Abstract
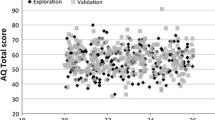
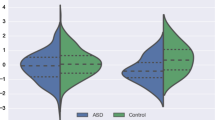
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) have numerous etiologies, including structural brain malformations such as agenesis of the corpus callosum (AgCC). We sought to directly measure the occurrence of autism traits in a cohort of individuals with AgCC and to investigate the neural underpinnings of this association. We screened a large AgCC cohort (n = 106) with the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ) and found that 45 % of children, 35 % of adolescents, and 18 % of adults exceeded the predetermined autism-screening cut-off. Interestingly, performance on the AQ’s imagination domain was inversely correlated with magnetoencephalography measures of resting-state functional connectivity in the right superior temporal gyrus. Individuals with AgCC should be screened for ASD and disorders of the corpus callosum should be considered in autism diagnostic evaluations as well.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs, R., Sears, L., & Piven, J. (2001). Abnormal processing of social information from faces in autism. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 13(2), 232–240.
Akiyama, T., Kato, M., Muramatsu, T., Saito, F., Nakachi, R., & Kashima, H. (2006). A deficit in discriminating gaze direction in a case with right superior temporal gyrus lesion. Neuropsychologia, 44(2), 161–170. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.05.018.
Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M., Boudos, R., DuBray, M. B., Oakes, T. R., et al. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of the corpus callosum in autism. Neuroimage, 34(1), 61–73. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.032.
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic criteria from DSM-IV-TR. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Auyeung, B., Baron-Cohen, S., Wheelwright, S., & Allison, C. (2008). The Autism Spectrum Quotient: Children’s Version (AQ-Child). Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(7), 1230–1240. doi:10.1007/s10803-007-0504-z.
Badaruddin, D. H., Andrews, G. L., Bolte, S., Schilmoeller, K. J., Schilmoeller, G., Paul, L. K., et al. (2007). Social and behavioral problems of children with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 38(4), 287–302. doi:10.1007/s10578-007-0065-6.
Bailey, D. B., Jr., Hatton, D. D., Skinner, M., & Mesibov, G. (2001). Autistic behavior, FMR1 protein, and developmental trajectories in young males with fragile X syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(2), 165–174.
Baron-Cohen, S., Hoekstra, R. A., Knickmeyer, R., & Wheelwright, S. (2006). The Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ)—Adolescent version. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36(3), 343–350. doi:10.1007/s10803-006-0073-6.
Baron-Cohen, S., Scahill, V. L., Izaguirre, J., Hornsey, H., & Robertson, M. M. (1999). The prevalence of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome in children and adolescents with autism: A large scale study. Psychological Medicine, 29(5), 1151–1159.
Baron-Cohen, S., Wheelwright, S., Skinner, R., Martin, J., & Clubley, E. (2001). The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): Evidence from Asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(1), 5–17.
Belmonte, M. K., Allen, G., Beckel-Mitchener, A., Boulanger, L. M., Carper, R. A., & Webb, S. J. (2004). Autism and abnormal development of brain connectivity. Journal of Neuroscience, 24(42), 9228–9231. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3340-04.2004.
Bishop, S. L., & Seltzer, M. M. (2012). Self-reported autism symptoms in adults with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders,. doi:10.1007/s10803-012-1483-2.
Brown, W. S., & Paul, L. K. (2000). Cognitive and psychosocial deficits in agenesis of the corpus callosum with normal intelligence. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 5(2), 135–157.
Casanova, M. F., Buxhoeveden, D. P., & Brown, C. (2002). Clinical and macroscopic correlates of minicolumnar pathology in autism. Journal of Child Neurology, 17(9), 692–695.
Casanova, M. F., El-Baz, A., Mott, M., Mannheim, G., Hassan, H., Fahmi, R., et al. (2009). Reduced gyral window and corpus callosum size in autism: possible macroscopic correlates of a minicolumnopathy. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(5), 751–764. doi:10.1007/s10803-008-0681-4.
