Abstract
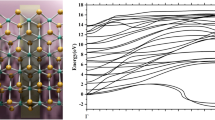
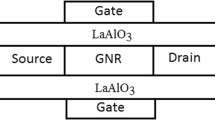
Physisorption of hydrogen molecules on armchair germanene nanoribbon (GeNR) is studied with density functional methods. The adsorption geometries, adsorption energies and transferred charge are obtained. To take the Van der Waals forces into account, the Grimme correction is added to the calculation method. The physisorption effect on the electrical properties of the ribbon is explored as a function of \(\hbox {H}_{2}\) concentration through the Green’s function techniques. Sensing features of the GeNR are investigated as a channel of a back gated field effect transistor. The optical properties of the nanoribbon are obtained for parallel and perpendicular polarizations. The results point out that, the germanene is a suitable substrate for \(\hbox {H}_{2}\) encapsulation. Moreover, \(\hbox {H}_{2}\) physisorption can improve the I–V characteristics and suppress the optical spectrum of the GeNR. The current through the nanoribbon increases by increasing \(\hbox {H}_{2}\) concentration at the same bias voltage. Also, the germanene back gated FET improve the sensing properties. The results show that the GeNR dielectric function is anisotropic and the GeNR becomes more transparent by increasing \(\hbox {H}_{2}\) density. Finally, by applying the spin-orbit coupling (SOC) effect, the obtained results are re-calculated and the changes in the results are studied. The SOC opens up the electronic band gap of the GeNR about 20 meV and increases the current slightly through the GeNR.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Y., Yeow, J.T.W.: A review of carbon nanotubes-based gas sensors. J. Sens. 2009, Article ID 493904 (2009)
Guzmn-Verri, G.G., Voon, L.C.L.Y.: Electronic structure of silicon-based nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 76, 075131 (2007)
Lebègue, S., Eriksson, O.: Electronic structure of two-dimensional crystals from ab initio theory. Phys. Rev. B 79, 115409 (2009)
Brumfiel, G.: Sticky problem snares wonder material. Nature 495, 153 (2013)
Vogt, P., De Padova, P., Quaresima, C., Avila, J., Frantzeskakis, E., Asensio, M.C., Resta, A., Ealet, B., Le Lay, G.: Silicene: compelling experimental evidence for graphene like two-dimensional silicon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 15550 (2012)
Fleurence, A., Friedlein, R., Osaki, T., Kawai, H., Wang, Y., Yamada-Takamura, Y.: Experimental evidence for epitaxial silicene on diboride thin films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 245501 (2012)
Cahangirov, S., Topsakal, M., Akturk, E., Sahin, H., Ciraci, S.: Two- and one-dimensional honeycomb structures of silicon and germanium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 236804 (2009)
Takeda, K., Shiraishi, K.: Theoretical possibility of stage corrugation in Si and Ge analogs of graphite. Phys. Rev. B 50, 14916 (1994)
Vogt, P., De Padova, P., Quaresima, C., Avila, J., Frantzeskakis, E., Asensio, M.C., Resta, A., Ealet, B., Le Lay, G.: Silicene: compelling experimental evidence for graphene like two-dimensional silicon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 155501 (2012)
Bianco, E., Butler, S., Jiang, S., Restrepo, O.D., Windl, W., Goldberger, J.E.: Stability and exfoliation of germanane: a germanium graphane analogue. ACS Nano 7, 4414–4421 (2013)
Acun, A., Zhang, L., Bampoulis, P., Farmanbar, M., Van Houselt, A., Rudenko, A.N., Lingenfelder, M., Brocks, G., Poelsema, B., Katsnelson, M.I., Zandvliet, H.J.W.: Germanene: the germanium analogue of graphene. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 27, 443002 (2015)
Nijamudheen, A., Bhattacharjee, R., Choudhury, S., Datta, A.: Electronic and chemical properties of germanene: the crucial role of buckling. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(7), 3802–3809 (2015)
Liu, C.-C., Feng, W., Yao, Y.: Quantum Spin Hall effect in silicene and two-dimensional germanium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 076802 (2011)
