Abstract
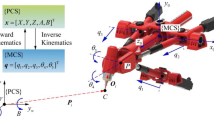
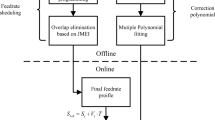
In this paper, a CAD-based trajectory planning scheme for parallel machining robots is introduced using the parametric Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) curves. First, a trajectory is designed via a NURBS curve then, a motion scheduling architecture consisting of time-dependent and constant feedrate profiles is advised to generate the position commands on the represented NURBS curve as the tool path. Using the generated commands, the inverse kinematics is elaborated to obtain the joints motions of the parallel machining robot. This paper investigates the NURBS trajectory generation for a parallel robot with 4(UPS)-PU mechanism as the case study. In order to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, the inverse kinematic results for the parallel machining robot of 4(UPS)-PU is compared with the simulation results obtained from the CATIA software. The results confirmed that the proposed trajectory planning scheme along with the advised motion planning architecture is not only feasible for the parallel machining robots but also yields a smooth trajectory with a satisfactory performance for all the joints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai, G.Q., Hu, M., Guo, C., Li, B., Wang, Q.M.: Development of a robotized grinding machine with tripod linkage. Manuf. Technol. Mach. Tool 435, 4–6 (1998)
Gough, V.E.: Contribution to discussion to papers on research in automobile stability and control and in type performance. Pro Auto Device Instruction Mech. Eng., 392–395 (1957)
Stewart, D.: A platform with six degree of freedom. Proc. In srn. Mech. Engrs. Part 1 180(15), 371–376 (1965)
Cleary, K., Brooks, T.: Kinematics analysis of a novel 6 DOFs parallel manipulator. In: IEEE Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 708–713 (1993)
Salcudean, S.E., Drexel, P.A., Ben-Dov, D., Tayor, A.J., Lawrence, P.D.: A six degree-of-freedom, hydraulic, one person motion simulator. In: IEEE Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2437–2443 (1994)
Fattah, A., Kasaei, G.: Kinematics and dynamics of a parallel manipulator with a new architecture. Robotica 18, 535–543 (2000)
Reboulet, C., Pigeyre, R.: Hybrid control of a 6-DOFs in-parallel actuated micro-manipulator mounted on a scara robot. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 7(1), 10–14 (1992)
Valenti, M.: Machine tools get smarter. ASME Mechanical Engineering 17(11), 70–75 (1995)
Cox, D.J., Tesar, D.: The Dynamic Modeling and Command Signal Formulation for Parallel Multi-Parameter Robotic, Devic Internal Rep. CIMAR, Univ. Florida, Gainesville (1981)
Hunt, K.J.: Structure kinematics of in-parallel actuated robot-arms. Tran. ASME, J. Mech. Trans. Auto Des. 105, 705–712 (1983)
Earl, C.F., Rooney, J.: Some kinematic structure for robot manipulator design. Trans. ASME, J. Mech. Trans. Auto Des. 105, 15–22 (1983)
Merlet, J.P.: Les robot parallels. Hermes, Paris (1990)
Griffis, M., Duffy, J.: A forward displacement analysis of a class of Stewart platform 6(6), 703–720 (1989)
Gosselin, C.M., Sefrioui, J., Richard, M.J.: On the direct kinematics of general spherical three-degree-of-freedom parallel manipulators. In: Proceedings of 22nd ASME Biennial Mechanisms Conference, vol. 45, pp. 7–11, Scottsdale, AZ (1992)
Wang, J., Tan, X.: Analysis and dimensional design of a novel hybrid machine tool. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 43, 647–655 (2003)
Khan, W.A., Hayhurst, D.R., Cannings, C.: Determination of optimal path under approach and exit constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 117(2), 310–325 (1999)
Castelino, K., D’Souza, R., Wright, P.: Toolpath optimization for minimizing airtime during machining. J. Manuf. Syst. 22(3), 173–180 (2003)
DeBoor, C.: A Practical Guide to Splines. Springer, New York (1978)
Rogers, D., Adams, J.A.: Mathematical Elements for Computer Graphics. McGraw-Hill (1976). L.J
Paul, R.P., Zong, H.: Robot motion trajectory specification and generation. In: 2nd International Symposium on Robotics Research, pp. 373–380, Kyoto (1984)
Taylor, R.: Planning and execution of straight line manipulator trajectories. In: Robot Motion. MIT Press (1983)
Gasparetto, A., Zanotto, V.: A technique for time-jerk optimal planning of robot trajectories. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 24, 415–426 (2008)
Farouki, R.T., Tsai, Y.F.: Exact Taylor series coefficients for variable-feed rate CNC curve interpolators. Comput. Aided Des. 33, 155–165 (2001)
Wang, Y.: B-spline path planning for manipulator in joint coordinates. Anhui Institute of Mechanical 15(2), 21–26 (2000)
Wang, Y.m., Xu, W.h.: Bézier path planning for manipulator in joint coordinates. Anhui Institute of Mechanical 15(3), 59–64 (2000)
Cheng, X.: Cubic trigonometric Bézier spline interpolation. Journal of Jiamusi University 27(3), 445–448 (2009)
Wang, Y.j., Xu, W.l., Sun, N.l.: Manipulator trajectory planning based on the cubic triangular Bézier spline. In: 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA), pp. 6485–6488 (2010)
