Abstract
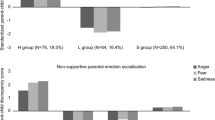
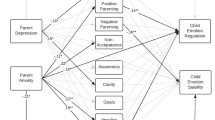
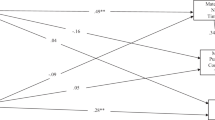
This study examined the relation between parent psychopathology symptoms and emotion socialization practices in a sample of mothers and fathers of preschool-aged children with behavior problems (N = 109, M age = 44.60 months, 50 % male). Each parent completed a self-report rating scale of their psychopathology symptoms and audio-recorded naturalistic interactions with their children, which were coded for reactions to child negative affect. Results supported a spillover hypothesis for mothers. Specifically, mothers who reported greater overall psychopathology symptoms, anxiety symptoms, substance use, and borderline and Cluster A personality symptoms were more likely to exhibit non-supportive reactions. Additionally, mothers who reported greater anxiety and Cluster A personality symptoms were more likely to not respond to child negative affect. Compensatory and crossover hypotheses were also supported. Partners of mothers who reported high levels of anxiety were more likely to use supportive reactions to child negative affect. In contrast, partners of mothers who reported high levels of borderline and Cluster A personality symptoms and overall psychopathology symptoms were more likely to show non-supportive reactions. With the exception of borderline personality symptoms, fathers’ psychopathology was unrelated to parental responses to child negative affect. Results highlight the importance of maternal psychopathology in parental emotion socialization practices.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Harvey et al. (2011) found that narcissistic, histrionic, and compulsive subscales almost always correlated negatively with other subscales, suggesting that within this nonclinical sample, these subscales may actually measure healthy narcissism, flamboyance, and organization, respectively. Thus, these subscales were not included in analyses.
References
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. S. (1978). The classification of child psychopathology: a review and analysis of empirical efforts. Psychological Bulletin, 85, 1275–1301. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.85.6.1275.
Achenbach, T. M., Conners, C. K., Quay, H. C., Verhulst, F. C., & Howell, C. T. (1989). Replication of empirically derived syndromes as a basis for taxonomy of child/adolescent psychopathology. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 17, 299–323. doi:10.1007/BF00917401.
Barlow, D. H. (2000). Unraveling the mysteries of anxiety and its disorders from the perspective of emotion theory. American Psychologist, 55, 1247–1263. doi:10.1037/0003066X.55.11.1247.
Belsky, J. (1984). The determinants of parenting: a process model. Child Development, 55, 8396. doi:10.2307/1129836.
Bronte-Tinkew, J., Moore, K. A., Matthews, G., & Carrano, J. (2007). Symptoms of major depression in a sample of fathers of infants: sociodemographic correlates and links to father involvement. Journal of Family Issues, 28, 61–99. doi:10.1177/0192513X06293609.
Campbell, S. B. (1994). Hard-to-manage preschool boys: externalizing behavior, social competence, and family context at two-year followup. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22, 147–166. doi:10.1007=BF02167897.
Capaldi, D. M., Pears, K. C., Kerr, D. C. R., & Owen, L. D. (2008). Intergenerational and partner influences on fathers’ negative discipline. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36, 347–350. doi:10.1007/S10802-007-9182-8.
Caspi, A., Houts, R. M., Belsky, D. W., Goldman-Mellor, S. J., Harrington, H., Israel, S., & Moffitt, T. E. (2014). The p factor one general psychopathology factor in the structure of psychiatric disorders? Clinical Psychological Science, 2, 119–137. doi:10.1177/2167702613497473.
Chilcoat, H., Breslau, N., & Anthony, J. C. (1996). Impact of parent monitoring on initiation of drug use through late childhood. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 91–100. doi:10.1097/00004583-199601000-00017.
Cole, P. M., Michel, M. K., & Teti, L. O. (1994). The development of emotion regulation and dysregulation: a clinical perspective. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 59, 73–100. doi:10.2307/1166139.
Cole, P. M., Dennis, T. A., Smith-Simon, K. E., & Cohen, L. H. (2009). Preschoolers’ emotion regulation strategy understanding: relations with emotion socialization and child self-regulation. Social Development, 18, 324–352. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9507.2008.00503.x.
Collignon, O., Girard, S., Gosselin, F., Saint-Amour, D., Lepore, F., & Lassonde, M. (2010). Women process multisensory emotion expressions more efficiently than men. Neuropsychologia, 48, 220–225. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.09.007.
