Abstract
Purpose
Remote magnetic navigation (RMN) has been used in various electrophysiological procedures, including atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation. Atrial-esophageal fistula (AEF) is one of most disastrous complications of AF ablation. We aimed to evaluate the incidence of AEF during AF ablation using RMN in comparison to manual ablation.
Methods
We conducted the first international survey among RMN operators for assessment of the prevalence of AEF and procedural parameters affecting the risk. Data from parallel survey of AEF among Canadian interventional electrophysiologists (CIE) using only manual catheters served as control.
Results
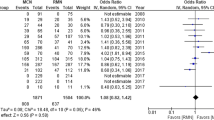
Fifteen RMN operators (who performed 3637 procedures) and 25 manual CIE operators (7016 procedures) responded to the survey. RMN operators were more experienced than CIE operators (16.3 ± 8.3 vs. 9.2 ± 5.4 practice years in electrophysiology, p = 0.007). The maximal energy output in the posterior wall was higher in the operator using RMN (33 ± 5 vs. 28.6 ± 4.9 W; p = 0.02). Other parameters including use of preprocedural images, irrigated catheter, pump flow rate, esophageal temperature monitoring, intracardiac echocardiography (ICE), and general anesthesia were similar. CIE operators administered proton-pump inhibitors postoperatively significantly more than RMN operators (76 vs. 35 %, p = 0.01). AEF was reported in 5 of the 7016 patients in the control group (0.07 %) but in none of the RMN group (p = 0.11).
Conclusions
AEF is a rare complication and its evaluation necessitates large-scale studies. Although no AEF case with RMN was reported in this large study or previously on the literature, the rarity of this complication prevents firm conclusion about the risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darby, A. E., & DiMarco, J. P. (2012). Management of atrial fibrillation in patients with structural heart disease. Circulation, 125, 945–957.
2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert Consensus Statement on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: Recommendations for Patient Selection, Procedural Techniques, Patient Management and Follow-up, Definitions, Endpoints, and Research Trial Design. Europace 2012; 14: 528–606
Arbelo, E., Brugada, J., Hindricks, G., Maggioni, A., Tavazzi, L., Vardas, P., Anselme, F., on behalf of the Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Pilot Study Investigators, et al. (2012). ESC-EURObservational Research Program: the Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Pilot Study, conducted by the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace, 14, 1094–1103.
Cappato, R., Calkins, H., Chen, S. A., Davies, W., Iesaka, Y., Kalman, J., Kim, Y. H., et al. (2005). Worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 111, 1100–1105.
Pappone, C., Oral, H., Santinelli, V., Vicedomini, G., Lang, C. C., Manguso, F., Torracca, L., et al. (2004). Atrio-esophageal fistula as a complication of percutaneous transcatheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 109, 2724–2726.
Singh, S. M., d’Avila, A., Doshi, S. K., Brugge, W. R., Bedford, R. A., Mela, T., Ruskin, J. N., et al. (2008). Esophageal injury and temperature monitoring during atrial fibrillation ablation. Circulation Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 1, 162–168.
Konstantinidou, M., Wissner, E., Chun, J. K. R., Koektuerk, B., Metzner, A., Tilz, R. R., Rilig, A., et al. (2011). Luminal esophageal temperature rise and esophageal lesion formation following remote-controlled magnetic pulmonary vein isolation. Heart Rhythm, 8, 1875–1880.
Chugh, A., Rubenstein, J., Good, E., Ebinger, M., Jongnarangsin, K., Fortino, J., et al. (2009). Mechanical displacement of the esophagus in patients undergoing left atrial ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 6, 319–322.
Arruda, M. S., Armaganijan, L., Biase, L. B., Rashidi, R., & Natale, A. (2009). Feasibility and safety of using an esophageal protective system to eliminate esophageal thermal injury. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20, 1272.
Zellerhoff, S., Lenze, F., & Eckardt, L. (2011). Prophylactic proton pump inhibition after atrial fibrillation ablation: is there any evidence? Europace, 13, 1219–1221.
Schmidt, M., Nölker, G., Marschang, H., Gutleben, K. J., Schibgilla, V., Rittger, H., Sinha, A. M., et al. (2008). Incidence of oesophageal wall injury post-pulmonary vein antrum isolation for treatment of patients with atrial fibrillation. Europace, 10, 205–209.
Nair, K. K. M., Shurrab, M., Skanes, A., Danon, A., Birnie, D., Morillo, C., Chauhan, V., Mangat, I., et al. (2014). The prevalence and risk factors for atrioesophageal fistula after percutaneous radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: the Canadian experience. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 39, 139–144.
Ghia, K. K., Chugh, A., Good, E., Pelosi, F., Jongnarangsin, K., Bogun, F., Morady, F., et al. (2009). A nationwide survey on the prevalence of atrioesophageal fistula after left atrial radiofrequency catheter ablation. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 24, 33–36.
Pappone, C., Vicedomini, G., Manguso, F., Gugliotta, F., Mazzone, P., Gulletta, S., Sora, N., et al. (2006). Robotic magnetic navigation for atrial fibrillation ablation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 47, 1390–1400.
Faddis, M. N., Chen, J., Osborn, J., Talcott, M., Cain, M. E., & Lindsay, B. D. (2003). Magnetic guidance system for cardiac electrophysiology—a prospective trial of safety and efficacy in humans. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 42, 1952–1958.
Kim, A., Turakhia, M., Lu, J., Badhwar, N., Lee, B. K., Lee, R. J., Marcus, G. M., et al. (2008). Impact of remote magnetic catheter navigation on ablation fluoroscopy and procedure time. PACE, 31, 1399–1404.
Shurrab, M., Danon, A., Lashevsky, I., Kiss, A., Newman, D., Szili-Torok, T., & Crystal, E. (2013). Robotically assisted ablation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Cardiology, 169, 157–165.
Grubina, R., Cha, Y.-M., Bell, M. R., Sinak, L. J., & Asirvatham, S. J. (2010). Pneumopericardium following radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation: insights into the natural history of atrial esophageal fistula formation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 21, 1046–1049.
Davis, D. R., Tang, A. S. L., Gollob, M. H., Lemery, R., Green, M. S., & Birnie, D. H. (2008). Remote magnetic navigation-assisted catheter ablation enhances catheter stability and ablation success with lower catheter temperatures. PACE, 31, 893–898.
Faddis, M. N., Blume, W., Finney, J., Hall, A., Rauch, J., Sell, J., Bae, K. T., et al. (2002). Novel, magnetically guided catheter for endocardial mapping and radiofrequency catheter ablation. Circulation, 106, 2980–2985.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danon, A., Shurrab, M., Nair, K.M. et al. Atrial fibrillation ablation using remote magnetic navigation and the risk of atrial-esophageal fistula: international multicenter experience. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 43, 169–174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-015-0003-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-015-0003-7