Cheng, Y., Chou, K. H., Chen, I. Y., Fan, Y. T., Decety, J., & Lin, C. P. (2010). Atypical development of white matter microstructure in adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Neuroimage, 50(3), 873–882. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.011.
Constantino, J. N., & Todd, R. D. (2005). Intergenerational transmission of subthreshold autistic traits in the general population. Biological Psychiatry, 57(6), 655–660. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.12.014.
Dalal, S. S., Guggisberg, A. G., Edwards, E., Sekihara, K., Findlay, A. M., Canolty, R. T., et al. (2008). Five-dimensional neuroimaging: localization of the time–frequency dynamics of cortical activity. Neuroimage, 40(4), 1686–1700. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.01.023.
Doherty, D., Tu, S., Schilmoeller, K., & Schilmoeller, G. (2006). Health-related issues in individuals with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Child: Care, Health and Development, 32(3), 333–342. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2214.2006.00602.x.
Filipek, P. A., Accardo, P. J., Ashwal, S., Baranek, G. T., Cook, E. H., Jr., Dawson, G., et al. (2000). Practice parameter: Screening and diagnosis of autism: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Child Neurology Society. Neurology, 55(4), 468–479.
Frazier, T. W., & Hardan, A. Y. (2009). A meta-analysis of the corpus callosum in autism. Biological Psychiatry, 66(10), 935–941. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.07.022.
Friauf, E., & Lohmann, C. (1999). Development of auditory brainstem circuitry. Activity-dependent and activity-independent processes. Cell and Tissue Research, 297(2), 187–195.
Glass, H. C., Shaw, G. M., Ma, C., & Sherr, E. H. (2008). Agenesis of the corpus callosum in California 1983–2003: A population-based study. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A, 146A(19), 2495–2500. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32418.
Guggisberg, A. G., Honma, S. M., Findlay, A. M., Dalal, S. S., Kirsch, H. E., Berger, M. S., et al. (2008). Mapping functional connectivity in patients with brain lesions. Annals of Neurology, 63(2), 193–203. doi:10.1002/ana.21224.
Hadjikhani, N., Joseph, R. M., Snyder, J., & Tager-Flusberg, H. (2006). Anatomical differences in the mirror neuron system and social cognition network in autism. Cerebral Cortex, 16(9), 1276–1282. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj069.
Hallmayer, J., Cleveland, S., Torres, A., Phillips, J., Cohen, B., Torigoe, T., et al. (2011). Genetic heritability and shared environmental factors among twin pairs with autism. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68(11), 1095–1102. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.76.
Halpern, A. R., & Zatorre, R. J. (1999). When that tune runs through your head: A PET investigation of auditory imagery for familiar melodies. Cerebral Cortex, 9(7), 697–704.
Hardan, A. Y., Pabalan, M., Gupta, N., Bansal, R., Melhem, N. M., Fedorov, S., et al. (2009). Corpus callosum volume in children with autism. Psychiatry Research, 174(1), 57–61. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2009.03.005.
Hatton, D. D., Sideris, J., Skinner, M., Mankowski, J., Bailey, D. B., Jr., Roberts, J., et al. (2006). Autistic behavior in children with fragile X syndrome: prevalence, stability, and the impact of FMRP. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A, 140A(17), 1804–1813. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.31286.
Hetts, S. W., Sherr, E. H., Chao, S., Gobuty, S., & Barkovich, A. J. (2006). Anomalies of the corpus callosum: An MR analysis of the phenotypic spectrum of associated malformations. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology, 187(5), 1343–1348. doi:10.2214/AJR.05.0146.
Hinkley, L. B., Vinogradov, S., Guggisberg, A. G., Fisher, M., Findlay, A. M., & Nagarajan, S. S. (2011). Clinical symptoms and alpha band resting-state functional connectivity imaging in patients with schizophrenia: implications for novel approaches to treatment. Biological Psychiatry, 70(12), 1134–1142. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.06.029.
