Abstract
Purpose
The stiff left atrial (LA) syndrome is defined as pulmonary hypertension (PH) secondary to reduced LA compliance and has recently been shown to be one cause of PH after atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation. We aimed to determine the incidence of an increase in pulmonary arterial (PA) pressure post-ablation and examine the clinical and echocardiographic associations.
Methods
Patients who underwent AF ablation between 1999 and 2011 were included if they had both an echocardiogram pre-ablation and 3 months post-ablation. Patients were then separated into two groups with the increased PA pressure group defined as patients with >10 mmHg increase in right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) post-ablation and a post-ablation RVSP >35 mmHg.
Results
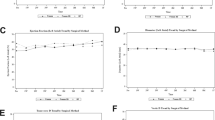
Of the 499 patients meeting the study criteria, 41 (8.2 %) had an increase in RVSP >10 mmHg and RVSP >35 mmHg post-ablation. On echocardiogram, the two groups had similar E/A and E/e’ ratios pre-ablation. However, post-ablation, the increased PA pressure group had higher E/A (2.12 vs. 1.49, p < 0.01) and E/e’ (14.7 vs. 11.2, p < 0.01) ratios. LA expansion index values were lower in the increased PA pressure group pre-ablation (51 vs. 92 %, p < 0.01), but not significantly different post-ablation (82 vs. 88 %, p = 0.44).
Conclusions
Around 8 % of patients develop an increase in estimated PA pressure after AF ablation. Echocardiographic parameters suggest that patients who develop increased PA pressure are developing (or unmasking) left ventricular diastolic dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- LA:
-
Left atrial or left atrium
- PA:
-
Pulmonary artery
- PH:
-
Pulmonary hypertension
- RVSP:
-
Right ventricular systolic pressure
- TTE:
-
Transthoracic echocardiogram
- LV:
-
Left ventricular
References
McLaughlin, V. V., Archer, S. L., Badesch, D. B., Barst, R. J., Farber, H. W., Lindner, J. R., et al. (2009). ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association: developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 53(17), 1573–1619.
Pilote, L., Hüttner, I., Marpole, D., & Sniderman, A. (1988). Stiff left atrial syndrome. Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 4, 255–257.
Gibson, D. N., Di Biase, L., Mohanty, P., Patel, J. D., Bai, R., Sanchez, J., et al. (2011). Stiff left atrial syndrome after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: clinical characterization, prevalence, and predictors. Heart Rhythm, 8(9), 1364–1371.
Cappato, R., Calkins, H., Chen, S.-A., Davies, W., Iesaka, Y., Kalman, J., et al. (2010). Updated worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation. Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 3(1), 32–38.
Roşca, M., Lancellotti, P., Popescu, B. A., & Piérard, L. A. (2011). Left atrial function: pathophysiology, echocardiographic assessment, and clinical applications. Heart, 97(23), 1982–1989.
Yoon, Y. E., Kim, H.-J., Kim, S.-A., Kim, S. H., Park, J.-H., Park, K.-H., et al. (2012). Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Ultrasound, 20(3), 140–145.
Financial support
This work was supported by the Division of Cardiovascular Diseases, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN.
Potential conflicts of interest
No relevant conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Witt, C.M., Fenstad, E.R., Cha, YM. et al. Increase in pulmonary arterial pressure after atrial fibrillation ablation: incidence and associated findings. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 40, 47–52 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-014-9875-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-014-9875-1