Cook, W. L., & Kenny, D. A. (2005). The actor–partner interdependence model: a model of bidirectional effects in developmental studies. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 29, 101–109. doi:10.1080/01650250444000405.
Crouter, A. C., Bumpus, M. F., Head, M. R., & McHale, S. M. (2001). Implications of overwork and overload for the quality of men’s marriages. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 63, 404–417. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2001.00404.x.
Cummings, E. M., & Davies, P. T. (1994). Maternal depression and child development. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 35, 73–112. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1994.tb01133.x.
Das Eiden, R., & Leonard, K. E. (2000). Paternal alcoholism, parental psychopathology, and aggravation with infants. Journal of Substance Abuse, 11, 17–29. doi:10.1016/S08993289(99)00016-4.
Denham, S. (1998). Emotional development in young children. New York: The Guilford Press.
Denham, S., & Kochanoff, A. T. (2002). Parental contributions to preschoolers’ understanding of emotion. Marriage & Family Review, 34, 311–343. doi:10.1300/J002v34n03_06.
Denham, S. A., Workman, E., Cole, P. M., Weissbrod, C., Kendziora, K. T., & Zahn-Waxler, C. (2000). Prediction of externalizing behavior problems from early to middle childhood: the role of parental socialization and emotion expression. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 23–45. doi:10.1017/S0954579400001024.
Denham, S. A., Bassett, H. H., & Wyatt, T. (2007). The socialization of emotional competence. In J. Grusec & P. Hastings (Eds.), Handbook of socialization: Theory and research (pp. 614–637). New York: Guilford Press.
Dix, T., & Meunier, L. N. (2009). Depressive symptoms and parenting competence: an analysis of 13 regulatory processes. Developmental Review, 29, 45–68. doi:10.1016/j.dr.2008.11.002.
DuPaul, G. J., McGoey, K. E., Eckert, T. L., & VanBrakle, J. (2001). Preschool children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: impairments in behavioral, social, and school functioning. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 508–515. doi:10.1097/00004583-200105000-00009.
Edwards, E. P., Homish, G. G., Eiden, R. D., Grohman, K. K., & Leonard, K. E. (2009). Longitudinal prediction of early childhood discipline styles among heavy drinking parents. Addictive Behaviors, 34, 100–106. doi:10.1016/J.Addbeh.2008.08.006.
Eiden, R. D., Edwards, E. P., & Leonard, K. E. (2007). A conceptual model for the development of externalizing behavior problems among kindergarten children of alcoholic families: role of parenting and children’s self-regulation. Developmental Psychology, 43, 11871201. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.43.5.1187.
Eisenberg, N., Cumberland, A., & Spinrad, T. L. (1998). Parental socialization of emotion. Psychological Inquiry, 9, 241–273. doi:10.1207/s15327965pli0904_1.
Elgar, F. J., Mills, R. S. L., Mcgrath, P. J., Waschbusch, D. A., & Brownridge, D. A. (2007). Maternal and paternal depressive symptoms and child maladjustment: the mediating role of parental behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 35, 943–955. doi:10.1007/S10802-007-9145-0.
Fabes, R. A., Eisenberg, N., & Bernzweig, J. (1990). The coping with children’s negative emotions scale: Procedures and scoring. Available from authors. Tempe: Arizona State University.
Friedlmeier, W., Corapci, F., & Cole, P. M. (2011). Emotion socialization in cross‐cultural perspective. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 5, 410–427. doi:10.1111/j.1751-9004.2011.00362.x.
Goodman, J. H. (2008). Influences of maternal postpartum depression on fathers and their father-infant interaction. Infant Mental Health Journal, 29, 624–643. doi:10.1002/Imhj.20199.
Gross, J. J., & Levenson, R. W. (1997). Hiding feelings: the acute effects of inhibiting positive and negative emotions. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 106, 95–103. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.106.1.95.
Harvey, E. A., Youngwirth, S. D., Thakar, D. A., & Errazuriz, P. A. (2009). Predicting attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiant disorder from preschool diagnostic assessments. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 2, 349–354. doi:10.1037/a0014638.
Harvey, E., Stoessel, B., & Herbert, S. (2011). Psychopathology and parenting practices of parents of preschool children with behavior problems. Parenting: Science and Practice, 11, 239–263. doi:10.1080/15295192.2011.613722.
