Abstract
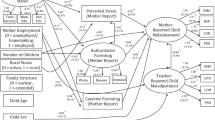
This study examined the relationships between family financial stress, mental health problems, child rearing practice, and school involvement using a sample of 431 parents with children in grades 1–4 from one elementary school in a rural area of Taiwan. Financial stress was hypothesized to be associated with parental mental health problems, which in turn were expected to be linked to poorer child rearing practice and less parental involvement in school. Structural equation models were constructed and tested in a stepwise manner. Results showed that financial stress was significantly associated with higher mental health problems, poorer child rearing effort, and decreased parental school involvement while parents’ mental health problems were not significantly associated with their child rearing efforts or involvement in school. These findings suggest that the impact of family financial stress on Taiwanese parents’ child rearing practice is largely direct rather than mediated through their mental health problems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benzies, K., & Mychasiuk, R. (2009). Fostering family resiliency: A review of the key protective factors. Child and Family Social Work, 14(1), 103–114. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2206.2008.00586.x.
Berger, L. M. (2004). Income, family structure, and child maltreatment risk. Children and Youth Services Review, 26(8), 725–748. doi:10.1016/j.childyouth.2004.02.017.
Bisgaier, J., & Rhodes, K. V. (2011). Cumulative adverse financial circumstances: Associations with patient health status and behaviors. Health and Social Work, 36(2), 129–137.
Black, K., & Lobo, M. (2008). A conceptual review of family resilience factors. Journal of Family Nursing, 14(1), 33–55. doi:10.1177/1074840707312237.
Butterworth, P., Rodgers, B., & Windsor, T. (2009). Financial hardship, socio-economic position and depression: Results from the PATH Through Life Survey. Social Science and Medicine, 69(2), 229–237.
Cadzow, S. P., Armstrong, K. L., & Fraser, J. A. (1999). Stressed parents with infants: Reassessing physical abuse risk factors. Child Abuse and Neglect, 23(9), 845–853. doi:10.1016/S0145-2134(99)00063-0.
Carter, V., & Myers, M. R. (2007). Exploring the risks of substantiated physical neglect related to poverty and parental characteristics: A national sample. Children and Youth Services Review, 29(1), 110–121. doi:10.1016/j.childyouth.2006.08.002.
Catalano, R., Dooley, D., Novaco, R., Wilson, G., & Hough, R. (1993). Using ECA survey data to examine the effect of job layoffs on violent behavior. Hospital and Community Psychiatry, 44, 874–887.
Catalano, R., Goldman-Mellor, S., Saxton, K., Margerison-Zilko, C., Subbaraman, M., LeWinn, K., et al. (2011). The health effects of economic decline. Annual Review of Public Health, 32, 431–450. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031210-101146.
Chao, R., & Tseng, V. (2002). Parenting of Asians. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting: Vol. 4 Social conditions and applied parenting (pp. 59–93). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Chen, F., & Luster, T. (2002). Factors related to parenting practices in Taiwan. Early Child Development and Care, 172(5), 413–430. doi:10.1080/03004430214549.
Chen, C. H., Chou, J. Y., Lai, T. J., & Lee, T. C. (2010). Suicide and unemployment rate in Taiwan, a population-based study, 1978–2006. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 45(4), 447–452. doi:10.1007/s00127-009-0083-8.
Cheng, Y. W., Chen, C. W., Chen, C. J., & Chiang, T. L. (2005). Job insecurity and its association with health among employees in the Taiwanese general population. Social Science and Medicine, 61(1), 41–52.
Cheung, C., & Pomerantz, E. M. (2012). Why does parents’ involvement enhance children’s achievement? The role of parent-oriented motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104, 820–832. doi:10.1037/a0027183.
Chiang, W. (2012). The suppression of emotional expression in interpersonal context. Bulletin of Educational Psychology, 43(3), 657–680.
