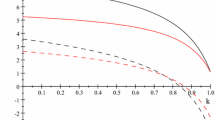
Abstract
In contemporary electronic commerce, an infomediary displays electronic word-of-mouth (eWOM) information of customers and links shoppers to retail websites, thus acting as an intermediary between buyers and sellers. This paper studies an online supply chain system in which the infomediary presents demand-referral services to online retailers based on eWOM of customer information. It is assumed that online demand is affected by retailer price, referral service effort, and eWOM. The demand function is extended and developed based on Bass’s model. A Stackelberg game model of service cooperation is presented, and then the optimal decisions on retailers’ prices and infomediary service efforts in the decentralized supply chain are analyzed. Moreover, the profits and cumulative sales in supply chain equilibrium are analyzed under several parameters. A computational experiment is implemented to verify the validity and effectiveness of the model. The results show that price sensitivity has a significant negative effect on cumulative retailer sales and the profits of retailers and infomediary, but the effect of service sensitivity and sales periods on profits is absolutely positive. Specifically, eWOM has two different impacts on the profit of the retailer and infomediary respectively. Finally, conclusions and management implications for supply chain parties are presented, along with some possible directions for further research.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y, Sun Y, Hu J (2013) Channel selection in e-commerce age: a strategic analysis of co-op advertising models. J Ind Eng Manag 6(1):89–103
Chu W, Choi B, Song MR (2005) The role of on-line retailer brand and infomediary reputation in increasing consumer purchase intention. Int J Electron Commer 9(3):115–127
Adelaar T (2000) Electronic commerce and the implications for market structure. J Comput Med Commun 5(3):1–20
Hagel J III, Rayport JF (1997) The new infomediaries. McKinsey Quart 4:54–70
Viswanathan S, Kuruzovich J, Gosain S, Agarwal R (2007) Online infomediaries and price discrimination: evidence from the automotive retailing sector. J Mark 71(3):89–107
Ordanini A, Pol A (2001) Infomediation and competitive advantage in B2B digital marketplaces. Eur Manag J 19(3):276–285
Trusov M, Bucklin RE, Pauwels K (2009) Effects of word-of-mouth versus traditional marketing: findings from an internet social networking site. J Mark 73(5):90–102
Cheung CMK, Thadani DR (2012) The impact of electronic word-of-mouth communication: a literature analysis and integrative model. Decis Support Syst 54(1):461–470
Jeong E, Jang S (2011) Restaurant experiences triggering positive electronic word-of-mouth (eWOM) motivations. Int J Hosp Manag 30(2):356–366
Litvin SW, Goldsmith RE, Pan B (2008) Electronic word-of-mouth in hospitality and tourism management. Tour Manag 29(3):458–468
Park C, Lee TM (2009) Information direction, website reputation and eWOM effect: a moderating role of product type. J Bus Res 62(1):61–67
Hu N, Bose I, Gao Y, Liu L (2011) Manipulation in digital word-of-mouth: a reality check for book reviews. Decis Support Syst 50(3):627–635
Chen Y, Xie J (2008) Online consumer review: word-of-mouth as a new element of marketing communication mix. Manag Sci 54(3):477–491
Khammash M, Griffiths GH (2011) `Arrivederci CIAO.com, Buongiorno Bing.com’–Electronic word-of-mouth (eWOM), antecedences and consequences. Int J Inf Manag 31(1):82–87
Luo X (2009) Quantifying the long-term impact of negative word of mouth on cash flows and stock prices. Mark Sci 28(1):148–165
Cheung CMK, Lee MKO (2012) What drives consumers to spread electronic word of mouth in online consumer-opinion platforms. Decis Support Syst 53(1):218–225
Dai H, Salam AF (2011) Antecedents and consequents of service consumption experience in electronic mediated environment: empirical evidence from electronic service industry in China. J Syst Manag Sci 1(1):141–151
Craig CS, Greene WH, Versaci A (2015) E-word of mouth: early predictor of audience engagement. J Advert Res 55(1):62–72
Ziegele M, Weber M (2015) Example, please! Comparing the effects of single customer reviews and aggregate review scores on online shoppers’ product evaluations. J Consum Behav 14(2):103–114
Hennig-Thurau T, Gwinner KP, Walsh G, Gremler DD (2004) Electronic word-of-mouth via consumer-opinion platforms: what motivates consumers to articulate themselves on the Internet? J Interact Mark 18(1):38–52
Chen Y, Iyer G, Padmanabhan V (2002) Referral infomediaries. Mark Sci 21(4):412–434
Chen Y, Xie J (2005) Third-party product review and firm marketing strategy. Mark Sci 24(2):218–240
Yan X, Liu K (2009) Optimal control problems for a new product with word-of-mouth. Int J Prod Econ 119(2):402–414
Phuc PNK, Yu VF, Chou S-Y (2013) Manufacturing production plan optimization in three-stage supply chains under Bass model market effects. Comput Ind Eng 65(3):509–516
Liu Y, Cheng HK, Tang QC, Eryarsoy E (2011) Optimal software pricing in the presence of piracy and word-of-mouth effect. Decis Support Syst 51(1):99–107
Huang L, Zhang J, Liu H, Liang L (2014) The effect of online and offline word-of-mouth on new product diffusion. J Strateg Mark 22(2):177–189
Chen Y, Yao J (2012) Referral service of infomediary in B2C supply chain. Int J Netw Virtual Organ 10(3/4):414–426
Chen Y, Zhang W, Yang S, Wang Z, Chen S (2014) Referral service and customer incentive in online retail supply Chain. J Appl Res Technol 12(4):261–269
Bass FM (1969) A new product growth for model consumer durables. Manag Sci 15(5):215–227
Bass FM (2004) Comments on “A new product growth for model consumer durables”: the bass model. Manag Sci 50(12):1833–1840
Lee S-H, Noh S-E, Kim H-W (2013) A mixed methods approach to electronic word-of-mouth in the open-market context. Int J Inf Manag 33(4):687–696
Martin WC, Lueg JE (2013) Modeling word-of-mouth usage. J Bus Res 66(7):801–808
Guo Z (2012) Optimal decision making for online referral marketing. Decis Support Syst 52(2):373–383
Krishnan H, Kapuscinski R, Butz DA (2004) Coordinating contracts for decentralized supply chains with retailer promotional effort. Manag Sci 50(1):48–63
Tsay AA, Agrawal N (2004) Channel conflict and coordination in the e-commerce age. Prod Oper Manag 13(1):93–110
Yang CC, Chung A (2004) Intelligent infomediary for web financial information. Decis Support Syst 38(1):65–80
Son JY, Kim SS, Riggins FJ (2006) Consumer adoption of net-enabled infomediaries: theoretical explanations and an empirical test. J Assoc Inf Syst 7(7):473–508
Ghose A, Mukhopadhyay T, Rajan U (2007) The impact of Internet referral services on a supply chain. Inf Syst Res 18(3):300–319
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the Philosophy and Social Science Research Project of Zhejiang Province under Grant No. 13NDJC054YB and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 71271188 and 71472163.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Yang, S. & Wang, Z. Service cooperation and marketing strategies of infomediary and online retailer with eWOM effect. Inf Technol Manag 17, 109–118 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10799-015-0237-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10799-015-0237-1