Hunt, A., & Shepherd, C. (1993). A prevalence study of autism in tuberous sclerosis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 23(2), 323–339.
Hyde, K. L., Samson, F., Evans, A. C., & Mottron, L. (2010). Neuroanatomical differences in brain areas implicated in perceptual and other core features of autism revealed by cortical thickness analysis and voxel-based morphometry. Human Brain Mapping, 31(4), 556–566. doi:10.1002/hbm.20887.
Johnson, C. P., & Myers, S. M. (2007). Identification and evaluation of children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics, 120(5), 1183–1215. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2361.
Jou, R. J., Minshew, N. J., Keshavan, M. S., Vitale, M. P., & Hardan, A. Y. (2010). Enlarged right superior temporal gyrus in children and adolescents with autism. Brain Research, 1360, 205–212. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.005.
Just, M. A., Cherkassky, V. L., Keller, T. A., & Minshew, N. J. (2004). Cortical activation and synchronization during sentence comprehension in high-functioning autism: Evidence of underconnectivity. Brain, 127(Pt 8), 1811–1821.
Just, M. A., Cherkassky, V. L., Keller, T. A., Kana, R. K., & Minshew, N. J. (2007). Functional and anatomical cortical underconnectivity in autism: evidence from an FMRI study of an executive function task and corpus callosum morphometry. Cerebral Cortex, 17(4), 951–961. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhl006.
Kanner, L. (1971). Follow-up study of eleven autistic children originally reported in 1943. Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 1(2), 119–145.
Keary, C. J., Minshew, N. J., Bansal, R., Goradia, D., Fedorov, S., Keshavan, M. S., et al. (2009). Corpus callosum volume and neurocognition in autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(6), 834–841. doi:10.1007/s10803-009-0689-4.
Ketelaars, C., Horwitz, E., Sytema, S., Bos, J., Wiersma, D., Minderaa, R., et al. (2008). Brief report: adults with mild autism spectrum disorders (ASD): Scores on the autism spectrum quotient (AQ) and comorbid psychopathology. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(1), 176–180. doi:10.1007/s10803-007-0358-4.
Kleinhans, N. M., Muller, R. A., Cohen, D. N., & Courchesne, E. (2008). Atypical functional lateralization of language in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Research, 1221, 115–125. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.04.080.
Kurita, H., Koyama, T., & Osada, H. (2005). Autism-Spectrum Quotient—Japanese version and its short forms for screening normally intelligent persons with pervasive developmental disorders. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 59(4), 490–496. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.2005.01403.x.
la Fougere, C., Zwergal, A., Rominger, A., Forster, S., Fesl, G., Dieterich, M., et al. (2010). Real versus imagined locomotion: A [18F]-FDG PET-fMRI comparison. Neuroimage, 50(4), 1589–1598. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.060.
Lukose, R., Schmidt, E., Wolski, T. P., Jr., Murawski, N. J., & Kulesza, R. J., Jr. (2011). Malformation of the superior olivary complex in an animal model of autism. Brain Research, 1398, 102–112. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.05.013.
Mason, R. A., Williams, D. L., Kana, R. K., Minshew, N., & Just, M. A. (2008). Theory of mind disruption and recruitment of the right hemisphere during narrative comprehension in autism. Neuropsychologia, 46(1), 269–280. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.07.018.
Moes, P., Schilmoeller, K., & Schilmoeller, G. (2009). Physical, motor, sensory and developmental features associated with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Child: Care, Health and Development, 35(5), 656–672. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2214.2009.00942.x.
Mottron, L., Peretz, I., & Menard, E. (2000). Local and global processing of music in high-functioning persons with autism: Beyond central coherence? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 41(8), 1057–1065.
Nolte, G., Bai, O., Wheaton, L., Mari, Z., Vorbach, S., & Hallett, M. (2004). Identifying true brain interaction from EEG data using the imaginary part of coherency. Clinical Neurophysiology, 115(10), 2292–2307. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2004.04.029.
