Abstract
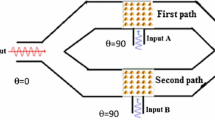
In this paper, a coherent perfect absorption (CPA)-type AND gate based on plasmonic nano particles is proposed. It consists of two gold nano sphere arrays on top of two serial arms with quartz substrate. The operation principle is based on the absorbable formation of a conductive path in the dielectric layer of a plasmonic nano-particle waveguide. Since the CPA efficiency depends strongly on the number of gold nano-sphere and the locations of nano-spheres, an efficient binary optimization method based the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm is used to design an optimized array of the plasmonic nano-sphere in order to achieve the maximum absorption coefficient in the ‘off’ state and the minimum absorption coefficient in the ‘on’ state. In Binary PSO, a group of birds consists a matrix with binary entries, control the presence (‘1’) or the absence (‘0’) of nano sphere in the array.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maier, S.A., Mark, L.B., Pieter, G.K., Scheffer, M., Ari, A.G.R., Harry, A.A.: Plasmonics—a route to nanoscale optical devices. Adv. Mater. 13, 1501–1505 (2001)
Tuchscherer, P., Christian, R., Dmitri, V.V., Javier, G.D.A., Walter, P., Tobias, B.: Analytic coherent control of plasmon propagation in nanostructures. Opt. Express 17, 14235–14259 (2009)
Giannini, V., Antonio, I., Fernández, D., Yannick, S., Tyler, R., Roberto, F., Stefan, A.M.: Controlling light localization and light-matter interactions with nanoplasmonics. Small 6, 2498–2507 (2010)
Schuller, J.A., Edward, S.B., Wenshan, C., Young, C.J., Justin, S.W., Mark, L.B.: Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation. Nat. Mater. 9, 193–204 (2010)
Gramotnev, D.K., Sergey, I.B.: Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat. Photonics 4, 83–91 (2010)
Dolatabady, A., Nosrat, G.: All optical logic gates based on two dimensional plasmonic waveguides with nanodisk resonators. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 16, 432–442 (2012)
Jafarian, B., Najmeh, N., Nosrat, G.: Analysis of a triangular-shaped plasmonic metal–insulator–metal Bragg grating waveguide. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 15, 118–123 (2011)
Lu, H., Xueming, L., Yongkang, G., Leiran, W., Dong, M.: Multi-channel plasmonic waveguide filters with disk-shaped nanocavities. Opt. Commun. 284, 2613–2616 (2011)
Setayesh, A., Sayyed, R.M., Mohammad, S.A.: Numerical investigation of tunable band-pass\(\backslash \) band-stop plasmonic filters with hollow-core circular ring resonator. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 15, 82–89 (2011)
Wang, G., Lu, H., Liu, X., Mao, D., Duan, L.: Tunable multi-channel wavelength demultiplexer based on MIM plasmonic nanodisk resonator at telecommunication regime. Opt. Express. 19, 3513–3518 (2011)
Lu, Z., Zhao, W.: Nanoscale electro-optic modulators based on grapheme-slot waveguides. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29, 1490–1496 (2012)
Kim, S.H., Young, T.B., Doo, G.K., Nadir, D., Young, C.C.: Widely tunable coupled-ring reflector laser diode consisting of square ring resonators. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 14, 38–41 (2010)
Farahani, M., Nosrat, G., Mohammad, R.: Broadband zero reflection plasmonic junctions. JOSA B 29, 1722–1730 (2012)
Jung, J.H., Kim, Min-Wook: Optimal design of fiber-optic surface plasmon resonance sensors. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 11(2), 55–58 (2007)
Byun, K.M.: Development of nanostructured plasmonic substrates for enhanced optical biosensing. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 14, 65–76 (2010)
Lu, H., Xueming, L., Leiran, W., Yongkang, G., Dong, M.: Ultrafast all-optical switching in nanoplasmonic waveguide with Kerr nonlinear resonator. Opt. Express 19, 2910–2915 (2011)
Wei, H., Zhuoxian, W., Xiaorui, T., Mikael, K., Hongxing, X.: Cascaded logic gates in nanophotonic plasmon networks. Nat. Commun. 2, 387 (2011)
Maksymov, I.S.: Optical switching and logic gates with hybrid plasmonic-photonic crystal nanobeam cavities. Phys. Lett. A 375, 918–921 (2011)
Oh, G.Y., Doo, G.K., Young, W.C.: All-optical logic gate using waveguide-type SPR with Au/ZnO plasmon stack. In: IEEE OptoElectronics and Communications Conference (OECC), 2010 15th, pp. 374–375 (2010)
