87:117
Dulub O, Diebold U, Kresse G (2003) Phys Rev Lett 90:016102
Hörlin T, Svensson G, Olson E (1998) J Mater Chem 8:2465
Wolf F, Freitag BH, Mader W (2007) Micron 38:549
Köster-Scherger O, Schmid H, Vanderschäge N, Wolf F, Mader W (2007) J Am Ceram Soc 90:3984
Barf J, Walther T, Mader W (2004) Interface Sci 12:213
Rečnik A, Čeh M, Kolar D (2001) J Eur Ceram Soc 21:2117
Kolar D, Kunaver U, Rečnik A (1998) Phys Stat Sol (a) 166:219
Šturm S, Rečnik A, Čeh M (2001) J Eur Ceram Soc 21:2141
Daneu N, Rečnik A, Bernik S (2003) J Am Ceram Soc 86:1379
Daneu N, Rečnik A, Bernik S (2011) J Am Ceram Soc 94:1619
Lee JS, Wiederhorn SM (2004) J Am Ceram Soc 87:1319
Bernik S, Podlogar M, Daneu N, Rečnik A (2007) Mat Sci Forum 558(559):857
Bernik S, Bernard J, Daneu N, Rečnik A (2007) J Am Ceram Soc 90:3239
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the national research project J2-6453-0106-04: “Nanostructural engineering of semiconducting materials”. The support of the FP7-NMP-2008-CSA-2 project: “Merging atomistic and continuum analysis of nanometer length-scale” (MACAN) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rečnik, A., Bernik, S. & Daneu, N. Microstructural engineering of ZnO-based varistor ceramics. J Mater Sci 47, 1655–1668 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5937-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5937-2