Purpose: This study investigated the effects of HB-EGF on expression of integrin \(\alpha\nu\beta\hbox{{\it 3}}\) and implantation of embryos.
Methods: Two-cell embryos were recovered and cultured with or without 10 ng/mL HB-EGF for 96h. Expression of integrin \(\alpha\nu\beta\hbox{{\it 3}}\) in cultured embryos was examined by real time-RT-PCR and immunofluorescence analysis; embryos were cultured with or without HB-EGF, then transferred into the uteri of pseudo-pregnant female mice in order to analyze their implantation rate.
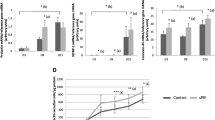
Results: HB-EGF improved embryonic hatching and outgrowth during extended culture, and up-regulated expression of integrin \(\alpha\nu\beta\hbox{{\it 3}}\) in both the preimplantation embryo and outgrowing blastocyst. Also, integrin \(\alpha\nu\beta\hbox{{\it 3}}\) subunits were localized at the pericellular borders and cell–cell contact areas. The number of successful implantation sites of transferred HB-EGF-treated embryos in the uterus was increased when compared to number of implantation sites with non-treated controls.
Conclusions: HB-EGF may improve implantation by accelerating expression of integrin \(\alpha\nu\beta\hbox{{\it 3}}\) in peri-implantation mouse embryos.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tamada H, Higashiyama C, Takano H, Kwate N, Inaba T, Sawada T: The effect of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor on preimplantation-embryo development and implantation in the rat. Life Sci. 1999;64:1967– 1973
Higashiyama S, Abraham JA, Miller J, Fiddes JC, Klagsbrun M: A heparin-binding growth factor secreted by macrophage-like cells that is related to EGF. Science 1991;251:936– 939
Das SK, Wang XN, Paria BC, Damm D, Abraham JA, Klagsbrun M, Andrews GK, and Dey SK: Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor gene is induced in the mouse uterus temporally by the blastocyst solely at the site of its apposition: a possible ligand for interaction with blastocyst EGF-receptor in implantation. Development 1994;120:1071–1083
Aviezer D, Yayon A: Heparin-dependent binding and auto-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor by heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor but not EGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1994;91:12173–12177
Paria BC, Elenius K, Klagsbrun M, Dey SK: HB-EGF interacts with mouse blastocysts independently of ErbB1: A possible role for heparin sulfate proteoglycans and ErbB4 in blastocyst implantation. Development 1999;126:1997–2005
Paria BC, Huet-Hudson YM, Das SK: Blastocyst's state of activity determines the “window” of implantation in the receptive mouse uterus. Dev Biol 1993;90:10159–10162
Sutherland AE, Calarco PG, Damsky CH: Developmental regulation of integrin expression at the time of implantation in the mouse embryo. Development 1993;119:1175–1186
Albelda SM, Buck CA: Integrins and other cell adhesion molecules. FASEB J 1990;11:2868–2880
Tabibzadeh S: Patterns of expression of integrin molecules in human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle. Hum Reprod 1992;6:876–882
Lessey BA: Regulated expression of HB-EGF in the human endometrium: a potential paracrine role during implantation. Mol Reprod Dev 2002;62:446–455
Simon C, Martin JC, Pellicer A: Paracrine regulators of implantation. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2000;14(5):815–826
Hierck BP, Thorsteinsdottir S, Niessen CM, Freund E, Iperen LV, Feyen A, Hogervorst F, Poelmann RE, Mummery CL, Sonnenberg A: Variants of the alpha 6 beta 1 laminin receptor in early murine development: distribution, molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of the mouse integrin alpha 6 subunit. Cell Adhes Commun 1993;1:33–53
Cullinan E, Illera MJ, Gui Y, Yuan L, Beyler SA, Lessey BA: Blockade of the alpha(v)beta(3) integrin adversely affects implantation in the mouse. Biol Reprod 2000;62:1285–1290
Somkuti SG, Yuan L, Fritz MA, Lessey BA: Epidermal growth factor and sex steroids dynamically regulate a marker of endome-trial receptivity in ishikawa cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997;82:2192–2197
Apparao KBC, Murray MJ, Fritz MA, Meyer WR, Chambers AF, Truong PL, Lessey BA: Osteopontin and its receptor αvβ3 integrin are co expressed in the human endometrium during the menstrual cycle but regulated differentially. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:4991–5000
Hong SH, Nah HY, Lee JY, Kim JH, Kim CH, Chea HD, Kang BM, Kim MK: Effect of heparin-binding growth factor on the expression of MMP-9 and ATPase γ-subunit mRNA in the mouse embryo. Kor J Fertil Steril 2001;28:87–93
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001;25:402–408
Seshagiri PB, Mishra A, Ramesh G, Rao RP: Regulation of peri-implantation embryo development in golden hamster: role of growth factors. J Reprod Immunol. 2002;53:203–213
Martin KL, Barlow DH, Sargent IL: HB-EGF significantly improves human blastocyst development and hatching in serum-free medium. Hum Reprod 1998:13:1645–1652
Narita T, Kawakami-Kimura N, Sato M, Matsuura N, Higashiyama S, Taniguchi N, Kannagi R: Alteration of integrins by heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in human breast cancer cells. Oncology 1996;53:374–381.
Yoshimura M, Nishikawa A, Nishiura T, Ihara Y, Kanayama Y, Matsuzawa Y, Taniguchi N: Cell spreading in Colo 201 by staurosporin is alpha 3 beta 1 integrin-mediated with tyrosine phosphorylation of Src and tensin. J Biol Chem 1995;270(5):2298–2304
Lim H, Das SK, Dey SK: ErbB genes in the mouse uterus: cell-specific signaling by epidermal growth factor (EGF) family of growth factors during implantation. Dev Biol 1998;204:97–110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J.J. Lim and D.R. Lee contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, J.J., Lee, D.R., Song, HS. et al. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) may improve embryonic development and implantation by increasing vitronectin receptor (integrin ανβ3) expression in peri-implantation mouse embryos. J Assist Reprod Genet 23, 111–119 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-006-9021-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-006-9021-9