Abstract
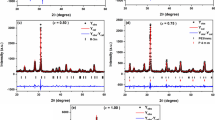
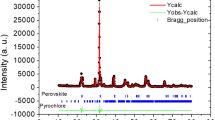
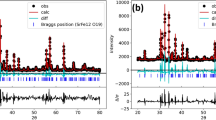
In this paper, the structural and dielectric properties of SrBi2Nb2O9 (SBN) as a function of Bi2O3 or La2O3 addition level in the radio (RF) and microwave frequencies were investigated. The SBN, were prepared by using a new procedure in the solid-state reaction method with the addition of 3; 5; 10 and 15 wt.% of Bi2O3 or La2O3. A single orthorhombic phase was formed after calcination at 900 °C for 2 h. The analysis by x-ray diffraction (XRD) using the Rietveld refinement confirmed the formation of single-phase compound with a crystal structure (a = 5.5129 Å, b = 5.5183 Å and c = 25.0819 Å; α = β = γ = 90°). Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) micrograph of the material shows globular morphologies (nearly spherical) of grains throughout the surface of the samples. The Curie temperature found for the undoped sample was about 400 °C, with additions of Bi3+, the temperature decreases and with additions of La3+ the Curie temperature increased significantly above 450 °C. In the measurements of the dielectric properties of SBN at room temperature, one observe that at 10 MHz the highest values of permittivity was observed for SBN5LaP (5%La2O3) with values of 116,71 and the lower loss (0.0057) was obtained for SBN15LaP (15%La2O3). In the microwave frequency region, Bi2O3 added samples have shown higher dielectric permittivity than La2O3 added samples, we highlight the SBN15BiG (15 % Bi2O3) with the highest dielectric permittivity of 70.32 (3.4 GHz). The dielectric permittivity values are in the range of 28–71 and dielectric losses are of the order of 10−2. The samples were investigated for possible applications in RF and microwave components.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Aurivillius, Ark. Kemi (1950) 519
J.F. Scott, C.A.P. de Araujo, Science 246, 1400 (1989)
B. Aurivillius, Ark. Kemi (1949) 463
J. Robertson, C.W. Chen, W.L. Warren, C.C. Gutleben, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 1704 (1996)
C.A.P. de Araujo, J.D. Cuchiaro, L.D. McMillan, M.C. Scott, J.F. Scott, Nature 374, 627 (1995)
Y. Wu, G.Z. Cao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 2650 (1999)
Y. Wu, G.Z. Cao, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19, 267 (2000)
S. Ezhilvalavan, J.M. Xue, J. Wang, J. Phys D:Appl Phys 35, 2254 (2002)
G.Z. Liu, H.S. Gu, C. Wang, J. Qiu, H.B. Lu, Chin. Phys. Lett. 24, 2387 (2007)
G.Z. Liu, C. Wang, H.S. Gu, H.B. Lu, J. Phys D:Appl Phys 40, 7817 (2007)
E.C. Subbarao, Phys. Rev. 122, 804 (1961)
X-ray Laboratory, Federal University of Ceará, Available at:<http://www.raiosx.ufc.br/site/>. Accessed on: April 7, 2012.
A.J. Moulson, J.M. Herbert, Electroceramics (Chapman and Hall, London, 1990)
C. Yeh, F.I. Shimabukuro, The Essence of Dielectric Waveguides (Springer Science + Business Media, New York, 2008)
M.N. Afsar, K.J. Button, Millimeter-wave dielectric measurement of materials. Proc. IEEE 73, 131 (1985)
B.W. Hakki, P.D. Coleman, Microw. Theory Tech. 3, 402–410 (1960)
D. Dhak, P. Dhak, P. Pramanik, Appl Surf Sci 254, 3078 (2008)
R.C. Buchanan, Ceramic Material for Electronics: Processing, Properties and Applications, 2nd edn. (Marcel Dekker INC., United States of American, 1991), p. 532
D.H. Wang, W.C. Goh, M. Ning, C.K. Ong, Appl Phys. Lett. 88, 212907 (2006)
M.M. Kumar, K.L.J. Yadav, Phys.: Condens. Matter 18, L503 (2006)
F. Gerrero, J.J. Portejes, H. Amorin, A. Fundora, J. Siqueiros, G. Hirata, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 18, 745 (1998)
V. Shrivstava, A.K. Jha, R.G. Mendiratta, Dielectric studies of La and Pb doped SrBi2Nb2O9 ferroelectric ceramic. Mater Lett 60, 1459–1462 (2006)
M.J.S. Rocha, M.C.C. Filho, K.R.B. Theophilo, J.C. Denardin, I.F. Vasconcelos, E.B. Araújo, A.S.B. Sombra, Ferrimagnetism and ferroelectricity of the composite matrix: SrBi2Nb2O9 (SBN)X-BaFe12019(BFO)100–X. Mater Sci Appl 3, 6–17 (2012). doi:10.4236/msa.2012.31002
C.C. Silva, A.S.B. Sombra, Temperature dependence of the magnetic and electric properties of Ca2Fe2O5. Mater Sci Appl 2(n.9), 1349–1353 (2011). doi:10.4236/msa.2011.29183
Acknowledgments
This work was partly sponsored by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and X-ray Laboratory, Federal University of Ceará Process: 402561/2007-4 (Edital MCT/CNPq no 10/2007) and the U. S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) (FA9550-11-1-0095)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sancho, E.O., Silva, P.M.O., Júnior, G.F.M.P. et al. High dielectric permittivity of SrBi2Nb2O9(SBN) added Bi2O3 and La2O3 . J Electroceram 30, 119–128 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-012-9772-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-012-9772-x