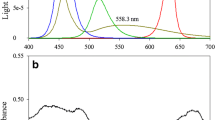
Abstract
The strategy of light environment control was applied to improve biomass and extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) production of the cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme by adjusting multiple wavelengths (red 660 nm, blue 460 nm, green 520 nm) and light intensity assisted by nitrogen source optimization. A mixed wavelength with low light intensity was more suitable for cell growth. Wavelength shift approach, i.e., manipulation of light wavelength at appropriate culture stages, increased both biomass and EPS production, and optimum shift time was at 9 days. The effects of four nitrogen sources under different light conditions were subsequently evaluated, and urea showed the best performance. The optimized wavelength shift approach (9-day illumination with white light followed by 9-day culture with mixed wavelengths of red/blue/green = 12:5:5) with urea as nitrogen source improved the biomass from 0.72 ± 0.02 to 1.20 ± 0.02 g L−1 (i.e., by 66 %) and EPS production from 27.31 ± 1.00 to 86.65 ± 2.56 mg L−1 (i.e., by 217.3 %). These results provide information on novel culture strategies for microalgal biotechnology by applying light environment control.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atta M, Idris A, Bukhari A, Wahidin S (2013) Intensity of blue LED light: a potential stimulus for biomass and lipid content in fresh water microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour Technol 148:373–378
Beardall J, Raven JA (2016) Carbon acquisition by microalgae. In: Borowitzka MA, Beardall J, Raven JA (eds) The physiology of microalgae. Springer, Dordrecht, pp. 89–90
Cheng Y, Zheng Z (2014) Performance of mixed LED light wavelengths on biogas upgrade and biogas fluid removal by microalga Chlorella sp. Appl Energy 113:1008–1014
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306
David MK (2010) Chromatic adaptation and the evolution of light color sensing in cyanobacteria. Proc Nat Acad Sci 107:9029–9030
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Gao KS (1998) Chinese studies on edible blue-green alga, Nostoc flagelliforme: a review. J Appl Phycol 10:37–49
Han PP, Sun Y, Jia SR, Zhong C, Tan ZL (2014b) Effects of light wavelengths on extracellular and capsular polysaccharide production by Nostoc flagelliforme. Carbohyd Polym 105:145–151
Han PP, Sun Y, XY W, Yuan YJ, Dai YJ, Jia SR (2014a) Emulsifying, flocculating, and physicochemical properties of exopolysaccharide produced by cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:36–49
Han PP, Shen SG, Wang HY, Sun Y, Dai YJ, Jia SR (2015) Comparative metabolomic analysis of the effects of light quality on polysaccharide production of cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme. Algal Res 9:143–150
Hase R, Oikawa H, Sasao C, Morita M, Watanabe Y (2000) Photosynthetic production of microalgal biomass in a raceway system under green house conditions in Sendai city. J Biosci Bioeng 89:157–163
Kanekiyo K, Lee JB, Hayashi K, Takenaka H, Hayakawa Y, Endo S, Hayashi T (2005) Isolation of an antiviral polysaccharide, nostoflan, from a terrestrial cyanobacterium, Nostoc flagelliforme. J Nat Prod 68:1037–1041
Kim TH, Lee Y, Han SH, Hwang SJ (2013) The effects of wavelength and wavelength mixing ratios on microalgae growth and nitrogen, phosphorus removal using Scenedesmus sp. for wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 130:75–80
Kim JK, Mao YX, Kraemer G, Yarish C (2015) Growth and pigment content of Gracilaria tikvahiae McLachlan under fluorescent and LED lighting. Aquaculture 436:52–57
Li X, HY H, Gan K, Yang J (2010) Growth and nutrient removal properties of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. LX1 under different kinds of nitrogen sources. Ecol Eng 36:379–381
Li Z, Wakao S, Fischer BB, Niyogi KK (2009) Sensing and responding to excess light. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:239–260