Herbert, S. D., Harvey, E. A., Lugo-Candelas, C. I., & Breaux, R. P. (2013). Early fathering as a predictor of later psychosocial functioning among preschool children with behavior problems. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 41, 691–703. doi:10.1007/s10802-012-9706-8.
Hersh, M. A., & Hussong, A. M. (2009). The association between observed parental emotion socialization and adolescent self-medication. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 493–506. doi:10.1007/s10802-008-9291-z.
Hops, H., Biglan, A., Sherman, L., Arthur, J., Friedman, L., & Osteen, V. (1987). Home observations of family interactions of depressed women. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 55, 341–346. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.55.3.341.
Hussong, A. M., Bauer, D. J., Huang, W., Chassin, L., Sher, K. J., & Zucker, R. A. (2008). Characterizing the life stressors of children of alcoholic parents. Journal of Family Psychology, 22, 819–832. doi:10.1037/a0013704.
Jacob, T., & Johnson, S. L. (1997). Parent–child interaction among depressed fathers and mothers: impact on child functioning. Journal of Family Psychology, 11, 391–409. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.11.4.391.
Johnson, J. G., Cohen, P., Kasen, S., & Brook, J. S. (2004). Paternal psychiatric symptoms and maladaptive paternal behavior in the home during the child rearing years. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 13, 421–437. doi:10.1023/B:JCFS.0000044725.76533.66.
Johnson, J. G., Cohen, P., Kasen, S., & Brook, J. S. (2006a). Maternal psychiatric disorders, parenting, and maternal behavior in the home during the child rearing years. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 15, 97–114. doi:10.1007/S10826-005-9003-Z.
Johnson, J. G., Cohen, P., Kasen, S., Ehrensaft, M. K., & Crawford, T. N. (2006b). Associations of parental personality disorders and axis I disorders with childrearing behavior. Psychiatry Interpersonal and Biological Processes, 69, 336–350. doi:10.1521/psyc.2006.69.4.336.
Kashdan, T. B., Jacob, R. G., Pelham, W. E., Lang, A. R., Hoza, B., Blumenthal, J. D., & Gnagy, E. M. (2004). Depression and anxiety in parents of children with ADHD and varying levels of oppositional defiant behaviors: modeling relationships with family functioning. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33, 169–181. doi:10.1207/S15374424JCCP3301_16.
Kessler, R. C., Chiu, W. T., Demler, O., & Walters, E. E. (2005). Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of general psychiatry, 62, 617–627. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.617.
Kring, A. M., & Werner, K. H. (2004). Emotion regulation and psychopathology. In P. Philippot & R. S. Feldman (Eds.), The regulation of emotion (pp. 359–385). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Krueger, R. F., & Markon, K. E. (2006). Reinterpreting comorbidity: a model-based approach to understanding and classifying psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 2, 111–133. doi:10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.2.022305.095213.
Lahey, B. B., Applegate, B., Hakes, J. K., Zald, D. H., Hariri, A. R., & Rathouz, P. J. (2012). Is there a general factor of prevalent psychopathology during adulthood? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121, 971–977. doi:10.1037/a0028355.
Li, H., Yuan, J., & Lin, C. (2008). The neural mechanism underlying the female advantage in identifying negative emotions: an event-related potential study. NeuroImage, 40, 19211929. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.01.033.
Lithari, C., Frantzidis, C. A., Papadelis, C., Vivas, A. B., Klados, M. A., Kourtidou-Papadeli, C., & Bamidis, P. D. (2010). Are females more responsive to emotional stimuli? A neurophysiological study across arousal and valence dimensions. Brain Topography, 23, 27–40. doi:10.1007/s10548-009-0130-5.
Lovejoy, M. C., Graczyk, P. A., O’Hare, E., & Neuman, G. (2000). Maternal depression and parenting behavior: a meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 20, 561–592. doi:10.1016/S0272-7358(98)00100-7.
Markon, K. E. (2010). Modeling psychopathology structure: a symptom-level analysis of Axis I and II disorders. Psychological Medicine, 40, 273–288. doi:10.1017/S0033291709990183.
McElwain, L. N., Halberstadt, A. G., & Volling, B. L. (2007). Mother- and father-reported reactions to children’s negative emotions: relations to young children’s emotional understanding and friendship quality. Child Development, 78, 1407–1425. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2007.01074.x.
McWayne, C., Campos, R., & Owsianik, M. (2008). A multidimensional, multilevel examination of mother and father involvement among culturally diverse head start families. Journal of School Psychology, 46, 551–573. doi:10.1016/j.jsp.2008.06.001.
