Abstract
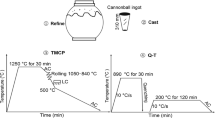
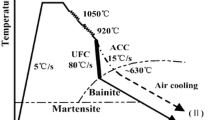
The yield strength and impact energy properties for martensitic steel fabricated by vacuum induction melting are investigated. It is found that the addition of Ti can improve the yield strength property of the martensitic steel after reheat quenching process, which can be attributed to increase in precipitation hardening from formation of TiC precipitates in the martensitic matrix and a superfine sized (~8 μm) grains in the martensitic structure. Moreover, the yield strength can be further enhanced by tempering and reheat quenching process, which can be ascribed to a large amount of freshly nano-sized (1–10 nm) precipitates in the final martensitic structure for martensitic steel-containing Ti. The experimental and theoretical results on the contribution of TiC precipitates to hardening of the martensitic steel are in excellent agreement. In addition, the impact toughness also has been improved along with yield strength followed by the heat treatment, which can be attributed to the high ratio of high-angle grain boundaries after tempering and reheat quenching process.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Allah NM, El-Fadaly MS, Megahed MM, Eleiche AM (2001) J Mater Eng Perform 10:576
Ezugwu EO, Olajire KA (2002) Tribol Lett 12:183
Yilmaz R, Türkyilmazoglu A (2007) Adv Mater Res 23:319
Bhavsar RB, Montani E (1998) Corrosion 98:22
Oliver DA, Harris GT (1952) Iron Steel Inst 43:46
Davies WT, Hall B (1967) Iron Steel Inst 97:561
Angeliu T, Hall EL, Larsen M, Linsebigler A, Mukira C (1999) Inst Mater 708:234
Parameswaran P, Vijayalakshmi M, Shankar P, Raghunathan VS (1992) J Mater Sci 27:5426. doi:10.1007/BF00367811
Martin R, Mari D, Schaller R (2009) Mater Sci Eng A 521–522:117
Song YY, Ping DH, Yin FX, Li XY, Li YY (2010) Mater Sci Eng A 527:614
Bhambri SK (1986) J Mater Sci 21:1741. doi:10.1007/BF01114734
Ikeda S, Sakai T, Fine ME (1977) J Mater Sci 12:675. doi:10.1007/BF00548157
Barani AA, Li F, Romano P, Ponge D, Raabe D (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 463:138
Yaggee FL, Gilbert ER, Styles JW (1969) J Less Common Met 19:39
Baviera P, Harel S, Garem H, Grosbras M (2001) Scr Mater 44:2721
Mani A, Aubert P, Mercier F, Khodja H, Berthier C, Houdy P (2005) Surf Coat Technol 194:190
Li SB, Xiang WH, Zhai HX, Zhou Y (2008) Powder Technol 185:49
Friedman LH, Chrzan DC (1998) Phys Rev Lett 83:2715
Cao JC, Yong QL, Liu QY, Sun XJ (2007) J Mater Sci 42:10080. doi:10.1007/s10853-007-2000-4
Sagaradze VS (1970) Met Sci Heat Treat 12:198
Diaz-Fuentes M, Iza-Mendia A, Gutierrez I (2003) Metall Mater Trans 34A:2505
Wang BH, Kim YG, Lee S, Kim YM, Kim NJ, Yoo JY (2005) Metall Mater Trans 36A:2107
Acknowledgement
This research is supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 program) No. 2010CB630803 and National High-tech R&D Programs (863 programs) No. 2511 and No. 2009AA033401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Shi, J., Cao, W.Q. et al. Improved mechanical properties in Ti-bearing martensitic steel by precipitation and grain refinement. J Mater Sci 46, 6384–6389 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5586-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5586-5