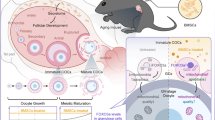
Abstract
Purpose
To assess the impact of peritoneal endometriosis on oocyte and embryo quality in a mouse model.
Methods
Peritoneal endometriosis was surgically induced in 33 B6CBA/F1 female mice (endometriosis group, N = 17) and sham-operated were used as control (sham group, N = 16). Mice were superovulated 4 weeks after surgery and mated or not, to collect E0.5-embryos or MII-oocytes. Evaluation of oocyte and zygote quality was done by immunofluorescence under spinning disk confocal microscopy.
Results
Endometriosis-like lesions were observed in all mice of endometriosis group. In both groups, a similar mean number of MII oocytes per mouse was observed in non-mated mice (30.2 vs 32.6), with a lower proportion of normal oocytes in the endometriosis group (61 vs 83 %, p < 0.0001). Abnormalities were incomplete extrusion or division of the first polar body and spindle abnormalities. The mean number of zygotes per mouse was lower in the endometriosis group (21 vs 35.5, p = 0.02) without difference in embryo quality.
Conclusions
Our results support that induced peritoneal endometriosis in a mouse model is associated with a decrease in oocyte quality and embryo number. This experimental model allows further studies to understand mechanisms of endometriosis-associated infertility.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Endometriosis and infertility. Fertil Steril. 2004;82 Suppl 1:S40–5.
Witz CA, Burns WN. Endometriosis and infertility: is there a cause and effect relationship? Gynecol Obstet Investig. 2002;53 Suppl 1:2–11.
Porpora MG, Pultrone DC, Bellavia M, Franco C, Crobu M, Cosmi EV. Reproductive outcome after laparoscopic treatment of endometriosis. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2002;29:271–3.
Jacobson TZ, Duffy JM, Barlow D, Farquhar C, Koninckx PR, Olive D. Laparoscopic surgery for subfertility associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010: CD001398.
Marcoux S, Maheux R, Berube S. Laparoscopic surgery in infertile women with minimal or mild endometriosis. Canadian collaborative group on endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:217–22.
Parazzini F. Ablation of lesions or no treatment in minimal-mild endometriosis in infertile women: a randomized trial. Gruppo Italiano per lo studio dell’Endometriosi. Hum Reprod. 1999;14:1332–4.
Halme J, Becker S, Hammond MG, Raj MH, Raj S. Increased activation of pelvic macrophages in infertile women with mild endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983;145:333–7.
Rana N, Braun DP, House R, Gebel H, Rotman C, Dmowski WP. Basal and stimulated secretion of cytokines by peritoneal macrophages in women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1996;65:925–30.
Wang Y, Sharma RK, Falcone T, Goldberg J, Agarwal A. Importance of reactive oxygen species in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis or idiopathic infertility. Fertil Steril. 1997;68:826–30.
Oosterlynck DJ, Meuleman C, Waer M, Vandeputte M, Koninckx PR. The natural killer activity of peritoneal fluid lymphocytes is decreased in women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1992;58:290–5.
Yoshida S, Harada T, Iwabe T, Taniguchi F, Mitsunari M, Yamauchi N, et al. A combination of interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor impairs sperm motility: implications in infertility associated with endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:1821–5.
Mansour G, Aziz N, Sharma R, Falcone T, Goldberg J, Agarwal A. The impact of peritoneal fluid from healthy women and from women with endometriosis on sperm DNA and its relationship to the sperm deformity index. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:61–7.
Perdichizzi A, Nicoletti F, La Vignera S, Barone N, D’Agata R, Vicari E, et al. Effects of tumour necrosis factor-alpha on human sperm motility and apoptosis. J Clin Immunol. 2007;27:152–62.
Mansour G, Sharma RK, Agarwal A, Falcone T. Endometriosis-induced alterations in mouse metaphase II oocyte microtubules and chromosomal alignment: a possible cause of infertility. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:1894–9.
