Abstract
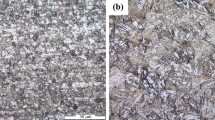
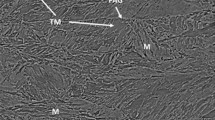
Ball indentation technique (BIT) is employed to study the effect of post-weld heat treatment on the mechanical properties of a high strength low alloy (HSLA) steel and subsequently on the quality of the weldment. Well-defined load-deflection curves and corresponding true stress–strain curves for different zones (base, HAZ, weld) of sectioned sample (top and middle) and their validation with mechanical properties obtained by conventional method established the effectiveness of the present ball indentation (BI) set up. Investigations on microstructure of all the zones have been carried out to find out a correlation with the obtained mechanical properties. Evaluation of the mechanical properties of materials through BIT could characterize the heat-affected zone in weld HSLA steel.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webster PJ (1992) Welding handbook, 8th edn. American Welding Society, Miami
Hara T, Asahi H (2000) Corrosion 56:533
Bala Srinivasan P, Sharkawy SW, Dietzel W (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 385:6. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.03.029
Brass AM, Chêne J (2006) Corros Sci 48:481. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.01.007
Carter TJ, Cornish LA (2001) Eng Fail Anal 8:113. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1350-6307(99)00040-0
Haggag FM, Byun TS, Hong JH, Miraglia PQ, Murty KL (1998) Scr Mater 38:645. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(98)00519-3
Murty KL, Miraglia PQ, Mathew MD, Shah VN, Haggag FM (1999) Int J Pres Ves Pip 76:361. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-0161(99)00006-X
Haggag FM (2001) Residual stress measurement and general non-destructive evaluation. ASME 429:99
Byun TS, Hong JH, Haggag FM, Farrell K, Lee FH (1997) Int J Pres Ves Pip 74:231. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-0161(97)00114-2
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (1992) J Mater Res 7(5):1564
Bolshakov A, Pharr GM (1998) J Mater Res 13(4):1049
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (2004) J Mater Res 19(1):3
Field JS, Swain MV (1995) J Mater Res 10(1):101
Norbury AL, Samuel T (1928) JISI 117:673
Alcala J, Barone AC, Anglanda M (2000) Acta Mater 48:3451. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(00)00140-3
Jang J-I, Choi Y, Lee Y-H, Kim D-J, Kim J-T (2003) J Mater Sci Lett 22:499. doi:https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022926100980
Das G, Ghosh S, Sahay SK, Ranganath VR, Vaze KK (2003) Trans Indian Inst Met 56(5):465
Das G, Ghosh S, Ghosh S (2006) NDT Int 39:155. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2005.06.011
Tabor D (1951) The hardness of metals. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Haggag FM, Namstad RK, Hutton JT, Thomas DL, Swain RL (1990) ASTM 1092, Philadelphia, p 188
Timoshenko S (1934) Theory of elasticity. McGraw Hill, New York
Dieter GE (1998) Mechanical metallurgy. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Singapore
Meyer E (1908) Z Ver Dtsch Ing 52:645
Mathew MD, Murty KL, Rao KBS, Mannan SL (1999) Mater Sci Eng A 264:159. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01098-3
Das G, Ghosh S, Sahay SK, Ranganath VR, Vaze KK (2004) Int J Mater Res Adv Tech Metallkunde 95:1120
Das G, Ghosh S, Ghosh S, Ghosh RN (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 408:158. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2005.07.026
Das G, Ghosh S, Sahay SK (2005) Mater Lett 59(18):2246. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2005.01.074
Das G, Ghosh S, Bose SC, Ghosh S (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 424:326. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.03.011
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Prof. S. P. Mehrotra, Director, National Metallurgical Laboratory (NML), for his encouragement and permission to carry out and publish this work. They are also thankful to Dr. I. Chattoraj and Dr. G. V. S. Murthy of NML for their valuable assistance. One of the authors (Sabita Ghosh) thanks the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), India, for a fellowship to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Pal, T.K., Mukherjee, S. et al. Comparative study of heat-affected zone with weld and base material after post-weld heat treatment of HSLA steel using ball indentation technique. J Mater Sci 43, 5474–5482 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2840-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2840-6