Paul, L. K. (2011). Developmental malformation of the corpus callosum: A review of typical callosal development and examples of developmental disorders with callosal involvement. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 3(1), 3–27. doi:10.1007/s11689-010-9059-y.
Paul, L. K., Brown, W. S., Adolphs, R., Tyszka, J. M., Richards, L. J., Mukherjee, P., et al. (2007). Agenesis of the corpus callosum: Genetic, developmental and functional aspects of connectivity. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(4), 287–299. doi:10.1038/nrn2107.
Paul, L. K., Lautzenhiser, A., Brown, W. S., Hart, A., Neumann, D., Spezio, M., et al. (2006). Emotional arousal in agenesis of the corpus callosum. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 61(1), 47–56. doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2005.10.017.
Paul, L. K., Schieffer, B., & Brown, W. S. (2004). Social processing deficits in agenesis of the corpus callosum: Narratives from the Thematic Appreciation Test. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 19(2), 215–225. doi:10.1016/S0887-6177(03)00024-6.
Paul, L. K., Van Lancker-Sidtis, D., Schieffer, B., Dietrich, R., & Brown, W. S. (2003). Communicative deficits in agenesis of the corpus callosum: Nonliteral language and affective prosody. Brain and Language, 85(2), 313–324.
Pickles, A., Starr, E., Kazak, S., Bolton, P., Papanikolaou, K., Bailey, A., et al. (2000). Variable expression of the autism broader phenotype: Findings from extended pedigrees. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 41(4), 491–502.
Piven, J., Palmer, P., Jacobi, D., Childress, D., & Arndt, S. (1997). Broader autism phenotype: Evidence from a family history study of multiple-incidence autism families. American Journal of Psychiatry, 154(2), 185–190.
Redcay, E. (2008). The superior temporal sulcus performs a common function for social and speech perception: Implications for the emergence of autism. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 32(1), 123–142. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.06.004.
Roberts, T. P., Cannon, K. M., Tavabi, K., Blaskey, L., Khan, S. Y., Monroe, J. F., et al. (2011). Auditory magnetic mismatch field latency: A biomarker for language impairment in autism. Biological Psychiatry, 70(3), 263–269. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.01.015.
Roberts, T. P., Khan, S. Y., Rey, M., Monroe, J. F., Cannon, K., Blaskey, L., et al. (2010). MEG detection of delayed auditory evoked responses in autism spectrum disorders: Towards an imaging biomarker for autism. Autism Research, 3(1), 8–18. doi:10.1002/aur.111.
Robins, D. L., Fein, D., Barton, M. L., & Green, J. A. (2001). The Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers: An initial study investigating the early detection of autism and pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(2), 131–144.
Rubenstein, J. L., & Merzenich, M. M. (2003). Model of autism: Increased ratio of excitation/inhibition in key neural systems. Genes, Brain, and Behavior, 2(5), 255–267.
Rutter, M., Bailey, A., & Lord, C. (2003). Social Communication Questionnaire manual. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Schilmoeller, G., Schilmoeller, K., & Doherty, D. (2004). Social interaction in individuals with and without a corpus callosum. Paper presented at the Journal of International Neuropsychology Society, Baltimore, MD.
Sherr, E. H. (2003). The ARX story (epilepsy, mental retardation, autism, and cerebral malformations): One gene leads to many phenotypes. Current Opinion in Pediatrics, 15(6), 567–571.
Sherr, E. H., Owen, R., Albertson, D. G., Pinkel, D., Cotter, P. D., Slavotinek, A. M., et al. (2005). Genomic microarray analysis identifies candidate loci in patients with corpus callosum anomalies. Neurology, 65(9), 1496–1498. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000183066.09239.b6.
Shukla, D. K., Keehn, B., Lincoln, A. J., & Muller, R. A. (2010). White matter compromise of callosal and subcortical fiber tracts in children with autism spectrum disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(12), 1269–1278, 1278.e1–2. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2010.08.018.
