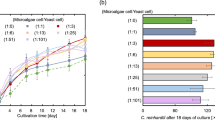
Abstract
The genus Coccomyxa comprises green microalgae, which can be found worldwide in remarkably versatile aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems including symbiotic associations with a number of different hosts. In this study, we describe a new species, Coccomyxa onubensis, based on 18S and ITS ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequence data. Coccomyxa onubensis was isolated from acidic water, and its ability to adapt to a wide range of acidic and alkaline pH values and to high salinity was analyzed. The long-term adaptation capacity of the microalga to such extreme conditions was evaluated by performing continuous repeated batches at selected salt concentrations and pH values. Adapted cultures of C. onubensis were found to yield high biomass productivities from pH 2.5 to 9, with maximum yields at acidic pH between 2.5 and 4.5. Moreover, C. onubensis was also found to adapt to salinities as high as 0.5 M NaCl, reaching biomass productivities that were similar to those of control cultures. Ultrastructural analysis by transmission electron microscopy of C. onubensis cells adapted to high salinity showed a robust response to hyperosmotic shock. Thus, C. onubensis was found to be acidotolerant and halotolerant. High biomass productivity over a wide range of pH and salinities denotes C. onubensis as an interesting candidate for various biotechnological applications including outdoor biomass production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertano P, Pinto G, Pollio A, Taddei R (1990) Morphology, ultrastructure and ecology of an acidophilic alga, Pseudococcomyxa simplex (Mainx) Fott (Chlorococcales). Algol Stud 59:81–95
Amils R, Fernández-Remolar D (2014) Río Tinto: a geochemical and mineralogical terrestrial analogue of Mars. Life 4:511–534
Balkos KD, Colman B (2007) Mechanism of CO2 acquisition in an acid-tolerant Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell Environ 30:745–752
Beardall J, Entwisle L (1984) Internal pH of the obligate acidophile Cyanidium caldarium Geitler (Rhodophyta?). Phycologia 23:397–399
Bérubé K, Dodge J, Ford T (1999) Effects of chronic salt stress on the ultrastructure of Dunaliella bioculata (Chlorophyta, Volvocales): mechanisms of response and recovery. Eur J Phycol 34:117–123
Blanc G, Agarkova I, Grimwood J, Kuo A, Brueggeman A, Dunigan DD, Gurnon J, Ladunga I, Lindquist E, Lucas S, Pangilinan J, Pröschold T, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Weeks D, Yamada T, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M, Claverie J-M, Grigoriev IV, Van Etten JL (2012) The genome of the polar eukaryotic microalga Coccomyxa subellipsoidea reveals traits of cold adaptation. Genome Biol 13:R39
Cosgrove J, Borowitzka MA (2011) Chlorophyll fluorescence terminology: an introduction. In: Suggett DJ, Prásil O, Borowitzka MA (eds) Chlorophyll a fluorescence in aquatic sciences: methods and applications. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–17
Cuaresma M, Janssen M, Vílchez C, Wijffels R (2011) Horizontal or vertical photobioreactors? How to improve microalgae photosynthetic efficiency. Bioresour Technol 102:5129–5137
Darienko T, Gustavs L, Eggert A, Wolf W, Pröschold T (2015) Evaluating the species boundaries of green microalgae (Coccomyxa, Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) using integrative taxonomy and DNA barcoding with further implications for the species identification in environmental samples. PLoS One 10(6):e0127838
Falagán C, Sánchez-España J, Johnson DB (2014) New insights into the biogeochemistry of extremely acidic environments revealed by a combined cultivation-based and culture-independent study of two stratified pit lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87:231–243
Ferroni L, Baldisserotto C, Pantaleoni L, Pancaldi S, Billi P, Fasulo MP (2007) High salinity alters chloroplast morpho-physiology in a freshwater Kirchneriella species (Selenastraceae) from Ethiopian Lake Awasa. Am J Bot 94:1972–1983