Liu XJ, Jiang Y, Chen F (2005) Fatty acid profile of the edible filamentous cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme at different temperatures and developmental stages in liquid suspension culture. Process Biochem 40:371–377
McNamara ME, Lonsdale DJ, Aller RC (2013) Elemental composition of Mnemiopsis leidyi A. Agassiz 1865 and its implications for nutrient recycling in a long island estuary. Estuar Coasts 36:1253–1264
Mishra SK, Shrivastav A, Maurya RR, Patidar SK, Haldar S, Sandhya M (2012) Effect of light quality on the C-phycoerythrin production in marine cyanobacteria Pseudanabaena sp. isolated from Gujarat coast, India. Protein Expres Purif 81:5–10
Murata N, Takahashi S, Nishiyama Y, Allakhverdiev SI (2007) Photoinhibition of photosystem II under environmental stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1767:414–421
Nixon PJ, Michoux F, Yu J, Boehm M, Komenda J (2010) Recent advances in understanding the assembly and repair of photosystem II. Ann Bot 106:1–16
Otero A, Vincenzini M (2003) Extracellular polysaccharide synthesis by Nostoc strains as affected by N source and light intensity. J Biotechnol 102:143–152
Parikh A, Madamwar D (2006) Partial characterization of extracellular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria. Bioresour Technol 97:1822–1827
Pereira S, Zill A, Micheletti E, Moradas-Ferreira P, Philippis RD, Tamagnini P (2009) Complexity of cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides: composition, structures, inducing factors and putative genes involved in their biosynthesis and assembly. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:917–941
Powles SB (1984) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis induced by visible light. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35:15–44
Ravelonandro PH, Ratianarivo DH, Joannis-Cassan C, Isambert A, Raherimandimby M (2008) Influence of light quality and intensity in the cultivation of Spirulina platensis from Toliara (Madagascar) in a closed system. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:842–848
Saeid A, Chojnacka K, Korczyński M, Korniewicz D, Dobrzański Z (2013) Biomass of Spirulina maxima enriched by biosorption process as a new feed supplement for swine. J Appl Phycol 25:667–675
Schitüter L, Bo R, Søndergaard M (1997) Nutrient limitation in relation to phytoplankton carotenoid/chlorophyll a ratios in freshwater mesocosms. J Plankton Res 19:891–906
Sforza E, Simionato D, Giacometti GM, Bertucco A, Morosinotto T (2012) Adjusted light and dark cycles can optimize photosynthetic efficiency in algae growing in photo bioreactors. PLoS One 7:e38975
Singh AK, Bhattacharyya-Pakrasi M, Elvitigala T, Ghosh B, Aurora R, Pakrasi HB (2009) A systems-level analysis of the effects of light quality on the metabolism of a cyanobacterium. Plant Physiol 151:1596–1608
Spolaore P, Joannis-Cassan C, Duran E, Isambert A (2006) Commercial applications of microalgae. J Biosci Bioeng 101:87–96
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. Plant Physiol 144:307–313
Yang Z, Geng LL, Wang W, Zhang J (2012) Combined effects of temperature, light intensity, and nitrogen concentration on the growth and polysaccharide content of Microcystis aeruginosa in batch culture. Biochem Syst Ecol 41:130–135
You T, Barnett SM (2004) Effect of light quality on production of extracellular polysaccharides and growth rate of Porphyridium cruentum. Biochem Eng J 19:251–258
Yun YS, Lee SB, Park JM, Lee CI, Yang JW (1997) Carbon dioxide fixation by algal cultivation using wastewater nutrients. J Chem Technol Biot 69:451–455
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31671842 and 31201405) and Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (Grant No. IRT1166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 125 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Pp., Shen, Sg., Wang, HY. et al. Applying the strategy of light environment control to improve the biomass and polysaccharide production of Nostoc flagelliforme . J Appl Phycol 29, 55–65 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0963-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0963-8