Shukla, D. K., Keehn, B., & Muller, R. A. (2011). Tract-specific analyses of diffusion tensor imaging show widespread white matter compromise in autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52(3), 286–295. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02342.x.
Spence, S. J., & Schneider, M. T. (2009). The role of epilepsy and epileptiform EEGs in autism spectrum disorders. Pediatric Research, 65(6), 599–606. doi:10.1203/01.pdr.0000352115.41382.65.
Stickles, J. L., Schilmoeller, G. L., & Kathyrn, J. (2002). A 23-year review of communication development in an individual with agenesis of the corpus callosum. International Journal of Disability, Development, and Education, 49(4), 367–383.
Symington, S. H., Paul, L. K., Symington, M. F., Ono, M., & Brown, W. S. (2010). Social cognition in individuals with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Social Neuroscience, 5(3), 296–308. doi:10.1080/17470910903462419.
Thomas, C., Humphreys, K., Jung, K. J., Minshew, N., & Behrmann, M. (2010). The anatomy of the callosal and visual-association pathways in high-functioning autism: A DTI tractography study. Cortex, 47(7), 863–873. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2010.07.006.
Turk, A. A., Brown, W. S., Symington, M., & Paul, L. K. (2010). Social narratives in agenesis of the corpus callosum: linguistic analysis of the Thematic Apperception Test. Neuropsychologia, 48(1), 43–50. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.08.009.
Vingan, R. D., Dow-Edwards, D. L., & Riley, E. P. (1986). Cerebral metabolic alterations in rats following prenatal alcohol exposure: A deoxyglucose study. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 10(1), 22–26.
Virkud, Y. V., Todd, R. D., Abbacchi, A. M., Zhang, Y., & Constantino, J. N. (2009). Familial aggregation of quantitative autistic traits in multiplex versus simplex autism. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 150B(3), 328–334. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30810.
Weiss, L. A., Shen, Y., Korn, J. M., Arking, D. E., Miller, D. T., Fossdal, R., et al. (2008). Association between microdeletion and microduplication at 16p11.2 and autism. New England Journal of Medicine, 358(7), 667–675. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa075974.
Wheelwright, S., Auyeung, B., Allison, C., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2010). Defining the broader, medium and narrow autism phenotype among parents using the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ). Molecular Autism, 1(1), 10. doi:10.1186/2040-2392-1-10.
Wicker, B., Perrett, D. I., Baron-Cohen, S., & Decety, J. (2003). Being the target of another’s emotion: A PET study. Neuropsychologia, 41(2), 139–146.
Williams, D. L., & Minshew, N. J. (2007). Understanding autism and related disorders: What has imaging taught us? Neuroimaging Clinics of North America, 17(4), 495–509. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2007.07.007.
Wolff, J. J., Gu, H., Gerig, G., Elison, J. T., Styner, M., Gouttard, S., et al. (2012). Differences in white matter fiber tract development present from 6 to 24 months in infants with autism. American Journal of Psychiatry,. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11091447.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NIH grants R01 DC004855, DC006435, DC010145, NS067962, NS64060, and by NSF grant BCS-0926196 to S.S.N, NIH grant K23 MH083890 to E.J.M., K02 NS052192 to E.H.S., KL2 RR024130 to E.J.M, E.H.S.), the Sandler Program for Breakthrough Biomedical Research (E.H.S.), the Simons Foundation (L.K.P), NARSAD (L.K.P.) and the Dystonia Medical Research Foundation (L.B.N.H.). This project was supported by NIH/NCRR UCSF-CTSI Grant Number UL1 RR024131. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. This project is made possible primarily through the efforts of our participants and their families.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, Y.C., Hinkley, L.B.N., Bukshpun, P. et al. Autism Traits in Individuals with Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum. J Autism Dev Disord 43, 1106–1118 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-012-1653-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-012-1653-2