Abstract
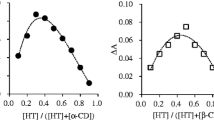
The characterization, inclusion complexation behavior and binding ability of the inclusion complexes of dihydroartemisinin with β-cyclodextrin and its derivatives, sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD), mono[6-(2-aminoethylamino)-6-deoxy]-β-cyclodextrin (en-β-CD) and mono{6-[2-(2-aminoethylamino)ethylamino]-6-deoxy}-β-cyclodextrin (dien-β-CD), were studied using phenolphthalein as a spectral probe. Spectral titration was performed in aqueous buffer solution (pH ca. 10.5) at 25 °C to determine the binding constants. The inclusion complexation behaviors were investigated in both solution and solid state by means of NMR, TG, XRD. The results showed that the water solubility and thermal stability of dihydroartemisinin were significantly increased in the inclusion complex with cyclodextrins (CDs). According to 1H NMR and 2D NMR spectroscopy (ROESY), the A, B rings of dihydroartemisinin can be included into the cavity of CDs. The enhanced binding ability of CDs towards dihydroartemisinin was discussed from the viewpoint of the size/shape-fit concept and multiple recognition mechanism between host and guest.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balter, M., Marshall, E., Vogel, G., Taubes, G., Pennisi, E., Enserink, M.: Special focus of articles on malaria. Science 290, 428–441 (2000)
Klayman, D.: An antimalarial drug from China. Science 228, 1049–1055 (1989)
Luo, X.D., Shen, C.C.: The chemistry, pharmacology, and clinical applications of Qinghaosu (artemisinin) and its derivatives. Med. Res. Rev. 7, 29–52 (1987)
O’Neill, P.M.: A worthy adversary for malaria. Nature 430, 838–839 (2004)
Dhingra, V., Vishweshwar, R.K., Lakshmi, N.M.: Current status of artemisinin and its derivatives as antimalarial drugs. Life Sci. 66, 279–300 (2000)
O’Neill, P.M., Posner, G.H.: A medicinal chemistry perspective on artemisinin and related endoperoxides. J. Med. Chem. 47, 2945–2964 (2004)
Wiesner, J., Ortmann, R., Jomaa, H., Schlitzer, M.: New antimalarial drugs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 42, 5274–5293 (2003)
Meshnick, S.R.: Mechanisms of action, resistance and toxicity. Int. J. Parasitol. 32, 1655–1660 (2002)
Lai, H., Singh, N.P.: Selective cancer cell cytotoxicity from exposure to dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin. Cancer Lett. 91, 41–46 (1995)
Efferth, T., Dunstan, H., Sauerbrey, A., Miyachi, H., Chitambar, C.R.: The anti-malarial artesunate is also active against cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 18, 767–773 (2001)
Efferth, T., Benakis, A., Romero, M.R., Tomicic, M., Rauh, R., Steinbach, D., Stamminger, T.: Enhancement of cytotoxicity of artemisinins toward cancer cells by ferrous iron. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 37, 998–1009 (2004)
Gabriëls, M.J., Plaizier, V.: Design of a dissolution system for the evaluation of the release rate characteristics of artemether and dihydroartemisinin form tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 274, 245–260 (2004)
Uekama, K., Hirayama, F., Irie, T.: Cyclodextrin drug carrier systems. Chem. Rev. 98, 2045–2076 (1998)
Loftsson, T., Järvinen, T.: Cyclodextrins in ophthalmic drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 36, 59–79 (1999)
Loftsson, T., Duchene, D.: Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 329, 1–11 (2007)
Khan, A.R., Forgo, P., Stine, K.J.: Methods for selective modification of cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 98, 1977–1996 (1998)
Liu, Y., Chen, G.-S., Li, L., Zhang, H.-Y., Cao, D.-X., Yuan, Y.-J.: Inclusion complexation and solubilization of paclitaxel by bridged bis (β-cyclodextrin)s containing a tetraethylenepentamine spacer. J. Med. Chem. 46, 4634–4637 (2003)
Yang, B., Yang, L.-J., Lin, J., Chen, Y., Liu, Y.: Binding behaviors of scutellarin with α-, β-, γ-cyclodextrins and their derivatives. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 64, 149–155 (2009)
Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M., Visser, A.J.W.G., van Hoek, A., Nolte, R.J.M., Engbersen, J.F.J., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Interconnective host-guest complexation of β-cyclodextrin-calix[4]arene couples. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 28–33 (1999)
Muhammad, T.A., Vivian, B.S.: Dihydroartemisinin-cyclodextrin complexation: solubility and stability. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 155–165 (2009)
Zhang, X.Y.: Increased stability and solubility of dihydroartemisinin in aqueous solution through the formation of complexes with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 18, 170–176 (2009)
Hitendra, S., SaurabhShah, K., Sanjay, J.: Nasal in situ gel containing hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex of artemether: development and in vitro evaluation. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 70, 49–58 (2011)
Wong, J.W., Yuen, K.H.: Improved oral bioavailability of artemisinin through inclusion complexation with β- and γ-cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 227, 177–185 (2001)
Hermine, Z.-D., Dive, G., Moudachirou, M., Michel, F., Evrard, B.: Understanding the interactions between artemisinin and cyclodextrins: spectroscopic studies and molecular modeling. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 74, 305–315 (2012)
Yang, B., Lin, J., Chen, Y., Liu, Y.: Artemether/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin host–guest system: characterization, phase-solubility and inclusion mode. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17, 6311–6317 (2009)
Yang, B., Wang, J., Huang, R., Zhao, Y.-L., Yang, J.: Binding behavior of artemether/sulfobutyl ether β-cyclodextrin in solution and the solid state. Monatsh. Chem. 143, 235–241 (2012)
Shen, B.-J., Tong, L.-H., Jin, D.-S.: Synthesis and characterization of novel multi-functional host compounds, 3. β-cyclodextrin derivatives bearing schiff base moiety. Synth. Commun. 21, 635–641 (1991)
Liu, Y., Han, B.H., Zhang, Y.M., Chen, R.: Molecular recognition study on supramolecular system (VII). Chin. Sci. Bull. 42, 1189–1192 (1997)
You, C.-C., Zhao, Y.-L., Liu, Y.: Molecular recognition study of β-cyclodextrin and its two derivatives with some aliphatic guests by competitive inclusion method. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 22, 218–222 (2001)
Inoue, Y., Yamamoto, K., Wada, T., Everitt, S., Gao, X.-M.: Inclusion complexation of (cyclo)alkanes and (cyclo)alkanols with 6-O-modified cyclodextrins. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, 1807–1816 (1998)
Ayala-Zavala, J.F., Del-Toro-Sánchez, L., Alvarez-Parrilla, E., González-Aguilar, G.A.: High relative humidity in-package of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables: advantage or disadvantage considering microbiological problems and antimicrobial delivering systems. J. Food Sci. 73, 41–47 (2008)
Liu, Y., Chen, G.-S., Chen, Y., Lin, J.: Inclusion complexes of azadirachtin with native and methylated cyclodextrins: solubilization and binding ability. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13, 4037–4042 (2005)
Schneider, H.J., Hacket, F.: NMR studies of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. Chem. Rev. 98, 1755–1785 (1998)
Vieira, E.K.B., Lázaro, G.S., Conegero, L.S., Almeida, L.E., Barreto, L.S., da Costa, N.B., Gimeneza, I.F.: Sulfadiazine/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin host–guest system: characterization, phase-solubility and molecular modeling. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16, 5788–5794 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NNSFC) (No. 21062009), and the Natural Science Foundation of Yunnan Province (No. 2011FZ059), which are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, D., Yang, B., Zhao, YL. et al. Inclusion complexes of dihydroartemisinin with cyclodextrin and its derivatives: characterization, solubilization and inclusion mode. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 79, 349–356 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-013-0358-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-013-0358-2