Conger, R. D., & Conger, K. J. (2002). Resilience in Midwestern families: Selected findings from the first decade of a prospective, longitudinal study. Journal of Marriage and Family, 64(2), 361–373. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2002.00361.x.
Conger, R. D., Conger, K. J., Elder, G. H., Lorenz, F. O., Simons, R. L., & Whitbeck, L. B. (1992). A family process model of economic hardship and adjustment of early adolescent boys. Child Development, 63(3), 526–541. doi:10.2307/1131344.
Conger, R. D., Lorenz, F. O., Elder, G. H., & Simons, R. L. (1993). Husband and wife differences in response to undesirable life events. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 34(1), 71–88. doi:10.2307/2137305.
Conger, R. D., Wallace, L., Sun, Y., Simons, R. L., McLoyd, V. C., & Brody, G. H. (2002). Economic pressure in African American families: A replication and extension of the family stress model. Developmental Psychology, 38(2), 179–193. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.38.2.179.
Dashiff, C., DiMicco, W., Myers, B., & Sheppard, K. (2009). Poverty and adolescent mental health. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing, 22(1), 23–32. doi:10.1111/j.1744-6171.2008.00166.x.
Dix, T., & Meunier, L. N. (2009). Depressive symptoms and parenting competence: An analysis of 13 regulatory processes. Developmental Review, 29(1), 45–68. doi:10.1016/j.dr.2008.11.002.
Dooley, D., & Catalano, R. (2003). Introduction to underemployment and its social costs. American Journal of Community Psychology, 32, 1–7.
Dooley, D., Prause, J., & Ham-Rowbottom, K. A. (2000). Underemployment and depression: longitudinal relationships. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 41(4), 421–436.
Fergusson, D. M., Swain-Campbell, N., & Horwood, J. (2004). How does childhood economic disadvantage lead to crime? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45(5), 956–966. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.t01-1-00288.x.
Fox, G., Benson, M. L., DeMaris, A. A., & Van Wyk, J. (2002). Economic distress and intimate violence: Testing family stress and resources theories. Journal of Marriage and Family, 64(3), 793–807. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2002.00793.x.
Friedland, D., & Price, R. (2003). Underemployment: Consequences for the health and well-being of workers. American Journal of Community Psychology, 32, 33–45.
Fu, L. L. (2008). The contemporary reflection on the familial ethics of Liji. Monthly Review of Philosophy and Culture, 35(10), 133–151.
Gonzales, N. A., Coxe, S., Roosa, M. W., White, R. B., Knight, G. P., Zeiders, K. H., et al. (2011). Economic hardship, neighborhood context, and parenting: Prospective effects on Mexican–American adolescent’s mental health. American Journal of Community Psychology, 47(1–2), 98–113. doi:10.1007/s10464-010-9366-1.
Hamilton, G. G. (1990). Patriarchy, patrimonialism, and filial piety: A comparison of China and Western Europe. British Journal of Sociology, 41(1), 77–104.
Hung, C. (2007). Family, schools and Taiwanese children’s outcomes. Educational Research, 49(2), 115–125. doi:10.1080/00131880701369644.
Jose, P. E., Huntsinger, C. S., Huntsinger, P. R., & Liaw, F. (2000). Parental values and practices relevant to young children’s social development in Taiwan and the United States. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 31(6), 677–702. doi:10.1177/0022022100031006002.
Kohl, G. O., Lengua, L. J., & McMahon, R. J. (2000). Parent involvement in school: Conceptualizing multiple dimensions and their relations with family and demographic risk factors. Journal of School Psychology, 38(6), 501–523. doi:10.1016/S0022-4405(00)00050-9.
König, H., Bernert, S., Angermeyer, M., Matschinger, H., Martinez, M., Vilagut, G., et al. (2009). Comparison of population health status in six European countries: Results of a representative survey using the EQ-5D questionnaire. Medical Care, 47(2), 251–261.