Michalik, N. M., Eisenberg, N., Spinrad, T. L., Ladd, B., Thompson, M., & Valiente, C. (2007). Longitudinal relations among parental emotional expressivity and sympathy and prosocial behavior in adolescence. Social Development, 16, 286–309. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00385.x.
Middleton, M., Scott, S. L., & Renk, K. (2009). Parental depression, parenting behaviours, and behaviour problems in young children. Infant and Child Development, 18, 323–336. doi:10.1002/icd.598.
Millon, T., Davis, R. D., Millon, C. (1997). MCMI-III Manual. National Computer Systems.
Mokrova, I., O'Brien, M., Calkins, S., & Keane, S. (2010). Parental ADHD symptomology and ineffective parenting: the connecting link of home chaos. Parenting Science and Practice, 10, 119–135. doi:10.1080/15295190903212844.
Morris, A. S., Silk, J. S., Steinberg, L., Myers, S. S., & Robinson, L. R. (2007). The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Social Development, 16, 361388. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00389.x.
Nelson, J. A., O’Brien, M., Blankson, A. N., Calkins, S. D., & Keane, S. P. (2009). Family stress and parental responses to children’s negative emotions: tests of the spillover, crossover, and compensatory hypotheses. Journal of Family Psychology, 23, 671–679. doi:10.1037/a0015977.
Newman, D. L., Moffitt, T. E., Caspi, A., & Silva, P. A. (1998). Comorbid mental disorders: implications for treatment and sample selection. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 107, 305–311. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.107.2.305.
Pfiffner, L. J., McBurnett, K., Rathouz, P. J., & Judice, S. (2005). Family correlates of oppositional and conduct disorders in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33, 551–563. doi:10.1007/s10802005-6737-4.
Raval, V. V., & Martini, T. S. (2009). Maternal socialization of children’s anger, sadness, and physical pain in two communities in Gujarat, India. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 33, 215–229. doi:10.1177/0165025408098022.
Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (1992). Behavior assessment system for children: Manual. Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
Riordan, D., Appleby, L., & Faragher, B. (1999). Mother–infant interaction in post-partum women with schizophrenia and affective disorders. Psychological Medicine, 29, 991–995. doi:10.1017/S0033291798007727.
Roberts, N. A., & Levenson, R. W. (2001). The remains of the workday: impact of job stress and exhaustion on marital interaction in police couples. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 63, 1052–1067. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3737.2001.01052.x.
Roopnarine, J. L. (2005). Mothers’ and fathers’ behaviors toward their 3- to 4-month-old infants in lower, middle, and upper socioeconomic African-American families. Developmental Psychology, 41, 723–732. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.41.5.723.
Takeda, T., Stotesbery, K., Power, T., Ambrosini, P. J., Berrettini, W., Hakonarson, H., & Elia, J. (2010). Parental ADHD status and its association with proband ADHD subtype and severity. Journal of Pediatrics, 157, 995–1000. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.05.053.
Valiente, C., Lemery-Chalfant, K., & Reiser, M. (2007). Pathways to problem behaviors: chaotic homes, parent and child effortful control, and parenting. Social Development, 16, 249–267. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00383.x.
Warren, H. K., & Stifter, C. A. (2008). Maternal emotion-related socialization and preschoolers’ developing emotion self-awareness. Social Development, 17, 239–256. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00423.x.
Westman, M. (2001). Stress and strain crossover. Human Relations, 54, 717–751. doi:10.1177/0018726701546002.
Whaley, S. E., Pinto, A., & Sigman, M. (1999). Characterizing interactions between anxious mothers and their children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67, 826–836. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.67.6.826.
Woodruff-Borden, J., Morrow, C., Bourland, S., & Cambron, S. (2002). The behavior of anxious parents: examining mechanisms of transmission of anxiety from parent to child. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 31, 364–374. doi:10.1207/S15374424JCCP3103_08.
Zahn-Waxler, C., Duggal, S., & Gruber, R. (2002). Parent psychopathology. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting (2nd ed., Vol. 3, pp. 295–327). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (MH60132) awarded to the second author. The authors wish to thank our wonderful team of undergraduate research assistants, especially Jenna Axelrod, for their hard work on coding the emotion socialization data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no competing or potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breaux, R.P., Harvey, E.A. & Lugo-Candelas, C.I. The Role of Parent Psychopathology in Emotion Socialization. J Abnorm Child Psychol 44, 731–743 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-015-0062-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-015-0062-3