Forján E, Navarro F, Cuaresma M, Vaquero I, Ruíz-Domínguez MC, Gojkovic Ž, Vázquez M, Márquez M, Mogedas B, Bermejo E, Girlich S, Domínguez MJ, Vílchez C, Vega JM, Garbayo I (2015) Microalgae: fast-growth sustainable green factories. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:1705–1755
Fuggi A, Pinto G, Pollio A, Taddei R (1988) The role of glycerol in osmoregulation of the acidophilic alga Dunaliella acidophila (Volvocales, Chlorophyta): effect of solute stress on photosynthesis, respiration and glycerol synthesis. Phycologia 27:439–446
Garbayo I, Torronteras R, Forján E, Cuaresma M, Casal C, Mogedas B, Ruíz-Domínguez MC, Márquez C, Vaquero I, Fuentes-Cordero JL, Fuentes R, González del Valle M, Vílchez C (2012) Identification and physiological aspects of a novel carotenoid-enriched, metal-resistant microalga isolated from an acidic river in Huelva (Spain). J Phycol 48:607–614
Gimmler H (2001) Acidophilic and acidotolerant algae. In: Rai LC, Gaur JP (eds) Algal adaptation to environmental stresses: physiological, biochemical and molecular mechanisms. Springer, Berlin, pp 259–290
Gimmler H, Kugel H, Leibfritz D, Mayer A (1988) Cytoplasmic pH of Dunaliella parva and Dunaliella acidophila as monitored by in vivo 31P-NMR spectroscopy and the DMO method. Physiol Plant 74:521–530
Goyal A (2007) Osmoregulation in Dunaliella, part II: photosynthesis and starch contribute carbon for glycerol synthesis during a salt stress in Dunaliella tertiolecta. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:705–710
Gross W (2000) Ecophysiology of algae living in highly acidic environments. Hydrobiologia 433:31–37
Huss VAR, Frank C, Hartmann EC, Hirmer M, Kloboucek A, Seidel BM, Wenzeler P, Kessler E (1999) Biochemical taxonomy and molecular phylogeny of the genus Chlorella sensu lato (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 35:587–598
Hutner SH, Provosoli L, Schatz A, Haskins CP (1950) Some approaches to the study of the role of metals in the metabolism of microorganisms. Proc Am Philos Soc 94:152–170
Liu X-D, Shen Y-G (2006) Salt shock induces state II transition of the photosynthetic apparatus in dark-adapted Dunaliella salina cells. Environ Exp Bot 57:19–24
Masojídek J, Torzillo G, Kopecký J, Koblížek M, Nidiaci L, Komenda J, Lukavská A, Sacchi A (2000) Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence quenching and pigment composition in the green alga Chlorococcum sp. grown under nitrogen deficiency and salinity stress. J Appl Phycol 12:417–426
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence—a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51:659–668
McNeill J, Barrie FR, Buck WR, Demoulin V, Greuter W, Hawksworth DL, Herendeen PS, Knapp S, Marhold K, Prado J, Prud’Homme Van Reine WF, Smith GF, Wiersma JH, Turland NJ (2012) International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi and plants (Melbourne Code) adopted by the Eighteenth International Botanical Congress Melbourne, Australia, July 2011. Regnum Vegetabile vol 154. Koeltz Scientific Books, Koenigstein
Messerli MA, Amaral-Zettler LA, Zettler E, Jung SK, Smith PJS, Sogin ML (2005) Life at acidic pH imposes an increased energetic cost for a eukaryotic acidophile. J Exp Biol J Exp Biol 208:2569–2579
Muscatine L, Gates RD, La Fontaine I (1994) Do symbiotic dinoflagellates secrete lipid droplets? Limnol Oceanogr 39:925–929
Nishikawa K, Onodera A, Tominaga N (2006) Phytochelatins do not correlate with the level of Cd accumulation in Chlamydomonas spp. Chemosphere 63:1553–1559
Olsen GJR, Overbeek R, Larsen N, Marsh TL, McCaughey MJ, Maciukenas MA, Kuan WM, Macke TJ, Xing Y, Woese CR (1992) The ribosomal database project. Nucleic Acids Res 20:2199–2200
Orosa M, Valero JF, Herrero C, Abalde J (2001) Comparison of the accumulation of astaxanthin in Haematococcus pluvialis and other green microalgae under N-starvation and high light conditions. Biotechnol Lett 23:1079–1085
Pelah D, Sintov A, Cohen E (2004) The effect of salt stress on the production of canthaxanthin and astaxanthin by Chlorella zofingiensis grown under limited light intensity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:483–486