Banerjee J, Sharma R, Agarwal A, Maitra D, Diamond MP, Abu-Soud HM. IL-6 and mouse oocyte spindle. PLoS One. 2012;7:e35535.
Piromlertamorn W, Saeng-anan U, Vutyavanich T. Effects of ovarian endometriotic fluid exposure on fertilization rate of mouse oocytes and subsequent embryo development. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2013;11:4.
Moon CE, Bertero MC, Curry TE, London SN, Muse KN, Sharpe KL, et al. The presence of luteinized unruptured follicle syndrome and altered folliculogenesis in rats with surgically induced endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:676–82.
Stilley JA, Woods-Marshall R, Sutovsky M, Sutovsky P, Sharpe-Timms KL. Reduced fecundity in female rats with surgically induced endometriosis and in their daughters: a potential role for tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase 1. Biol Reprod. 2009;80:649–56.
Pal AK, Biswas S, Goswami SK, Kabir SN. Effect of pelvic endometrial implants on overall reproductive functions of female rats. Biol Reprod. 1999;60:954–8.
Vernon MW, Wilson EA. Studies on the surgical induction of endometriosis in the rat. Fertil Steril. 1985;44:684–94.
Barragan JC, Brotons J, Ruiz JA, Acien P. Experimentally induced endometriosis in rats: effect on fertility and the effects of pregnancy and lactation on the ectopic endometrial tissue. Fertil Steril. 1992;58:1215–9.
Furukubo M, Fujino Y, Umesaki N, Ogita S. Effects of endometrial stromal cells and peritoneal fluid on fertility associated with endometriosis. Osaka City Med J. 1998;44:43–54.
Umezawa M, Saito Y, Tanaka-Hattori N, Takeda K, Ihara T, Sugamata M. Expression profile of extracellular matrix and adhesion molecules in the development of endometriosis in a mouse model. Reprod Sci. 2012;19:1365–72.
Han SJ, Hawkins SM, Begum K, Jung SY, Kovanci E, Qin J, et al. A new isoform of steroid receptor coactivator-1 is crucial for pathogenic progression of endometriosis. Nat Med. 2012;18:1102–11.
Laschke MW, Giebels C, Nickels RM, Scheuer C, Menger MD. Endothelial progenitor cells contribute to the vascularization of endometriotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:442–50.
Becker CM, Beaudry P, Funakoshi T, Benny O, Zaslavsky A, Zurakowski D, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells are up-regulated in a mouse model of endometriosis. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:1782–91.
Fang Z, Yang S, Gurates B, Tamura M, Simpson E, Evans D, et al. Genetic or enzymatic disruption of aromatase inhibits the growth of ectopic uterine tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:3460–6.
Rudzitis-Auth J, Menger MD, Laschke MW. Resveratrol is a potent inhibitor of vascularization and cell proliferation in experimental endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2013;28:1339–47.
Pelch KE, Sharpe-Timms KL, Nagel SC. Mouse model of surgically-induced endometriosis by auto-transplantation of uterine tissue. J Vis Exp. 2012: e3396.
Eroglu A, Toth TL, Toner M. Alterations of the cytoskeleton and polyploidy induced by cryopreservation of metaphase II mouse oocytes. Fertil Steril. 1998;69:944–57.
Schatten G, Simerly C, Schatten H. Microtubule configurations during fertilization, mitosis, and early development in the mouse and the requirement for egg microtubule-mediated motility during mammalian fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985;82:4152–6.
Boiso I, Marti M, Santalo J, Ponsa M, Barri PN, Veiga A. A confocal microscopy analysis of the spindle and chromosome configurations of human oocytes cryopreserved at the germinal vesicle and metaphase II stage. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:1885–91.
