Abstract
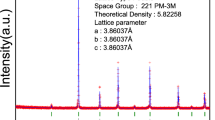
The oxygen partial pressure (pO2) dependent conductivity of Nd3+ doped PZT was investigated at different temperatures in order to get information on the nature of the conducting charge carriers and on the chemical oxygen diffusion coefficient. From a positive slope close to 0.25 in log (conductivity) vs. log (pO2) plots it is concluded that PZT with donor-type Nd3+ shows predominant hole conduction already at moderately high oxygen partial pressures, while under reducing conditions electron conduction prevails. This unexpected occurrence of hole conduction in a nominally donor doped system is interpreted in terms of the only partially controllable loss of lead oxide during preparation, which results in the formation of lead vacancies. Those act as acceptors at the temperatures employed in this study (560–615 °C) and turn the nominally donor doped material into a slightly acceptor doped one. From the conductivity relaxation after partial pressure changes, chemical oxygen diffusion coefficients could be extracted and values of about 6.5·10−9 cm2/s at 560 °C and 2·10−8 cm2/s at 611 °C are found in air.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Daniels, K.H. Härdtl, R. Wernicke, Philips Technol. Rev 38, 73–82 (1978)
J. Gerblinger, H. Meixner, Sensors Actuators B Chem. 4, 99–102 (1991)
W. Heywang, K. Lubitz, W. Wersing, Piezoelectricity, Evolution and Future of a Technology, (2008)
G.H. Haertling, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 797–818 (1999)
R. Waser, T. Baiatu, K.H. Härdtl, J. Am. Soc. 73(6), 1654–1662 (1990)
J. Daniels, K.H. Härdtl, Philips Res. Repts. 31, 489–504 (1976)
J. Daniels, K.H. Härdtl, R. Wernicke, Philips Technol. Rev 38, 73–82 (1976)
N.H. Chan, R.K. Sharma, D.M. Smyth, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 64, 556–562 (1981)
H. Neumann, G. Arlt, Ferroelectrics 69(1), 179–186 (1986)
H.L. Tuller, Solid State Ionics 94, 63–74 (1997)
R. Moos, K.H. Hardtl, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 2549–2562 (1997)
I. Denk, W. Münch, J. Maier, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 78, 3265–3272 (1995)
S. Rodewald, J. Fleig, J. Maier, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 1969–1976 (2000)
S. Steinsvik, R. Bugge, J.O.N. GjoeNnes, J. Taftoe, T. Norby, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 58, 969–976 (1997)
T. Frömling, A. Schintlmeister, H. Hutter, J. Fleig, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1173–1181 (2011)
M.V. Raymond, D.M. Smyth, Ferroelectrics 144, 129–135 (1993)
M.V. Raymond, D.M. Smyth, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 57, 1507–1511 (1996)
N.J. Donnelly, C.A. Randall, Applied Physics Letters 96 (2010) 052906-052906-052903.
L. Andrejs, J. Fleig, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33, 779–794 (2013)
M.V. Raymond, D.M. Smyth, Integr. Ferroelectr. 4, 145–154 (1994)
Y. Xu, X. Yuhuan, Ferroelectric materials and their applications, North-Holland Amsterdam ets, (1991)
J. Maier, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 5, 2164–2173 (2003)
D.L. Corker, R.W. Whatmore, E. Ringgaard, W.W. Wolny, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20, 2039–2045 (2000)
A.J. Moulson, J.M. Herbert, Electroceramics, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, (2003)
N.J. Donnelly, C.A. Randall, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 104107–104106 (2011)
B.A. Boukamp, M.T.N. Pham, D.H.A. Blank, H.J.M. Bouwmeester, Solid State Ionics 170, 239–254 (2004)
D.M. Smyth, Curr. Opinion Solid State Mater. Sci. 1, 692–697 (1996)
J.v. Rudolph, Zeitschrift Naturforschung Teil A 14 (1959) 727.
B. Jaffe, W.R. Cook, H. Jaffe, Piezoelectric Ceramics, Academic Press London and New York, (1971)
W. Long, W. Tien-Shou, W. Chung-Chuang, L. Hsi-Chuan, J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 16, 2823 (1983)
J. Maier, Physical Chemistry of Ionic Materials, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, (2005)
J. Jamnik, J. Maier, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 3, 1668–1678 (2001)
J. Jamnik, J. Maier, J. Electrochem. Soc. 146(11), 4183–4188 (1999)
J. Fleig, J. Maier, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1, 3315–3320 (1999)
J. Fleig, Solid State Ionics 150, 181–193 (2002)
D. Fasquelle, J.C. Carru, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 2071–2074 (2008)
A. Shafiei, C. Oprea, A. Alfantazi, T. Troczynski, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 114108 (2011)
M. Wu, H. Huang, B. Jiang, W. Chu, Y. Su, J. Li, L. Qiao, J. Mater. Sci. 44, 5768–5772 (2009)
Y. Shimakawa, Y. Kubo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 2590–2592 (2000)
Y.-M. Chiang, D.P. Birnie, W.D. Kingery, Physical ceramics, J. Wiley, (1997)
R. Moos, W. Menesklou, K.H. Härdtl, Appl. Phys. A 61, 389–395 (1995)
T. Frömling, H. Hutter, J. Fleig, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 1692–1700 (2012)
W. Preis, E. Bucher, W. Sitte, Solid State Ionics 175, 393–397 (2004)
G. Holzlechner, D. Kastner, C. Slouka, H. Hutter, J. Fleig, Solid State Ionics 262, 625–629 (2014)
Acknowledgement
Financial support by Christian Doppler Research Association (CDG) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slouka, C., Andrejs, L. & Fleig, J. Defect chemistry and transport properties of Nd-doped Pb(ZrxTi1−x)O3 . J Electroceram 33, 221–229 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-014-9954-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-014-9954-9