Richmond A (ed) (2004) Handbook of microalgal culture, biotechnology and applied phycology. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Rodríguez F, Feist SW, Guillou L, Harkestad LS, Bateman K, Renault T, Mortensen S (2008) Phylogenetic and morphological characterisation of the green algae infesting blue mussel Mytilus edulis in the North and South Atlantic oceans. Dis Aquat Org 81:231–240
Ruíz-Domínguez MC, Vaquero I, Obregón V, De la Morena B, Vílchez C, Vega JM (2015) Lipid accumulation and antioxidant activity in the eukaryotic acidophilic microalga Coccomyxa sp. (strain onubensis) under nutrient starvation. J Appl Phycol 27:1099–1108
Silverman MP, Lundgren DG (1959) Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 77:642–647
Spijkerman E (2008) What physiological acclimation supports increased growth at high CO2 conditions? Physiol Plant 133:41–48
Strizh IG, Popova LG, Balnokin YV (2004) Physiological aspects of adaptation of the marine microalga Tetraselmis (Platymonas) viridis to various medium salinity. Russ J Plant Physiol 51:176–182
Sudhir P, Murthy SDS (2004) Effects of salt stress on basic processes of photosynthesis. Photosynthetica 42:481–486
Sudhir PR, Pogoryelov D, Kovács L, Garab G, Murthy SDS (2005) The effects of salt stress on photosynthetic electron transport and thylakoid membrane proteins in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. J Biochem Mol Biol 38:481–485
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analyses using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4.0b 10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Takagi M, Karseno T, Yoshida T (2006) Effect of salt concentration on intracellular accumulation of lipids and triacylglyceride in marine microalgae Dunaliella cells. J Biosci Bioeng 101:223–226
Van der Auwera G, Chapelle S, De Wachter R (1994) Structure of the large ribosomal subunit RNA of Phytophtora megasperma, and phylogeny of the oomycetes. FEBS Lett 338:133–136
Vaquero I, Ruíz-Domínguez MC, Márquez M, Vílchez C (2012) Cu-mediated biomass productivity enhancement and lutein enrichment of the novel microalga Coccomyxa onubensis. Process Biochem 47:694–700
Vaquero I, Vázquez M, Ruíz-Domínguez MC, Vílchez C (2013) Enhanced production of a lutein-rich acidic environment microalga. J Appl Microbiol 116:839–850
Vaquero I, Mogedas B, Ruiz-Domínguez MC, Vega JM, Vílchez C (2014) Light-mediated lutein enrichment of an acid environment microalga. Algal Res 6:70–77
Varshney P, Mikulic P, Vonshak A, Beardall J, Wangikar PP (2015) Extremophilic micro-algae and their potential contribution in biotechnology. Bioresour Technol 184:363–372
Vázquez N, Rodríguez F, Ituarte C, Klaich J, Cremonte F (2010) Host-parasite relationship of the geoduck Panopea abbreviata and the green alga Coccomyxa parasitica in the Argentinean Patagonian coast. J Invertebr Pathol 105:254–260
Verma V, Bhatti S, Huss VAR, Colman B (2009) Photosynthetic inorganic carbon acquisition in an acid-tolerant, free-living species of Coccomyxa (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 45:847–854
Young EB, Beardall J (2003) Photosynthetic function in Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyta) during a nitrogen starvation and recovery cycle. J Phycol 39:897–905
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge the support from Junta de Andalucía (Grant no. AGR-4337) and CEIMAR (PhD Grant for Juan Luis Fuentes) and the technical support from Enrique Chaguaceda, María J. Vílchez, Gloria Blanco (Central Services, CIDERTA), and BioAvan SL. This is contribution No. 131 from the CEIMAR Journal Series.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0922-4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuentes, J.L., Huss, V.A.R., Montero, Z. et al. Phylogenetic characterization and morphological and physiological aspects of a novel acidotolerant and halotolerant microalga Coccomyxa onubensis sp. nov. (Chlorophyta, Trebouxiophyceae). J Appl Phycol 28, 3269–3279 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0887-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0887-3