Abstract
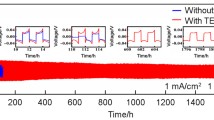
Electrodeposition and dissolution of zinc in sulfuric acid were studied as the negative electrode reactions in acidic zinc-based redox flow batteries. The zinc deposition and dissolution is a quasi-reversible reaction with a zinc ion diffusion coefficient of 4.6 × 10−6 cm2 s−1 obtained. The increase of acid concentration facilitates an improvement in the kinetics of zinc electrodeposition–dissolution process. But too high acid concentration would result in a significant decrease in charge efficiency. The performance of the zinc electrode in a three-electrode system with magnetic stirring was also studied as a function of Zn(II) ion concentration, sulfuric acid concentration, current density, and the addition of additives in 1 M H2SO4 medium. The optimum electrolyte composition is suggested at high zinc(II) concentration (1.25 M) and moderate sulfuric acid concentration (1.0–1.5 M) at a current density range of 20–30 mA cm−2. Whether in acid-free solution or in sulfuric acid solution with or without additives, no dendrite formation is observed after zinc electrodeposition for 1 h at 20 mA cm−2. The energy efficiency is improved from 77 % in the absence of additives in 1 M H2SO4 medium to over 80 % upon the addition of indium oxide or SLS–Sb(III) combined additive as hydrogen suppressants.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang KL, Li XG, Liu SQ (2008) Renew Energy 33:186
Yu JX, Yang HX, Ai XP (2001) J Power Sources 103:93
Butler PC, Eidler PA, Grimes PC, Klassen SE, Miles RC (1994) In: Linden D (ed) Handbook of batteries, 3rd edn. McGraw Hill, New York
Cheng J, Zhang L, Yang YS, Wen YH (2007) Electrochem Commun 9:2639
Wen YH, Cheng J, Ning SQ (2009) J Power Sources 188:301
Zhang L, Cheng J, Yang YS (2008) J Power Sources 179:381
Leung PK, Ponce de León C, Low CTJ, Walsh FC (2011) Electrochim Acta 56:6536
Leung PK, Ponce de León C, Low CTJ, Walsh FC (2011) Electrochim Acta 56:2145
Leung PK, Ponce de León C, Low CTJ, Shah AA, Walsh FC (2011) J Power Sources 196:5174
DiAZ-Arista P, Meas Y, Ortega R, Trejo G (2005) J Appl Electrochem 35:217
Trejo G, Ortega RB, Meas YV, Ozil P, Chainet E, Nguyen B (1998) J Electrochem Soc 145:4090
Yu JX, Chen YY, Yang HX, Huang QA (1999) J Electrochem Soc 146:1789
Saba AE, Elsherief AE (2000) Hydrometallurgy 54:91
Gomes A, da Silva Pereira MI (2006) Electrochim Acta 52:863
Alfantazi AM, Dreisinger DB (2003) Hydrometallurgy 69:99
Gomes A, Viana AS, da Silva Pereira MI (2007) J Electrochem Soc 154:D452
Gomes A, da Silva Pereira MI (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:1342
Youssef KMS, Koch CC, Fedkiw PS (2004) J Electrochem Soc 151:C103
Fang B, Iwasa S, Wei Y, Arai T, Kumagai M (2002) Electrochim Acta 47:3971
Fletcher S, Halliday CS (1983) J Electroanal Chem 159:267
Yu JX, Yang HX, Ai XP, Chen YY (2002) Russ J Electrochem 38:321
Zhang QB, Hua YX (2009) Hydrometallurgy 99:249
Saba AE, Elsherief AE (2000) Hydrometallurgy 54:91
Tripathy BC, Das SC, Misra VN (2003) Hydrometallurgy 69:81
Gomes A, da Silva Pereira MI (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:1342
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (2010CB227204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, J., Wen, Y., Cheng, J. et al. Zinc deposition and dissolution in sulfuric acid onto a graphite–resin composite electrode as the negative electrode reactions in acidic zinc-based redox flow batteries. J Appl Electrochem 43, 541–551 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-013-0538-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-013-0538-1