Xu, Q., Michal, L.: All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators. Opt. Express 15, 924–929 (2007)
Liang, T.K., Nunes, L.R.M., Tsuchiya, K.S., Abedin, T.M., Dries, V.T., Walter, B., Pieter, D., Roel, B., Tsang, H.K.: High speed logic gate using two-photon absorption in silicon waveguides. Opt. Commun. 265, 171–174 (2006)
Kim, J.H., Byoung, K.K., Yoon, H.P., Young, T.B., Seok, L., Deok, H.W., Sun, H.K.: All-optical AND gate using XPM wavelength converter. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 5, 25–28 (2001)
Kaur, S., Kaler, Rajinder S.: Ultrahigh speed reconfigurable logic operations based on single semiconductor optical amplifier. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 16, 13–16 (2012)
Yabu, T., Masahiro, G., Toshiaki, K., Kazuhiro, N., Shinnosuke, S.: All-optical logic gates containing a two-mode nonlinear waveguide. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 38, 37–46 (2002)
Pramono, Y.H., Endarko, : Nonlinear waveguides for optical logic and computation. J. Nonlinear Opt. Phys. Mater. 10, 209–222 (2001)
Akhlaghi, M., Emami, F., Najmeh, N.: TLBO algorithm assisted for designing plasmonic nano particles based absorptio coefficient. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater.-Rapid Commun. 8, 845–848 (2014)
Akhlaghi, M., Emami, F., Najmeh, N.: Binary TLBO algorithm assisted for designing plasmonic nano bi-pyramids-based absorption coefficient. J. Modern Opt. 61, 1092–1096 (2014)
Akhlaghi, M., Najmeh, N., Emami, F.: Investigating the optical switch using dimer plasmonic nano-rods. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 13, 1172–1175 (2014)
Taflove, A., Morris, E.B.: Numerical solution of steady-state electromagnetic scattering problems using the time-dependent Maxwell’s equations. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 23, 623–630 (1975)
Weiland, T.: A discretization model for the solution of Maxwell’s equations for six-component fields. Archiv Elektronik und Uebertragungstechnik 31, 116–120 (1977)
Harrington, R.F., Jan, L.H.: Field Computation by Moment Methods. Oxford University Press, New York (1996)
Kern, A.M., Olivier, J.M.: Surface integral formulation for 3D simulations of plasmonic and high permittivity nanostructures. JOSA A 26, 732–740 (2009)
Gallinet, B., Andreas, M.K., Olivier, J.M.: Accurate and versatile modeling of electromagnetic scattering on periodic nanostructures with a surface integral approach. JOSA A 27, 2261–2271 (2010)
Taboada, J.M., Javier, R., Fernando, O., Marta, G.A., Luis, L.: Method-of-moments formulation for the analysis of plasmonic nano-optical antennas. JOSA A 28, 1341–1348 (2011)
Taflove, A., Susan, C.H.: Computational Electrodynamics: The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method, 2nd edn. Artech House, Norwood (1995)
Jin, J.M.: The Finite Element Method in Electromagnetics, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2002)
Draine, B.T., Piotr, J.F.: Discrete-dipole approximation for scattering calculations. JOSA A 11, 1491–1499 (1994)
Forestiere, C., Giovanni, M., Svetlana, V.B., Luca, D.N.: The role of nanoparticle shapes and deterministic aperiodicity for the design of nanoplasmonic arrays. Opt. Express 17, 9648–9661 (2009)
Bohren, C.F., Donald, R.H.: Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles. Wiley, Hoboken (2008)
Loke, V.L.Y., Mengüç, M.P., Timo, A.N.: Discrete-dipole approximation with surface interaction: Computational toolbox for MATLAB. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 112, 1711–1725 (2011)
Emami, F., Akhlaghi, M.: Gain ripple decrement of S-band raman amplifiers. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 24, 1349–1352 (2012)
Akhlaghi, M., Emami, F.: Fuzzy adaptive modified PSO-algorithm assisted to design of photonic crystal fiber Raman amplifier. J. Opt. Soc. Korea. 17, 237–241 (2013)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.C.: Discrete binary version of the particle swarm algorithm. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (IEEE, 1997), Vol. 5, pp. 4104–4108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaboli, M., Akhlaghi, M. Investigating the optical AND gate using plasmonic nano-spheres. J Comput Electron 15, 295–300 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-015-0747-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-015-0747-4