Wang, C.H., Horng, J.G.: Constrained minimum-time path planning for robot manipulators via virtual knots of the cubic B-Spline functions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 35(5), 573–577 (1990)
Chen, Y.C.: Solving robot trajectory planning problems with uniform cubic B-splines. Optimal Control Applications & Methods 12, 247–262 (1991)
Martin, B.J., Bobrow, J.E.: Minimum effort motions for open chain manipulators with task-dependent end-effector constraints. Int. J. Robot. Res. 18(2), 213–224 (1999)
Gasparetto, A., Zanotto, V.: A new method for smooth trajectory planning of robot manipulators. Mech. Mach. Theory 42, 455–471 (2007)
Steuben, J., Steele, J., Turner, C.J.: NURBS for robot manipulator trajectory generation. In: Proceeding of the ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computes and Information in Engineering Conference IDETC/CIE, pp. 1121–1130 (2011)
Aleotti, J., Caselli, S., Maccherozzi, G.: Trajectory reconstruction with NURBS curves for robot programming by demonstration. In: IEEE International Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automation, pp. 73–78, Helsinki (2005)
Aleotti, J., Caselli, S.: Trajectory clustering and stochastic approximation for robot programming by demonstration. In: Proceeding of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 1029–1034 (2005)
Andreas, J.S., Heinz, W.: Path planning for a humanoid using NURBS curves. In: IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, pp. 351–356 (2005)
Zuo, Y.: Study on NURBS surface tool trajectory planning of 6R engraving robot. Adv. Mater. Res. 711, 422–425 (2013)
Tatematsu, N., Ohnishi, K.: Tracking motion of mobile robot for moving target using NURBS curve. In: International Conference on Industrial Technology, pp. 245–249, San Francisco (2003)
Chuang, H.Y., Chien, K.H.: A real-time NURBS motion interpolator for position control of a slide equilateral triangle parallel manipulator. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 34, 724–735 (2007)
Singh, A.K., Aggarwal, A., Vashisht, M., Siddavatam, R.: Robot motion planning in a dynamic environment using offset non-uniform rational B-Splines (NURBS). In: IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), pp. 312–317 (2011)
Chen, H., Sheng, W., Xi, N., Song, M., Chen, Y.: CAD-based automated robot trajectory planning for spray painting of free-form surfaces. Industrial Robot-an International Journal - IND ROBOT 29(5), 426–433 (2002)
Andrzej, J.C., Paul, J.Z.M.: NURBS to avoid boundary orientation poses in serial manipulators. J. Field Rob. 20(12), 723–736 (2003)
Spong, M.W.: Motion control of robot manipulators. In: Levine, W. (ed.) Handbook of Control, pp. 1339–1350. CRC Press (1996)
Piegl, L.A., Triller, W.: The NURBS book. In: Monographs in Visual Communications. 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (1997)
Jahanpour, J., Tsai, M.C., Cheng, M.Y.: High-speed contouring control with NURBS-based C 2PH spline curves. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 49(5), 663–674 (2010)
Liu, X., Ahmad, F., Yamazaki, K., Mori, M.: Adaptive interpolation scheme for NURBS curve with the integration of machining dynamics. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 45(4-5), 433–444 (2005)
Bhattacharjee, B., Azeem, A., Ali, S.M., Paul, S.K.: Development of a CNC interpolation scheme for CNC controller based on Runge-Kutta method. Int. J. Computer Aided Engineering and Technology 4(5), 445–464 (2012)
Jahanpour, J., Alizadeh, M.R.: A novel acc-jerk-limited NURBS interpolation enhanced with an optimized S-shaped quantic feedrate scheduling scheme. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 77, 1889–1905 (2015)
Tsai, Y.F., Farouki, R.T., Feldman, B.: Performance analysis of CNC interpolators for time-dependent federates along PH curves. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 18(3), 245–265 (2001)
Jahanpour, J., Ghadirifar, A.: The improved NURBS-based C2 PH spline curve contour following task with PDFF controller. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 70, 995–1007 (2014)
Jahanpour, J.: High speed contouring enhanced with C2 PH quintic spline curves. Scientia Iranica B 19(2), 311–31 (2012)
Zhang, D., Lei, J.: Kinematic analysis of a novel 3-DOF actuation redundant parallel manipulator using artificial intelligence approach. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 27, 157–163 (2011)
Gosselin, C.M., Sefrriouri, J., Richard, M.J.: On the direct kinematics of spherical three degree of freedom parallel manipulators of general architecture. ASME J. Mech. Des. 116(2), 594–598 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahanpour, J., Motallebi, M. & Porghoveh, M. A Novel Trajectory Planning Scheme for Parallel Machining Robots Enhanced with NURBS Curves. J Intell Robot Syst 82, 257–275 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-015-0239-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-015-0239-6