Liu, C.C., Jiang, H., Yao, Y.: Low-energy effective Hamiltonian involving spin-orbit coupling in silicene and two-dimensional germanium and tin. Phys. Rev. B 84, 195430 (2011)
Matthes, L., Pulci, O., Bechstedt, F.: Massive Dirac quasi-particles in the optical absorbance of graphene, silicene, germanene, and tinene. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 25, 395305 (2013)
Kaloni, T.P., Modarresi, M., Tahir, M., Rezaee Roknabadi, M., Schreckenbach, G., Freund, M.S.: Electrically engineered band gap in two-dimensional Ge, Sn, and Pb: a first-principles and tight-binding approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(21), 11896–11902 (2015)
Liu, H., Gao, J., Zhao, J.: Silicene on substrates: a way to preserve or tune its electronic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 10353–10359 (2013)
Dell’Angela, M., et al.: Relating energy level alignment and amine-linked single molecule junction conductance. Nano Lett. 10, 2470–2474 (2010)
Venkataraman, L., Klare, J.E., Tam, I.W., Nuckolls, C., Hybertsen, M.S., Steigerwald, M.L.: Single-molecule circuits with well-defined molecular conductance. Nano Lett. 6, 458–462 (2006)
Mowbray, D.J., Jones, G., Thygesen, K.S.: Influence of functional groups on charge transport in molecular junctions. J. Chem. Phys. 128, 111103 (2008)
Zhao, J., et al.: Gas molecule adsorption in carbon nanotubes. Nanotechnology 13, 195 (2002)
Matthes, L., Pulci, O., Bechstedt, F.: Optical properties of two-dimensional honeycomb crystals graphene, silicene, germanene, and tinene from first principles. N. J. Phys. 16, 105007 (2014)
Perdew, J.P., Burke, K., Wang, Y.: Generalized gradient approximation for the exchange-correlation hole of a many electron system. Phys. Rev. B 54, 16533–16539 (1996)
Perdew, J.P., Chevary, J.A., Vosko, S.H., Jackson, K.A., Pederson, M.R., Singh, D.J., Fiolhais, C.: Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation. Phys. Rev. B 46, 6671–6687 (1992)
Troullier, N., Martins, J.L.: Efficient pseudopotentials for planewave calculations. Phys. Rev. B 43, 1993–2006 (1991)
Giannozzi, P., et al.: QUANTUM ESPRESSO: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 21, 395502–19 (2009)
Grimme, S.: Semi-empirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correlation. J. Comput. Chem. 27, 1787 (2006)
Barone, V., et al.: Role and effective treatment of dispersive forces in materials: polyethylene and graphite crystals as test cases. J. Comput. Chem. 30, 934 (2009)
Soler, J.M., Artacho, E., Gale, J.D., Garcıa, A., Junquera, J., Ordejon, P., Portal, D.S.: The SIESTA method for ab initio order N materials simulation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 14, 2745–2779 (2002)
Monkhorst, H.J., Pack, J.D.: Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 13, 5188–5192 (1976)
Löwdin, P.-O.: Quantum theory of many-particle systems. I. Physical Interpretations by means of density matrices, natural spin-orbitals, and convergence problems in the method of configurational interaction. Phys. Rev. 97, 1474 (1955)
Brandbyge, M., Mozos, J.L., Ordejon, P., Taylor, J., Stokbro, K.: Density functional method for nonequilibrium electron transport. Phys. Rev. B 65, 165401 (2002)
Heyd, J.G., Scuseria, E., Ernzerhof, M.J.: Hybrid functionals based on a screened Coulomb potential. Chem. Phys. 118, 8207–8215 (2003)
Heyd, J.G., Scuseria, E., Ernzerhof, M.J.: Erratum. Hybrid functionals based on a screened Coulomb potential. Chem. Phys. 124, 219906 (2006)
Tsai, W., Huang, C., Chang, T., Lin, H., Jeng, H., Bansil, A.: Gated silicene as a tunable source of nearly 100% spin-polarized. Electrons. Nat. Commun. 4, 1500 (2013)
Ambrosch-Draxl, C., Sofo, J.O.: Linear optical properties of solids within the full-potential linearized augmented planewave method. Comput. Phys. Commun. 175, 1–14 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayani, A.H., Dideban, D. & Moezi, N. Hydrogen sensitive field-effect transistor based on germanene nanoribbon and optical properties of hydrogenated germanene. J Comput Electron 15, 381–388 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0797-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0797-2