Lau, A., & Takeuchi, D. (2001). Cultural factors in help-seeking for child behavior problems: Value orientation, affective responding, and severity appraisals among Chinese-American parents. Journal of Community Psychology, 29(6), 675–692. doi:10.1002/jcop.1042.
Lee, J., & Bowen, N. K. (2006). Parent involvement, cultural capital, and the achievement gap among elementary school children. American Educational Research Journal, 43(2), 193–218. doi:10.3102/00028312043002193.
Lee, M., & Mjelde-Mossey, L. (2004). Cultural dissonance among generations: A solution-focused approach with East Asian elders and their families. Journal of Marital And Family Therapy, 30(4), 497–513. doi:10.1111/j.1752-0606.2004.tb01258.x.
Lee, M., Lee, Y., Yen, L., Lin, M., & Lue, B. (1990). Reliability and validity of using a brief psychiatric symptom rating scale in clinical practice. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association, 89, 1081–1087.
Lee, C., Lee, J., & August, G. J. (2011). Financial stress, parental depressive symptoms, parenting practices, and children’s externalizing problem behaviors: Underlying processes. Family Relations: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Applied Family Studies, 60(4), 476–490. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3729.2011.00656.x.
Leung, J. Y., & Shek, D. L. (2011). “All I can do for my child”: Development of the Chinese Parental Sacrifice for Child’s Education Scale. International Journal on Disability and Human Development, 10(3), 201–208. doi:10.1515/IJDHD.2011.037.
Lin, C. C., & Fu, V. R. (1990). A comparison of child-rearing practices among Chinese, immigrant Chinese, and Caucasian-American parents. Child Development, 61(2), 429–433. doi:10.2307/1131104.
Lovejoy, M., Graczyk, P. A., O’Hare, E., & Neuman, G. (2000). Maternal depression and parenting behavior: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 20(5), 561–592. doi:10.1016/S0272-7358(98)00100-7.
Lund, C., Breen, A., Flisher, A. J., Kakuma, R., Corrigall, J., Joska, J. A., et al. (2010). Poverty and common mental disorders in low and middle income countries: A systematic review. Social Science and Medicine, 71(3), 517–528. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2010.04.027.
McKee-Ryan, F. M., Song, Z., Wanberg, C. R., & Kinicki, A. J. (2005). Psychological and physical well-being during unemployment: A meta analytic study. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(1), 53–76.
Ministry of the Interior. (2011). Statistical yearbook of interior. Retrieved from http://sowf.moi.gov.tw/stat/year/elist.htm.
Najman, J. M., Hayatbakhsh, M. R., Clavarino, A., Bor, W., O’Callaghan, M. J., & Williams, G. M. (2010). Family poverty over the early life course and recurrent adolescent and young adult anxiety and depression: A longitudinal study. American Journal of Public Health, 100(9), 1719–1723. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2009.180943.
Oyserman, D., Bybee, D., Mowbray, C., & Hart-Johnson, T. (2005). When mothers have serious mental health problems: Parenting as a proximal mediator. Journal of Adolescence, 28(4), 443–463. doi:10.1016/j.adolescence.2004.11.004.
Pan, Y. J., & Lee, M. B. (2008). Charcoal burning and maternal filicide-suicide trends in Taiwan: The impact of accessibility of lethal methods. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association, 107(10), 811–815.
Patterson, J. (2002). Integrating family resilience and family stress theory. Journal of Marriage and Family, 64(2), 349–360. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2002.00349.x.
Paul, K., & Moser, K. (2009). Unemployment impairs mental health: Meta-analyses. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 74(3), 264–282.
Scutella, R., & Wooden, M. (2008). The effects of household joblessness on mental health. Social Science and Medicine, 67(1), 88–100.
Shek, D. L. (2000). Parental marital quality and well-being, parent–child relational quality, and Chinese-adolescent adjustment. American Journal of Family Therapy, 28(2), 147–162. doi:10.1080/019261800261725.