Choi WJ, Banerjee J, Falcone T, Bena J, Agarwal A, Sharma RK. Oxidative stress and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced alterations in metaphase II mouse oocyte spindle structure. Fertil Steril. 2007;88:1220–31.
Tarin JJ, Vendrell FJ, Ten J, Blanes R, van Blerkom J, Cano A. The oxidizing agent tertiary butyl hydroperoxide induces disturbances in spindle organization, c-meiosis, and aneuploidy in mouse oocytes. Mol Hum Reprod. 1996;2:895–901.
Richter HE, Holley RL, Andrews WW, Owen J, Miller KB. The association of interleukin 6 with clinical and laboratory parameters of acute pelvic inflammatory disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;181:940–4.
Bedaiwy MA, Falcone T, Sharma RK, Goldberg JM, Attaran M, Nelson DR, et al. Prediction of endometriosis with serum and peritoneal fluid markers: a prospective controlled trial. Hum Reprod. 2002;17:426–31.
Ebner T, Moser M, Yaman C, Feichtinger O, Hartl J, Tews G. Elective transfer of embryos selected on the basis of first polar body morphology is associated with increased rates of implantation and pregnancy. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:599–603.
De Santis L, Cino I, Rabellotti E, Calzi F, Persico P, Borini A, et al. Polar body morphology and spindle imaging as predictors of oocyte quality. Reprod BioMed Online. 2005;11:36–42.
Rienzi L, Ubaldi FM, Iacobelli M, Minasi MG, Romano S, Ferrero S, et al. Significance of metaphase II human oocyte morphology on ICSI outcome. Fertil Steril. 2008;90:1692–700.
Choi T, Fukasawa K, Zhou R, Tessarollo L, Borror K, Resau J, et al. The Mos/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway regulates the size and degradation of the first polar body in maturing mouse oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:7032–5.
Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Peng H, et al. Hormonal regulation of ovarian bursa fluid in mice and involvement of aquaporins. PLoS One. 2013;8:e63823.
Rodriguez A, Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Garcia-Navarro S, Rotellar F, Valenti V, et al. Insulin- and leptin-mediated control of aquaglyceroporins in human adipocytes and hepatocytes is mediated via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:E586–97.
Shahine LK, Burney RO, Behr B, Milki AA, Westphal LM, Lathi RB. Embryo quality before and after surgical treatment of endometriosis in infertile patients. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2009;26:69–73.
Brizek CL, Schlaff S, Pellegrini VA, Frank JB, Worrilow KC. Increased incidence of aberrant morphological phenotypes in human embryogenesis–an association with endometriosis. J Assist Reprod Genet. 1995;12:106–12.
Pellicer A, Oliveira N, Ruiz A, Remohi J, Simon C. Exploring the mechanism(s) of endometriosis-related infertility: an analysis of embryo development and implantation in assisted reproduction. Hum Reprod. 1995;10 Suppl 2:91–7.
Grummer R. Animal models in endometriosis research. Hum Reprod Update. 2006;12:641–9.
Colette S, Donnez J. Animal models in endometriosis experimental research. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2012;40:494–6.
Ertzeid G, Storeng R. The impact of ovarian stimulation on implantation and fetal development in mice. Hum Reprod. 2001;16:221–5.
Rajkumar K, Schott PW, Simpson CW. The rat as an animal model for endometriosis to examine recurrence of ectopic endometrial tissue after regression. Fertil Steril. 1990;53:921–5.
Acknowledgments
We thank Romain Morichon for the use of the spinning disk confocal microscopy, Michele Oster for the histology, Lauriane Roche for her help in building the figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Capsule In a mouse model, peritoneal endometriosis was responsible for decrease in oocyte quality and embryo quantity. Number of ovulated oocytes was not impaired.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, J., Ziyyat, A., Naoura, I. et al. Effect of induced peritoneal endometriosis on oocyte and embryo quality in a mouse model. J Assist Reprod Genet 32, 263–270 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-014-0390-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-014-0390-1