Abstract
Background
The exact mechanism of eliminating atrial fibrillation (AF) by catheter ablation techniques is not known. We investigated whether the extent of atrial damage conferred by radiofrequency lesions is a predictor of success after ablation, regardless of the method employed for ablation.
Methods
Ninety consecutive patients with paroxysmal AF subjected to ostial–antral pulmonary vein isolation (n = 41) or circumferential (n = 49) catheter ablation were studied.
Results
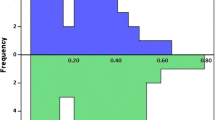
At 1 year follow-up, 16 out of 41 patients (39%) with ostial–antral ablation and 16 out of 49 patients (32.6%) with circumferential ablation had AF recurrences (p = 0.5). The mean duration of radiofrequency ablation lesions was statistically significantly shorter in patients with recurrence of AF compared to those with sinus rhythm 1 year after ablation (22.3 ± 4.2 min vs. 27.2 ± 4.5 min, respectively, p value < 0.001). Radiofrequency ablation time was inversely associated with the risk of recurrence of AF 1 year after ablation and this relationship remained even after adjustment for potential confounding factors such as age, sex, left atrial size, and type of ablation technique (ostial–antral or circumferential; HR = 0.80, 95% CI: 0.72–0.87, p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Duration of radiofrequency energy delivery is an independent predictor of clinical outcome at 1 year follow-up both among patients undergoing circumferential as well as ostial–antral ablation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ouyang, F., Antz, M., Ernst, S., et al. (2005). Recovered pulmonary vein conduction as a dominant factor for recurrent atrial tachyarrhythmias after complete circular isolation of the pulmonary veins: lessons from double Lasso technique. Circulation, 111, 127–135.
Cappato, R., Negroni, S., Pecora, D., Bentivegna, S., Lupo, P. P., Carolei, A., et al. (2003). Prospective assessment of late conduction recurrence across radiofrequency lesions producing electrical disconnection at the pulmonary vein ostium in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 108, 1599–604.
Hocini, M., Sanders, P., Jais, P., Hsu, L. F., Weerasoriya, R., Scavee, C., et al. (2005). Prevalence of pulmonary vein disconnection after anatomical ablation for atrial fibrillation: consequences of wide atrial encircling of the pulmonary veins. European Heart Journal, 26, 696–704.
Stabile, G., Turco, P., La Rocca, V., Nocerino, P., Stabile, E., & De Simone, A. (2003). Is pulmonary vein isolation necessary for curing atrial fibrillation? Circulation, 108, 657–660.
Katritsis, D., Ellenbogen, K. A., & Camm, A. J. (2004). Recurrence of pulmonary vein-left atrium conduction following successful disconnection in asymptomatic patients. Europace, 6, 425–432.
Lemola, K., Oral, H., Chugh, A., et al. (2005). Pulmonary vein isolation as an end point for left atrial circumferential ablation of atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 46, 1060–1066.
van Brakel, T. J., Bolotin, G., Nifong, L. W., Dekker, A. L., Allessie, M. A., Chitwood Jr, W. R., et al. (2005). Robot-assisted epicardial ablation of the pulmonary veins: is a completed isolation necessary? European Heart Journal, 26, 1321–1326.
Lemola, K., Hall, B., Cheung, P., Good, E., Han, J., Tamirisa, K., et al. (2004). Mechanisms of recurrent atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation by segmental ostial ablation. Heart Rhythm, 1, 197–202.
Oral, H., Chugh, A., Good, E., Igic, P., Elmouchi, D., Tschopp, D. R., et al. (2005). Randomized comparison of encircling and nonencircling left atrial ablation for chronic atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 2, 1165–1172.
Oral, H., Chugh, A., Good, E., Sankaran, S., Reich, S. S., Igic, P., et al. (2006). A tailored approach to catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 113, 1824–1831.
Essebag, V., Baldessin, F., Reynolds, M. R., McClennen, S., Shah, J., Kwaku, K. F., et al. (2005). Non-inducibility post-pulmonary vein isolation achieving exit block predicts freedom from atrial fibrillation. European Heart Journal, 26, 2550–2555.
Katritsis, D., Giazitzoglou, E., Korovesis, S., Kourlaba, G., Voridis, E., & Camm, A. J. (2007). Staged circumferential and ostial pulmonary vein ablation for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. PACE, 30, 102–108.
Oral, H., Chugh, A., Lemola, K., Cheung, P., Hall, B., Good, E., et al. (2004). Noninducibility of atrial fibrillation as an end point of left atrial circumferential ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a randomized study. Circulation, 110, 2797–2801.
Nademanee, K., McKenzie, J., Kosar, E., Schwab, M., Sunsaneewitayakul, B., Vasavakul, T., et al. (2004). A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 43, 2044–2053.
Lemola, K., Ting, M., Gupta, P., Anker, J. N., Chugh, A., Good, E., et al. (2006). Effects of two different catheter ablation techniques on spectral characteristics of atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College Cardiology, 48, 340–348.