Shek, D. L. (2005). Perceived parental control processes, parent-child relational qualities, and psychological well-being in Chinese adolescents with and without economic disadvantage. Journal of Genetic Psychology, 166(2), 171–188. doi:10.3200/GNTP.166.2.171-188.
Sheu, Y. H. (2000). Dilemmas of family policy in Taiwan: The family ideology really matters? Social Policy and Social Work, 4(1), 237–289.
Siahpush, M., Yong, H., Borland, R., Reid, J. L., & Hammond, D. (2009). Smokers with financial stress are more likely to want to quit but less likely to try or succeed: Findings from the International Tobacco Control (ITC) Four Country Survey. Addiction, 104(8), 1382–1390. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02599.x.
Sidebotham, P., Golding, J., & The ALSPAC Study, T. (2001). Child maltreatment in the ‘Children of the Nineties’: A longitudinal study of parental risk factors. Child Abuse and Neglect, 25(9), 1177–1200. doi:10.1016/S0145-2134(01)00261-7.
Slack, K., Holl, J. L., McDaniel, M., Yoo, J., & Bolger, K. (2004). Understanding the Risks of Child Neglect: An Exploration of Poverty and Parenting Characteristics. Child Maltreatment, 9(4), 395–408.
Suizzo, M., & Cheng, C. (2007). Taiwanese and American mothers’ goals and values for their children’s futures. International Journal of Psychology, 42(5), 307–316. doi:10.1080/00207590601109342.
Van Velsor, P., & Orozco, G. L. (2007). Involving low-income parents in the schools: Communitycentric strategies for school counselors. Professional School Counseling, 11(1), 17–24.
Walsh, C., MacMillan, H., & Jamieson, E. (2002). The relationship between parental psychiatric disorder and child physical and sexual abuse: Findings from the Ontario Health Supplement. Child Abuse and Neglect, 26(1), 11–22. doi:10.1016/S0145-2134(01)00308-8.
Weatherburn, D., & Lind, B. (2006). What mediates the macro-level effects of economic and social stress on crime? Australian and New Zealand Journal of Criminology, 39(3), 384–397. doi:10.1375/acri.39.3.384.
Wei, H. S., & Chen, J. K. (under review). Filicide-suicide ideation among Taiwanese parents with school-aged children: Prevalence and associated factors.
Wei, M., Liao, K., Heppner, P., Chao, R., & Ku, T. (2012). Forbearance coping, identification with heritage culture, acculturative stress, and psychological distress among Chinese international students. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 59(1), 97–106. doi:10.1037/a0025473.
Wilson, S., & Durbin, C. (2010). Effects of paternal depression on fathers’ parenting behaviors: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 30(2), 167–180. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.10.007.
Ye, S., Leung, T., & Mok, B. (2011). Measuring mutual help willingness and criteria among Hong Kong people: Confirmatory factor analyses. Social Indicators Research, 103(1), 119–130. doi:10.1007/s11205-010-9700-x.
Yu, D. F., & Lee, D. F. (2012). Do medically unexplained somatic symptoms predict depression in older Chinese? International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 27(2), 119–126. doi:10.1002/gps.2692.
Yue, X. (2001). Culturally constructed coping among university students in Beijing. Journal of Psychology in Chinese Societies, 2(1), 119–137.
Zhang, J., & Wang, M. (2009). Relationships among mothers’ mental health, parenting behavior and preschool children’s anxiety. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 23(5), 353–357.
Zielinski, D. (2009). Child maltreatment and adult socioeconomic well-being. Child Abuse and Neglect, 33(10), 666–678.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, HS., Chen, JK. The Relationships Between Family Financial Stress, Mental Health Problems, Child Rearing Practice, and School Involvement Among Taiwanese Parents with School-Aged Children. J Child Fam Stud 23, 1145–1154 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9772-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9772-8