Pappone, C., Oreto, G., Rosanio, S., Vicedomini, G., Tocchi, M., Gugliotta, F., et al. (2001). Atrial electroanatomic remodeling after circumferential radiofrequency pulmonary vein ablation: efficacy of an anatomic approach in a large cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 104, 2539–2544.
Katritsis, D. G., Ellenbogen, K. A., Panagiotakos, D. B., Giazitzoglou, E., Karabinos, I., Papadopoulos, A., et al. (2004). Ablation of superior pulmonary veins compared to ablation of all four pulmonary veins: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 15, 641–645.
Katritsis, D. G., Wood, M. A., Shepard, R. K., Giazitzoglou, E., Kourlaba, G., & Ellenbogen, K. A. (2006). Atrial arrhythmias following ostial or circumferential pulmonary vein ablation. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 16, 123–130.
Allessie, M. A., Boyden, P. A., Camm, A. J., Kleber, A. G., Lab, M. J., Legato, M. J., et al. (2001). Pathophysiology and prevention of atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 103, 769–777.
Katritsis, D. G., & Camm, A. J. (2007). Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Do we know what we are doing? Europace, 9, 1002–1005.
Kumagai, K., Ogawa, M., Noguchi, H., Yasuda, T., Nakashima, H., & Saku, K. (2004). Electrophysiologic properties of pulmonary veins assessed using a multielectrode basket catheter. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 43, 2281–2289.
Kalifa, J., Tanaka, K., Zaitsev, A. V., Warren, M., Vaidyanathan, R., Auerbach, D., et al. (2006). Mechanisms of wave fractionation at boundaries of high-frequency excitation in the posterior left atrium of the isolated sheep heart during atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 113, 626–633.
Katritsis, D., Giazitzoglou, E., Korovesis, S., Paxinos, G., Anagnostopoulos, C. E., & Camm, A. J. (2002). Epicardial foci of atrial arrhythmias apparently originating in the left pulmonary veins. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 13, 319–323.
Liu, L., & Nattel, S. (1997). Differing sympathetic and vagal effects on atrial fibrillation in dogs: role of refractoriness heterogeneity. American Journal of Physiology, 273(2 Pt 2), H805–H816.
Allessie, M. A., Bonke, F. I., & Schopman, F. J. (1977). Circus movement in rabbit atrial muscle as a mechanism of tachycardia. III. The “leading circle” concept: A new model of circus movement in cardiac tissue without the involvement of an anatomical obstacle. Circulation Research, 41, 9–18.
Mandapati, R., Skanes, A., Chen, J., Berenfeld, O., & Jalife, J. (2000). Stable microreentrant sources as a mechanism of atrial fibrillation in the isolated sheep heart. Circulation, 101, 194–199.
Pachon, M. J. C., Pachon, M. E. I., Pachon, M. J. C., Lobo, T. J., Pachon, M. Z., Vargas, R. N., et al. (2004). A new treatment for atrial fibrillation based on spectral analysis to guide the catheter RF-ablation. Europace, 6, 590–601.
Pratola, C., Baldo, E., Notarstefano, P., Toselli, T., & Ferrari, R. (2008). Radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation: is the persistence of all intraprocedural targets necessary for long-term maintenance of sinus rhythm? Circulation, 117, 136–143.
Lemola, K., Desjardins, B., Sneider, M., Case, I., Chugh, A., Good, E., et al. (2005). Effect of left atrial circumferential ablation for atrial fibrillation on left atrial transport function. Heart Rhythm, 2, 923–928.
Verma, A., Kilicaslan, F., Adams, J. R., Hao, S., Beheiry, S., Minor, S., et al. (2006). Extensive ablation during pulmonary vein antrum isolation has no adverse impact on left atrial function: an echocardiography and cine computed tomography analysis. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17, 741–746.
Lo, L. W., Tai, C. T., Lin, Y. J., Chang, S. L., Wongcharoen, W., Chang, S. H., et al. (2007). Progressive remodeling of the atrial substrate—A novel finding from consecutive voltage mapping in patients with recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18, 258–265.
Kostin, S., Klein, G., Szalay, Z., Hein, S., Bauer, E. P., & Schaper, J. (2002). Structural correlate of atrial fibrillation in human patients. Cardiovascular Research, 54, 361–379.
Hindricks, G., Piorkowski, C., Tanner, H., Kobza, R., Gerds-Li, J. H., Carbucicchio, C., et al. (2005). Perception of atrial fibrillation before and after radiofrequency catheter ablation: relevance of asymptomatic arrhythmia recurrence. Circulation, 112, 307–313.
Neumann, T., Erdogan, A., Dill, T., Greiss, H., Berkowitsch, A., Sperzel, J., et al. (2006). Asymptomatic recurrences of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation. Europace, 8, 495–498.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to be disclosed for any author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katritsis, D., Ellenbogen, K.A., Giazitzoglou, E. et al. Clinical outcome of left atrial ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation is related to the extent of radiofrequency ablation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 22, 31–37 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-008-9247-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-008-9247-9